J Korean Med Assoc.
2009 Jan;52(1):22-29. 10.5124/jkma.2009.52.1.22.
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: New Concept of Pathogenesis and Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Respiratory and Allergy Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Korea. uhstuhst@paran.com
- KMID: 2137730
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2009.52.1.22
Abstract
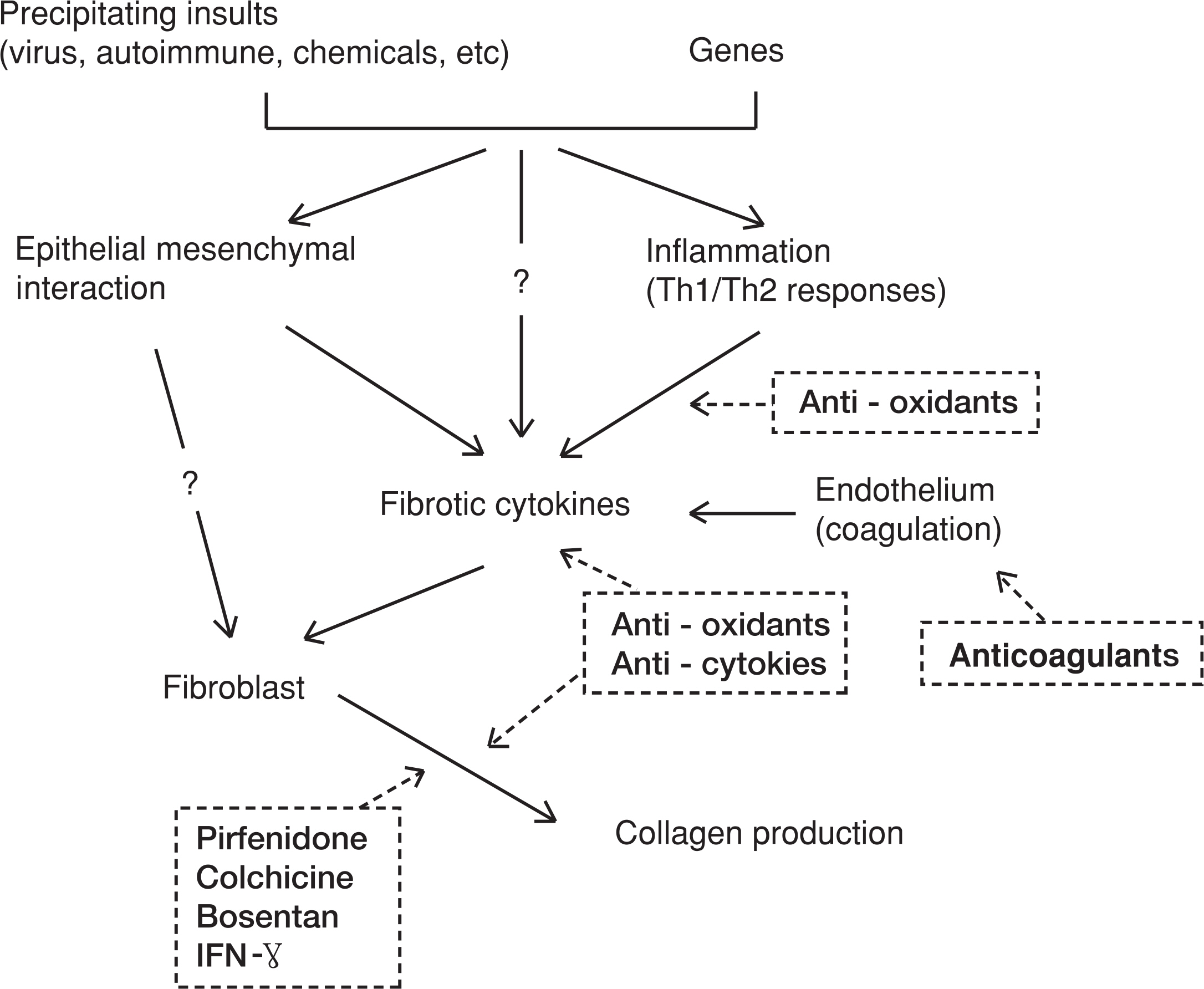
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is characterized by chronic progressive parenchymal lung fibrosis. Although extensive researches for IPF pathogenesis have been reported for several decades, the precise mechanisms are still unknown and the specific treatments for elimination of fibrosis and prolongation of survival are also still unknown. The role of inflammation as initial insult of lung fibrosis is still debating by controversial results of animal model experiments. The recent proposed mechanism for IPF is a dysregulation of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions which have critical role in tissue repair process and fibrosis. This hypothesis suggests impaired communications between epithelium and mesenchymal cells in terms of abnormal proliferation of mesenchymal cells instead of normal proliferation of epithelium. At recent, epithelial mesenchymal transition is regarded as an important source of myofiborblast which are major cells producing extracellular matrix. Classical treatment agents including steroid are already known to be ineffective in treatment of IPF, and also, IFN-gamma one of newly emerging drug, is proved to be ineffective in treatment of IPF. Now new drugs involved in the molecular levels of signal transduction of fibrotic pathway, inhibition of various growth factors (TGF, CTGF, VEGF), and direct inhibition of fibrotic cytokines are under investigated in animal experiments and human clinical studies. Further studies should be focused on the evaluation of precipitating factors, genetic markers, drugs for inhibiting specific molecules responsible for lung fibrosis, and agents for controlling ECM precipitation.
