Comparison Between Signature Cytokines of Nasal Tissues in Subtypes of Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital and Institute of New Frontier Research, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 2Clinical Mucosal Immunology Study Group, Seoul, Korea. kicubi@daum.net
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Allergy-Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, FL, USA.
- KMID: 2431852
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2019.11.2.201
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Endotype in chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) has been established in the last decade. However, the exact immunologic profile of CRS still has controversy because it has a considerable immunologic heterogeneity. Therefore, we investigated various inflammatory mediators according to different nasal tissues in chronic rhinosinusitis and compared them within the same subject.
METHODS
We collected uncinate process mucosa (UP) and nasal polyp (NP) tissues from controls, CRS without NP (CRSsNP) and CRS with NP (CRSwNP). Expression levels of 28 inflammatory mediators including T helper (Th) 1, Th2, Th17, proinflammatory cytokines and remodeling markers were determined by multiplex immunoassay and were analyzed using paired tests as well as principal component analysis (PCA) to investigate endotype in each subtype of CRS.
RESULTS
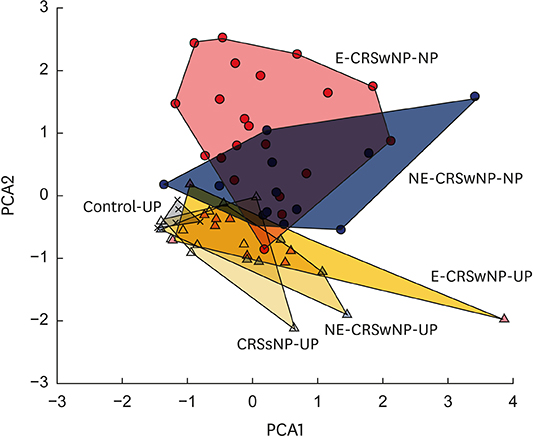
Signature inflammatory mediators are interleukin (IL)-5, C-C motif chemokine ligand (CCL)-24, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-4, and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1 in eosinophilic NP, whereas IL-17A, IL-1β, and matrix metallopeptidase (MMP)-9 were detected as signature inflammatory markers in non-eosinophilic NP. Despite differences in inflammatory cytokine profile between eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic NP, the common upregulation of IL-5, CCL-11, IL-23, IL-2Rα, VCAM-1, MMP-3 and MMP-9 were shown in NP compared to UP within the same subject. In the PCA, we observed that Th2 immune response was helpful in discriminating between nasal tissues in subtypes of CRS and that there was a partial overlap between non-eosinophilic NP and eosinophilic NP in terms of Th2 mediators.
CONCLUSIONS
Commonly upregulated mediators in NP were Th2-associated, compared with UP regardless of CRS subtypes, whereas signature markers were distinct in each NP subtype. These findings imply that Th2 inflammatory responses may play a role in the development of NP regardless of CRSwNP subtypes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Cytokines*
Eosinophils
Immunoassay
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-23
Interleukin-5
Interleukins
Monocytes
Mucous Membrane
Nasal Polyps
Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis
Population Characteristics
Principal Component Analysis
Rhinitis
Sinusitis
Up-Regulation
Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1
Cytokines
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-23
Interleukin-5
Interleukins
Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1
Figure
Cited by 8 articles
-
Does Inflammatory Endotype Change in Patients With Chronic Rhinosinusitis?
Dong-Kyu Kim, Dae Woo Kim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(2):153-155. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.2.153.Immunological Characteristics in Refractory Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps Undergoing Revision Surgeries
Gwanghui Ryu, Dong-Kyu Kim, Hun-Jong Dhong, Kyoung Mi Eun, Kyung Eun Lee, Il Gyu Kong, HyoYeol Kim, Seung-Kyu Chung, Dong-Young Kim, Chae-Seo Rhee, Seong-Ho Cho, Sang Duk Hong, Dae Woo Kim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(5):664-676. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.664.In-Depth, Proteomic Analysis of Nasal Secretions from Patients With Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps
Yi-Sook Kim, Dohyun Han, JinYoup Kim, Dae Woo Kim, Yong-Min Kim, Ji-Hun Mo, Hyo-Geun Choi, Jong-Wan Park, Hyun-Woo Shin
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(5):691-708. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.691.Elastase-Positive Neutrophils Are Associated With Refractoriness of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps in an Asian Population
Dong-Kyu Kim, Jin Youp Kim, Young Eun Han, Joon Kon Kim, Hee-Suk Lim, Kyoung Mi Eun, Seung Koo Yang, Dae Woo Kim
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2020;12(1):42-55. doi: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.1.42.Risk Model Establishment of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis: a Multicenter Study in Korea
Jin-Young Min, Yong Min Kim, Dae Woo Kim, Jeong-Whun Kim, Jin Kook Kim, Ji-Hun Mo, Jae-Min Shin, Kyu-Sup Cho, Sanggyu Kwak, Seung-Heon Shin
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(40):e264. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e264.Neutrophils as a Protagonist and Target in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Hai Wang, Li Pan, Zheng Liu
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;12(4):337-347. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2019.00654.Can Neutrophils Be a Cellular Biomarker in Asian Chronic Rhinosinusitis?
Dae Woo Kim
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;12(4):325-326. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2019.01452.Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyp According to Histopathological Endotypes and Staining Method for Neutrophilic Polyp Classification and Its Clinical Implication
Hyoyeon Kim, Shin Hyuk Yoo, Kwang Hyun Byun, Ji-Hun Mo
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2024;67(2):79-86. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2023.00332.
Reference
-
1. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012; 50:1–12.
