Lab Anim Res.
2015 Mar;31(1):40-45. 10.5625/lar.2015.31.1.40.
Estradiol attenuates down-regulation of PEA-15 and its two phosphorylated forms in ischemic brain injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine, Research Institute of Life Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. pokoh@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1787650
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2015.31.1.40
Abstract
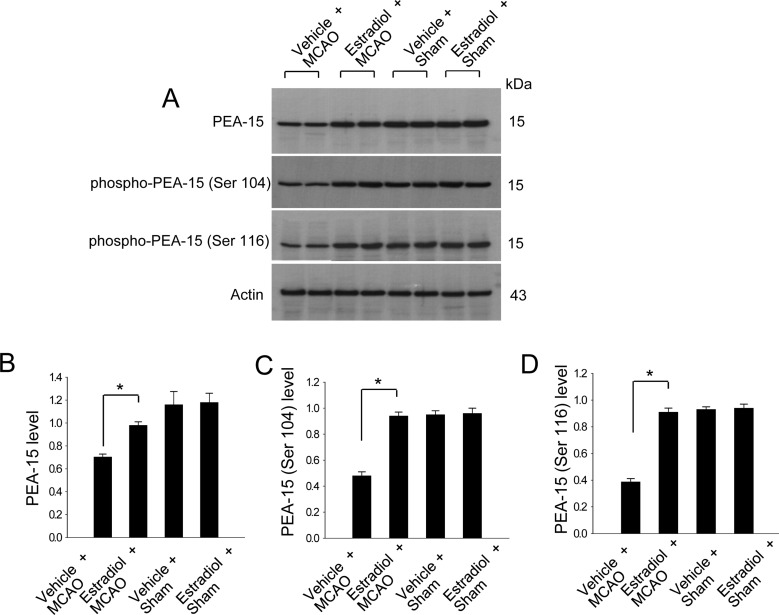
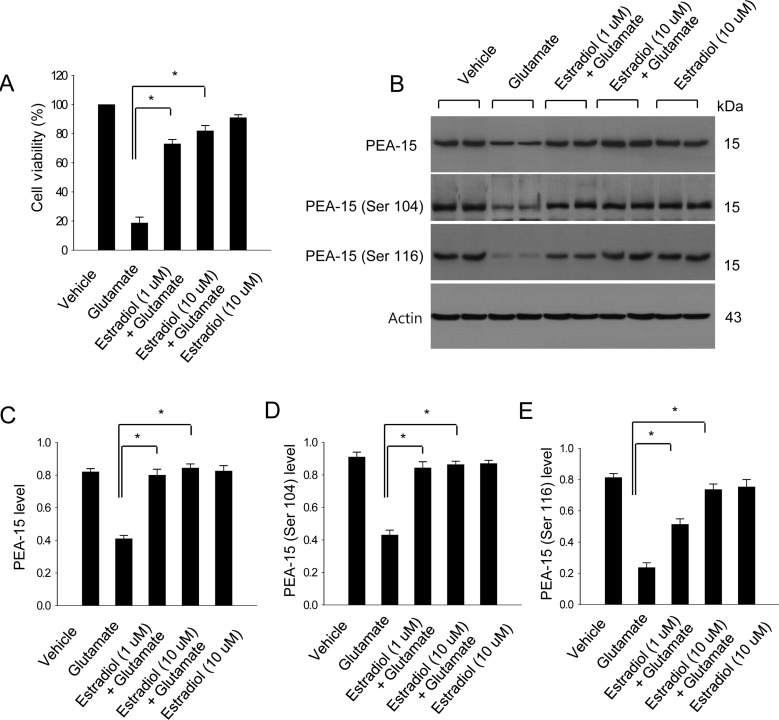
- Estradiol exerts a neuroprotective effect against focal cerebral ischemic injury through the inhibition of apoptotic signals. Phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes 15 (PEA-15) is mainly expressed in brain that perform anti-apoptotic functions. This study investigated whether estradiol modulates the expression of PEA-15 and two phosphorylated forms of PEA-15 (Ser 104 and Ser 116) in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)-induced injury and glutamate exposure-induced neuronal cell death. Adult female rats were ovariectomized to remove endogenous estradiol and treated with vehicle or estradiol prior to MCAO. Focal cerebral ischemia was induced by MCAO and cerebral cortices were collected 24 h after MCAO. Western blot analysis indicated that estradiol prevents the MCAO-induced decrease in PEA-15, phospho-PEA-15 (Ser 104), phospho-PEA-15 (Ser 116). Glutamate exposure induced a reduction in PEA-15, phospho-PEA-15 (Ser 104), phospho-PEA-15 (Ser 116) in cultured neurons, whereas estradiol treatment attenuated the glutamate toxicity-induced decrease in the expression of these proteins. It has been known that phosphorylation of PEA-15 is an important step in carrying out its anti-apoptotic function. Thus, these findings suggest that the regulation of PEA-15 phosphorylation by estradiol contributes to the neuroprotective function of estradiol in ischemic brain injury.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Behl C, Widmann M, Trapp T, Holsboer F. 17-beta estradiol protects neurons from oxidative stress-induced cell death in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995; 216(2):473–482. PMID: 7488136.2. Culmsee C, Vedder H, Ravati A, Junker V, Otto D, Ahlemeyer B, Krieg JC, Krieglstein J. Neuroprotection by estrogens in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia and in cultured neurons: evidence for a receptor-independent antioxidative mechanism. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999; 19(11):1263–1269. PMID: 10566973.