MeSH Terms
-
Animal Experimentation
Cytokines
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Epithelium
Extracellular Matrix
Fibrosis
Genetic Markers
Humans
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Inflammation
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Lung
Models, Animal
Precipitating Factors
Signal Transduction
Cytokines
Genetic Markers
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lok SS, Haider Y, Howell D, Stewart JP, Hasleton PS, Egan JJ. Murine gammaherpes virus as a cofactor in the development of pulmonary fibrosis in bleomycin resistant mice. Eur Respir J. 2002; 20:1228–1232.
Article2. Zamo A, Poletti V, Reghellin D, Montagna L, Pedron S, Piccoli P, Chilosi M. HHV-8 and EBV are not commonly found in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2005; 22:123–128.3. Baumgartner KB, Samet JM, Stidley CA, Colby TV, Waldron JA. Cigarette smoking: a risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997; 155:242–248.
Article4. Raghu G, Weycker D, Edelsberg J, Bradford WZ, Oster G. Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006; 174:810–816.
Article5. Raghu G, Yang ST, Spada C, Hayes J, Pellegrini CA. Sole treatment of acid gastroesophageal reflux in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a case series. Chest. 2006; 129:794–800.6. Steele MP, Speer MC, Loyd JE, Brown KK, Herron A, Sli-fer SH, Burch LH, Wahidi MM, Phillips JA 3rd, Sporn TA, McAdams HP, Schwarz MI, Schwartz DA. Clinical and pathologic features of familial interstitial pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 172:1146–1152.
Article7. Flaherty KR, Travis WD, Colby TV, Toews GB, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Jain A, Strawderman RL, Flint A, Lynch JP, Martinez FJ. Histopathologic variability in usual and nonspecific interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 164:1722–1727.
Article8. Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 157:1301–1315.9. Kolb M, Margetts PJ, Anthony DC, Pitossi F, Gauldie J. Transient expression of IL-1beta induces acute lung injury and chronic repair leading to pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:1529–1536.10. Pottier N, Chupin C, Defamie V, Cardinaud B, Sutherland R, Rios G, Gauthier F, Wolters PJ, Berthiaume Y, Barbry P, Mari B. Relationships between early inflammatory response to bleomycin and sensitivity to lung fibrosis: a role for dipeptidyl-peptidase I and tissue inhibitor of meta-lloproteinase-3? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 176:1098–1107.11. Adamson IY, Young L, Bowden DH. Relationship of alveolar epithelial injury and repair to the induction of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1988; 130:377–383.12. Huaux F, Louahed J, Hudspith B, Meredith C, Delos M, Renauld JC, Lison D. Role of interleukin-10 in the lung response to silica in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998; 18:51–59.
Article13. Sime PJ, Xing Z, Graham FL, Csaky KG, Gauldie J. Adeno-vector-mediated gene transfer of active transforming growth factor-beta1 induces prolonged severe fibrosis in rat lung. J Clin Invest. 1997; 100:768–776.
Article14. Warburton D, Tefft D, Mailleux A, Bellusci S, Thiery JP, Zhao J, Buckley S, Shi W, Driscoll B. Do lung remodeling, repair, and regeneration recapitulate respiratory ontogeny? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 164(S):59–62.
Article15. Desmouliere A, Chaponnier C, Gabbiani G. Tissue repair, contraction, and the myofibroblast. Wound Repair Regen. 2005; 13:7–12.16. Horowitz JC, Thannickal VJ. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006; 27:600–612.
Article17. Kuhn C, McDonald JA. The roles of the myofibroblast in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical features of sites of active extracellular matrix synthesis. Am J Pathol. 1991; 138:1257–1265.18. Wynn TA. Fibrotic disease and the T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004; 4:583–594.
Article19. Suga M, Iyonaga K, Ichiyasu H, Saita N, Yamasaki H, Ando M. Clinical significance of MCP-1 levels in BALF and serum in patients with interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 1999; 14:376–382.