Article2. Brandsted R, Sindwani R. Impact of depression on disease-specific symptoms and quality of life in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol. 2007; 21:50–54.
Article3. Kim DH, Han K, Kim SW. Effect of chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyp on quality of life in South Korea: 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Korean. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2016; 9:150–156.
Article4. Van Zele T, Claeys S, Gevaert P, Van Maele G, Holtappels G, Van Cauwenberge P, et al. Differentiation of chronic sinus diseases by measurement of inflammatory mediators. Allergy. 2006; 61:1280–1289.
Article5. Polzehl D, Moeller P, Riechelmann H, Perner S. Distinct features of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Allergy. 2006; 61:1275–1279.
Article6. Van Bruaene N, Pérez-Novo CA, Basinski TM, Van Zele T, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N, et al. T-cell regulation in chronic paranasal sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:1435–1441.
Article7. Kim DK, Kang SI, Kong IG, Cho YH, Song SK, Hyun SJ, et al. Two-track medical treatment strategy according to the clinical scoring system for chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10:490–502.
Article8. Tomassen P, Vandeplas G, Van Zele T, Cardell LO, Arebro J, Olze H, et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137:1449–1456.e4.
Article9. Liao B, Liu JX, Li ZY, Zhen Z, Cao PP, Yao Y, et al. Multidimensional endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis and their association with treatment outcomes. Allergy. 2018; 73:1459–1469.
Article10. Ikeda K, Shiozawa A, Ono N, Kusunoki T, Hirotsu M, Homma H, et al. Subclassification of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp based on eosinophil and neutrophil. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:E1–E9.
Article11. Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ, Cui YH, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:478–484.
Article12. Shi LL, Xiong P, Zhang L, Cao PP, Liao B, Lu X, et al. Features of airway remodeling in different types of Chinese chronic rhinosinusitis are associated with inflammation patterns. Allergy. 2013; 68:101–109.
Article13. Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, et al. Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122:961–968.
Article14. Kim DK, Jin HR, Eun KM, Mutusamy S, Cho SH, Oh S, et al. Non-eosinophilic nasal polyps shows increased epithelial proliferation and localized disease pattern in the early stage. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0139945.
Article15. Wang X, Zhang N, Bo M, Holtappels G, Zheng M, Lou H, et al. Diversity of TH cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: a multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 138:1344–1353.16. Mahdavinia M, Suh LA, Carter RG, Stevens WW, Norton JE, Kato A, et al. Increased noneosinophilic nasal polyps in chronic rhinosinusitis in US second-generation Asians suggest genetic regulation of eosinophilia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 135:576–579.
Article17. Shin HW, Kim DK, Park MH, Eun KM, Lee M, So D, et al. IL-25 as a novel therapeutic target in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 135:1476–1485.e7.
Article18. Kim DK, Jin HR, Eun KM, Mo JH, Cho SH, Oh S, et al. The role of interleukin-33 in chronic rhinosinusitis. Thorax. 2017; 72:635–645.
Article19. Lam M, Hull L, Imrie A, Snidvongs K, Chin D, Pratt E, et al. Interleukin-25 and interleukin-33 as mediators of eosinophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015; 29:175–181.
Article20. Jeong WJ, Lee CH, Cho SH, Rhee CS. Eosinophilic allergic polyp: a clinically oriented concept of nasal polyp. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 144:241–246.21. Liu X, Dong H, Wang M, Gao Y, Zhang T, Hu G, et al. IL-1α-induced microvascular endothelial cells promote neutrophil killing by increasing MMP-9 concentration and lysozyme activity. Immunol Res. 2016; 64:133–142.
Article22. Owen CA. Roles for proteinases in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2008; 3:253–268.23. Van Bruaene N, Derycke L, Perez-Novo CA, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N, et al. TGF-beta signaling and collagen deposition in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:253–259.24. Wang H, Li ZY, Jiang WX, Liao B, Zhai GT, Wang N, et al. The activation and function of IL-36γ in neutrophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141:1646–1658.
Article25. Shi LL, Song J, Xiong P, Cao PP, Liao B, Ma J, et al. Disease-specific T-helper cell polarizing function of lesional dendritic cells in different types of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 190:628–638.
Article26. Tan BK, Klingler AI, Poposki JA, Stevens WW, Peters AT, Suh LA, et al. Heterogeneous inflammatory patterns in chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps in Chicago, Illinois. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 139:699–703.e7.
Article27. Stevens WW, Ocampo CJ, Berdnikovs S, Sakashita M, Mahdavinia M, Suh L, et al. Cytokines in chronic rhinosinusitis. role in eosinophilia and aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 192:682–694.
Article28. Nagarkar DR, Poposki JA, Tan BK, Comeau MR, Peters AT, Hulse KE, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin activity is increased in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132:593–600.e12.
Article29. Tan BK, Chandra RK, Pollak J, Kato A, Conley DB, Peters AT, et al. Incidence and associated premorbid diagnoses of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:1350–1360.
Article30. Kim DW, Cho SH. Emerging endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis and its application to precision medicine. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9:299–306.
Article31. Stammberger H. Endoscopic endonasal surgery--concepts in treatment of recurring rhinosinusitis. Part I. Anatomic and pathophysiologic considerations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1986; 94:143–147.
Article32. Stammberger H, Posawetz W. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Concept, indications and results of the Messerklinger technique. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1990; 247:63–76.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical treatment according to phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis
- Neutrophils as a Protagonist and Target in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- Update on Biologics in Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyposis
- Emerging Endotypes of Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Its Application to Precision Medicine
- Role of Fungal and Bacterial Superantigen in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Polyps