Article3. Tnez I, Collado JA, Medina FJ, Pea J, Del C Muoz M, Jimena I, Franco F, Rueda I, Feijo M, Muntan J, Montilla P. 17 beta-Estradiol may affect vulnerability of striatum in a 3-nitropropionic acid-induced experimental model of Huntington's disease in ovariectomized rats. Neurochem Int. 2006; 48(5):367–373. PMID: 16420966.4. Kurata K, Takebayashi M, Morinobu S, Yamawaki S. beta-estradiol, dehydroepiandrosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate protect against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons by different mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004; 311(1):237–245. PMID: 15175425.5. Sribnick EA, Ray SK, Nowak MW, Li L, Banik NL. 17beta-estradiol attenuates glutamate-induced apoptosis and preserves electrophysiologic function in primary cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2004; 76(5):688–696. PMID: 15139027.6. Danziger N, Yokoyama M, Jay T, Cordier J, Glowinski J, Chneiweiss H. Cellular expression, developmental regulation, and phylogenic conservation of PEA-15, the astrocytic major phosphoprotein and protein kinase C substrate. J Neurochem. 1995; 64(3):1016–1025. PMID: 7861130.
Article7. Sharif A, Renault F, Beuvon F, Castellanos R, Canton B, Barbeito L, Junier MP, Chneiweiss H. The expression of PEA-15 (phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes of 15 kDa) defines subpopulations of astrocytes and neurons throughout the adult mouse brain. Neuroscience. 2004; 126(2):263–275. PMID: 15207344.
Article8. Krueger J, Chou FL, Glading A, Schaefer E, Ginsberg MH. Phosphorylation of phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes (PEA-15) regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent transcription and cell proliferation. Mol Biol Cell. 2005; 16(8):3552–3561. PMID: 15917297.
Article9. Renault F, Formstecher E, Callebaut I, Junier MP, Chneiweiss H. The multifunctional protein PEA-15 is involved in the control of apoptosis and cell cycle in astrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003; 66(8):1581–1588. PMID: 14555237.
Article10. Condorelli G, Vigliotta G, Cafieri A, Trencia A, Andal P, Oriente F, Miele C, Caruso M, Formisano P, Beguinot F. PED/PEA-15: an anti-apoptotic molecule that regulates FAS/TNFR1-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 1999; 18(31):4409–4415. PMID: 10442631.
Article11. Estells A, Charlton CA, Blau HM. The phosphoprotein protein PEA-15 inhibits Fas- but increases TNF-R1-mediated caspase-8 activity and apoptosis. Dev Biol. 1999; 216(1):16–28. PMID: 10588860.12. Kitsberg D, Formstecher E, Fauquet M, Kubes M, Cordier J, Canton B, Pan G, Rolli M, Glowinski J, Chneiweiss H. Knock-out of the neural death effector domain protein PEA-15 demonstrates that its expression protects astrocytes from TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. J Neurosci. 1999; 19(19):8244–8251. PMID: 10493725.13. Araujo H, Danziger N, Cordier J, Glowinski J, Chneiweiss H. Characterization of PEA-15, a major substrate for protein kinase C in astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993; 268(8):5911–5920. PMID: 8449955.