Article20. Jakubzick C, Choi ES, Kunkel SL, Evanoff H, Martinez FJ, Puri RK, Flaherty KR, Toews GB, Colby TV, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Travis WD, Hogaboam CM. Augmented pulmonary IL-4 and IL-13 receptor subunit expression in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. J Clin Pathol. 2004; 57:477–486.
Article21. Jakubzick C, Choi ES, Carpenter KJ, Kunkel SL, Evanoff H, Martinez FJ, Flaherty KR, Toews GB, Colby TV, Travis WD, Joshi BH, Puri RK, Hogaboam CM. Human pulmonary fibroblasts exhibit altered interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 receptor subunit expression in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Am J Pathol. 2004; 164:1989–2001.
Article22. Gurujeyalakshmi G, Giri SN. Molecular mechanisms of antifi-brotic effect of interferon gamma in bleomycin-mouse model of lung fibrosis: downregulation of TGF-beta and procollagen I and III gene expression. Exp Lung Res. 1995; 21:791–808.23. Ong C, Wong C, Roberts CR, Teh HS, Jirik FR. Anti-IL-4 Btreatment prevents dermal collagen deposition in the tight-skin mouse model of scleroderma. Eur J Immunol. 1998; 28:2619–2629.24. Magro CM, Allen J, Liff D, Pope-Haman A, Waldman WJ, Moh P, Rothrauff S, ERoss PJ. The role of microvascular injury in the evolution of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003; 119:556–567.
Article25. Magro CM, Waldman WJ, Knight DA, Allen JN, Nadasdy T, Frambach GE, Ross P, Marsh CB. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis related to endothelial injury and antiendothelial cell antibodies. Hum Immunol. 2006; 67:284–297.
Article26. Kotani I, Sato A, Hayakawa H, Urano T, Takada Y, Takada A. Increased procoagulant and antifibrinolytic activities in the lungs with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thromb Res. 1995; 77:493–504.
Article27. American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:646–664.28. Ziesche R, Hofbauer E, Wittmann K, Petkov V, Block LH. A preliminary study of longterm treatment with interferon gamma-1b and low-dose prednisolone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1264–1269.
Article29. Raghu G, Brown KK, Bradford WZ, Starko K, Noble PW, Schwartz DA, King TE Jr. A placebo-controlled trial of interferon gamma-1b in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:125–133.
Article30. Antoniou KM, Nicholson AG, Dimadi M, Malagari K, Latsi P, Rapti A, Tzanakis N, Trigidou R, Polychronopoulos V, Bouros D. Long-term clinical effects of interferon gamma-1b and colchicine in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2006; 28:496–504.
Article31. Iyer SN, Gurujeyalakshmi G, Giri SN. Effects of pirfenidone on procollagen gene expression at the transcriptional level in bleomycin hamster model of lung fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999; 289:211–218.32. Azuma A, Nukiwa T, Tsuboi E, Suga M, Abe S, Nakata K, Taguchi Y, Nagai S, Itoh H, Ohi M, Sato A, Kudoh S. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:1040–1047.
Article33. Saleh D, Furukawa K, Tsao MS, Maghazachi A, Corrin B, Yanagisawa M, Barnes PJ, Giaid A. Elevated expression of endothelin-1 and endothelin-converting enzyme-1 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: possible involvement of proinflammatory cytokines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997; 16:187–193.
Article34. King TE Jr., Behr J, Brown KK, du Bois RM, Lancaster L, de Andrade JA, Stahler G, Leconte I, Roux S, Raghu G. BUILD-1: a randomized placebo-controlled trial of bosentan in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 177:75–81.
Article35. Demedts M, Behr J, Buhl R, Costabel U, Dekhuijzen R, Jansen HM, MacNee W, Thomeer M, Wallaert B, Laurent F, Nicholson AG, Verbeken EK, Verschakelen J, Flower CD, Capron F, Petruzzelli S, De Vuyst P, van den Bosch JM, Rodriguez-Becerra E, Corvasce G, Lankhorst I, Sardina M, Montanari M. High-dose acetylcysteine in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:2229–2242.
Article36. Kubo H, Nakayama K, Yanai M, Suzuki T, Yamaya M, Watanabe M, Sasaki H. Anticoagulant therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2005; 128:1475–1482.
Article37. Raghu G, Brown KK, Costabel U, Cottin V, du Bois RM, Lasky JA, Thomeer M, Utz JP, Khandker RK, McDermott L, Fate-nejad S. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with etanercept: an exploratory, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 178:948–955.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Advances in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Two cases of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Pharmacological treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: current trends and future directions
- Pathogenesis and New Diagnosis Guideline of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial lung disease: focusing on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis