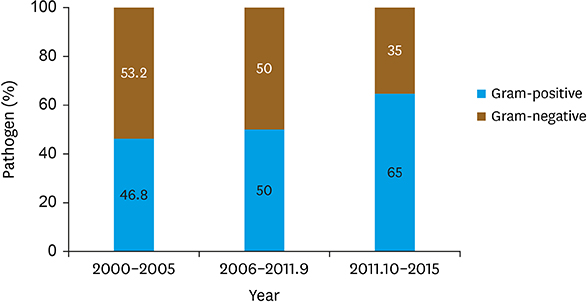Pediatr Infect Vaccine.
2018 Aug;25(2):82-90. 10.14776/piv.2018.25.e3.
Bacterial Infections after Liver Transplantation in Children: Single Center Study for 16 Years
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, the Republic of Korea. pedwilly@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, the Republic of Korea.
- 3Department of General Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, the Republic of Korea.
- 4Department of General Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, the Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2418540
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14776/piv.2018.25.e3
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Survival after liver transplantation (LT) has improved over the years, but infection is still a major complication. We aimed to identify the characteristics of bacterial infections in pediatric LT recipients.
METHODS
This study is a retrospective review of 189 consecutive children undergoing LT between 2000 and 2015 at a single center. In this study, the incidence of infection was determined for the following periods: within 1 month, between 1-5 months, and between 6-12 months. Patients who underwent liver transplants more than once or multiple organ transplants were excluded.
RESULTS
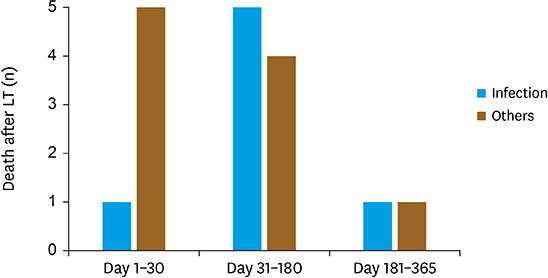
All patients had received postoperative antibiotic for 3 days. Only the maintenance immunosuppression with oral tacrolimus and steroids were performed. As a result, 132 bacterial infections developed in 87 (46.0%) patients (0.70 events per person-year). Bacterial infections occurred most frequently within the first month (n=84, 63.6%) after LT. In the pathogens, Staphylococcus aureus (15.2%), Enterococcus species (15.2%), and Klebsiella species (13.6%) were most common. Regarding the organ infected, bloodstream was most common (n=39, 29.5%), followed by peritoneum (n=28, 21.2%), urinary tract (n=25, 18.9%), and lungs (n=20, 15.2%). We changed prophylactic antibiotics from ampicillin-sulbactam to piperacillin-tazobactam at 2011, October, there were no significant effects in the prevalence of antibiotics resistant bacterial infections. The 1-year mortality was 9.0% (n=17), in which 41.2% (n=7) was attributable to bacterial infection; septicemia (n=4), pneumonia (n=2), and peritonitis (n=1).
CONCLUSIONS
The incidence and type of bacterial infectious complications after LT in pediatric patients were similar to those of previous studies. Bacterial complications affecting mortality occur within 6 months after transplantation, so proper prophylaxis and treatment in this period may improve the prognosis of LT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Bacterial Infections*
Child*
Enterococcus
Humans
Immunosuppression
Incidence
Klebsiella
Korea
Liver Transplantation*
Liver*
Lung
Mortality
Peritoneum
Peritonitis
Pneumonia
Prevalence
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Sepsis
Staphylococcus aureus
Steroids
Tacrolimus
Transplants
Urinary Tract
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Steroids
Tacrolimus
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moreno R, Berenguer M. Post-liver transplantation medical complications. Ann Hepatol. 2006; 5:77–85.
Article2. Roberts MS, Angus DC, Bryce CL, Valenta Z, Weissfeld L. Survival after liver transplantation in the United States: a disease-specific analysis of the UNOS database. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:886–897.
Article3. Bucuvalas JC, Ryckman FC. Long-term outcome after liver transplantation in children. Pediatr Transplant. 2002; 6:30–36.
Article4. Colombani PM, Dunn SP, Harmon WE, Magee JC, McDiarmid SV, Spray TL. Pediatric transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2003; 3:Suppl 4. 53–63.
Article5. D'Alessandro AM, Knechtle SJ, Chin LT, Fernandez LA, Yagci G, Leverson G, et al. Liver transplantation in pediatric patients: twenty years of experience at the University of Wisconsin. Pediatr Transplant. 2007; 11:661–670.6. Ryckman FC, Alonso MH, Bucuvalas JC, Balistreri WF. Long-term survival after liver transplantation. J Pediatr Surg. 1999; 34:845–850.
Article7. Winston DJ, Emmanouilides C, Busuttil RW. Infections in liver transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 1995; 21:1077–1091.
Article8. Kim JE, Oh SH, Kim KM, Choi BH, Kim DY, Cho HR, et al. Infections after living donor liver transplantation in children. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:527–531.
Article9. Shoji K, Funaki T, Kasahara M, Sakamoto S, Fukuda A, Vaida F, et al. Risk factors for bloodstream infection after living-donor liver transplantation in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015; 34:1063–1068.
Article10. Kusne S, Dummer JS, Singh N, Iwatsuki S, Makowka L, Esquivel C, et al. Infections after liver transplantation: an analysis of 101 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1988; 67:132–143.11. Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC, Hughes JM. CDC definitions for nosocomial infections, 1988. Am J Infect Control. 1988; 16:128–140.
Article12. Fishman JA. Infection in solid-organ transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:2601–2614.
Article13. Blair JE, Kusne S. Bacterial, mycobacterial, and protozoal infections after liver transplantation--part I. Liver Transpl. 2005; 11:1452–1459.
Article14. Shepherd RW, Turmelle Y, Nadler M, Lowell JA, Narkewicz MR, McDiarmid SV, et al. Risk factors for rejection and infection in pediatric liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8:396–403.
Article15. García S, Roque J, Ruza F, González M, Madero R, Alvarado F, et al. Infection and associated risk factors in the immediate postoperative period of pediatric liver transplantation: a study of 176 transplants. Clin Transplant. 1998; 12:190–197.16. Fulginiti VA, Scribner R, Groth CG, Putnam CW, Brettschneider L, Gilbert S, et al. Infections in recipients of liver homografts. N Engl J Med. 1968; 279:619–626.
Article17. Singh N, Wagener MM, Obman A, Cacciarelli TV, de Vera ME, Gayowski T. Bacteremias in liver transplant recipients: shift toward gram-negative bacteria as predominant pathogens. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:844–849.
Article18. Torbenson M, Wang J, Nichols L, Jain A, Fung J, Nalesnik MA. Causes of death in autopsied liver transplantation patients. Mod Pathol. 1998; 11:37–46.19. Bubak ME, Porayko MK, Krom RA, Wiesner RH. Complications of liver biopsy in liver transplant patients: increased sepsis associated with choledochojejunostomy. Hepatology. 1991; 14:1063–1065.
Article20. Kim YJ, Kim SI, Wie SH, Kim YR, Hur JA, Choi JY, et al. Infectious complications in living-donor liver transplant recipients: a 9-year single-center experience. Transpl Infect Dis. 2008; 10:316–324.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Pediatric Liver Transplantation
- Changes in the epidemiology and management of bacterial infections in cirrhosis
- Infections after Living Donor Liver Transplantation in Children
- Acute liver failure in children
- Infectious Complications after Liver Transplantation according to Donor: Comparison between Orthotopic and Living Donor Transplantation