Article14. Danziger N, Yokoyama M, Jay T, Cordier J, Glowinski J, Chneiweiss H. Cellular expression, developmental regulation, and phylogenic conservation of PEA-15, the astrocytic major phosphoprotein and protein kinase C substrate. J Neurochem. 1995; 64(3):1016–1025. PMID: 7861130.
Article15. Trencia A, Perfetti A, Cassese A, Vigliotta G, Miele C, Oriente F, Santopietro S, Giacco F, Condorelli G, Formisano P, Beguinot F. Protein kinase B/Akt binds and phosphorylates PED/PEA-15, stabilizing its antiapoptotic action. Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 23(13):4511–4521. PMID: 12808093.
Article16. Koh PO, Won CK, Cho JH. Estradiol prevents the injury-induced decrease of Akt/glycogen synthase kinase 3beta phosphorylation. Neurosci Lett. 2006; 404(3):303–308. PMID: 16815634.17. Koh PO. 17Beta-estradiol prevents the glutamate-induced decrease of Akt and its downstream targets in HT22 cells. J Vet Med Sci. 2007; 69(3):285–288. PMID: 17409645.
Article18. Dubal DB, Shughrue PJ, Wilson ME, Merchenthaler I, Wise PM. Estradiol modulates bcl-2 in cerebral ischemia: a potential role for estrogen receptors. J Neurosci. 1999; 19(15):6385–6393. PMID: 10414967.
Article19. Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989; 20(1):84–91. PMID: 2643202.
Article20. Mize AL, Shapiro RA, Dorsa DM. Estrogen receptor-mediated neuroprotection from oxidative stress requires activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Endocrinology. 2003; 144(1):306–312. PMID: 12488359.
Article21. Sung JH, Cho EH, Min W, Kim MJ, Kim MO, Jung EJ, Koh PO. Identification of proteins regulated by estradiol in focal cerebral ischemic injury--a proteomics approach. Neurosci Lett. 2010; 477(2):66–71. PMID: 20403413.
Article22. Sharif A, Canton B, Junier MP, Chneiweiss H. PEA-15 modulates TNFalpha intracellular signaling in astrocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003; 1010(1):43–50. PMID: 15033692.23. Dawson DA, Martin D, Hallenbeck JM. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha reduces focal cerebral ischemic injury in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Neurosci Lett. 1996; 218(1):41–44. PMID: 8939476.
Article24. Wetzel M, Li L, Harms KM, Roitbak T, Ventura PB, Rosenberg GA, Khokha R, Cunningham LA. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 facilitates Fas-mediated neuronal cell death following mild ischemia. Cell Death Differ. 2008; 15(1):143–151. PMID: 17962815.
Article25. Renganathan H, Vaidyanathan H, Knapinska A, Ramos JW. Phosphorylation of PEA-15 switches its binding specificity from ERK/MAPK to FADD. Biochem J. 2005; 390(3):729–735. PMID: 15916534.
Article26. Chen J, Chua KW, Chua CC, Yu H, Pei A, Chua BH, Hamdy RC, Xu X, Liu CF. Antioxidant activity of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone provides neuroprotection against glutamate-induced toxicity. Neurosci Lett. 2011; 499(3):181–185. PMID: 21651962.
Article27. Jin ML, Park SY, Kim YH, Oh JI, Lee SJ, Park G. The neuroprotective effects of cordycepin inhibit glutamate-induced oxidative and ER stress-associated apoptosis in hippocampal HT22 cells. Neurotoxicology. 2014; 41:102–111. PMID: 24486958.
Article28. Gursoy E, Cardounel A, Kalimi M. Pregnenolone protects mouse hippocampal (HT-22) cells against glutamate and amyloid beta protein toxicity. Neurochem Res. 2001; 26(1):15–21. PMID: 11358277.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Focal Cerebral Ischemia Induces Decrease of Astrocytic Phosphoprotein PEA-15 in Brain Tissue and HT22 Cells
- Gingko biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates ischemic brain injury-induced reduction in Ca2+ sensor protein hippocalcin
- Optimizing Stem Cell Therapy after Ischemic Brain Injury
- Repeated Exposure to beta-phenylethylamine Produces Locomotor Sensitization to Amphetamine, but Not Vice Versa, in the Rat
- Expression of ICAM-1 mRNA after Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats