Korean Diabetes J.
2010 Aug;34(4):237-243. 10.4093/kdj.2010.34.4.237.
The Relationship of Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio with Homeostasis Model Assessment Insulin Resistance Index and Metabolic Syndrome in Apparently Healthy Korean Male Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hongsiri@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2029877
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.4.237
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We investigated the relationships of adiponectin/leptin (A/L) ratio with cardiovascular risk factors, insulin resistance index, and metabolic syndrome (MS) in apparently healthy Korean male adults.
METHODS
Sixty-eight male subjects were enrolled among the participants of an annual health check-up program (mean age, 55.1 years). Percent body fat (%) was measured using a bioelectric impedance analyzer. Serum leptin level was measured via radioimmunoassay, and adiponectin level was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Homeostasis model assessment (HOMA)-insulin resistance (IR) index was calculated, and the presence of metabolic syndrome was assessed.
RESULTS
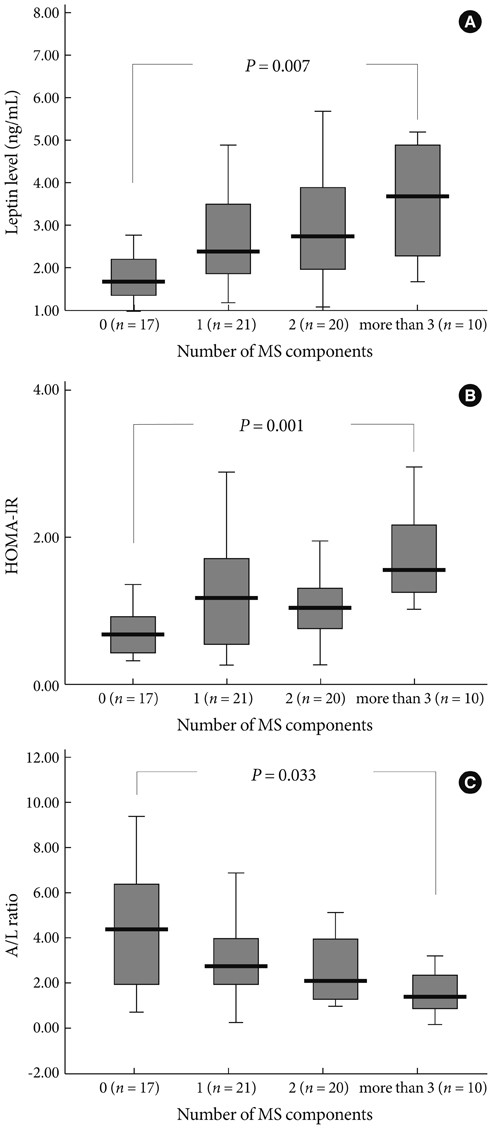
Adiponectin, leptin, and A/L ratio showed significant correlations with percent body fat, lipid profile, and HOMA-IR. Mean leptin and HOMA-IR levels were significantly higher, while A/L ratio was significantly lower in subjects with MS. With increasing number of MS components, the mean values of leptin and HOMA-IR increased and the A/L ratio decreased. In multiple regression analysis, HOMA-IR was significantly correlated with triglyceride, fasting glucose, and A/L ratio, while A/L ratio was significantly correlated with body mass index and HOMA-IR. HOMA-IR and A/L ratio were significant predictors for each other after adjustment for other factors.
CONCLUSION
A/L ratio correlated well with lipid profile, HOMA-IR, and the presence and number of MS components in Korean male subjects.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahima RS, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 11:327–332.2. Berg AH, Combs TP, Scherer PE. ACRP30/adiponectin: an adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 13:84–89.3. Baskin DG, Blevins JE, Schwartz MW. How the brain regulates food intake and body weight: the role of leptin. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 14:Suppl 6. 1417–1429.4. Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. 257:79–83.5. Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni PA. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:1930–1935.6. Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994. 372:425–432.7. Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentration in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med. 1996. 334:292–295.8. Kim JY, Shin HW, Jeong IK, Cho SW, Min SJ, Lee SJ, Park CY, Oh KW, Hong EG, Kim HK, Kim DM, Yu JM, Ihm SH, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Park SW. The relationship of adiponectin, leptin and ghrelin to insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in human obesity. Korean J Med. 2005. 69:631–641.9. Inoue M, Maehata E, Yano M, Taniyama M, Suzuki S. Correlation between the adiponectin-leptin ratio and parameters of insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism. 2005. 54:281–286.10. Inoue M, Yano M, Yamakado M, Maehata E, Suzuki S. Relationship between the adiponectin-leptin ratio and parameters of insulin resistance in subjects without hyperglycemia. Metabolism. 2006. 55:1248–1254.11. Finucane FM, Luan J, Wareham NJ, Sharp SJ, O'Rahilly S, Balkau B, Flyvbjerg A, Walker M, Hojlund K, Nolan JJ. European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance: Relationship between Insulin Sensitivity and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Study Group, Savage DB. Correlation of the leptin:adiponectin ratio with measures of insulin resistance in non-diabetic individuals. Diabetologia. 2009. 52:2345–2349.12. Zaletel J, Barlovic DP, Prezelj J. Adiponectin-leptin ratio: a useful estimate of insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Endocrinol Invest. Epub 2010 Feb 5.13. Norata GD, Raselli S, Grigore L, Garlaschelli K, Dozio E, Magni P, Catapano AL. Leptin:adiponectin ratio is an independent predictor of intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery. Stroke. 2007. 38:2844–2846.14. DeFronzo RA. Insulin resistance: multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis. Neth J Med. 1997. 50:191–197.15. Grundy SM. Hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1999. 83:25F–29F.16. Zhuo Q, Wang Z, Fu P, Piao J, Tian Y, Xu J, Yang X. Comparison of adiponectin, leptin and leptin to adiponectin ratio as diagnostic marker for metabolic syndrome in older adults of Chinese major cities. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009. 84:27–33.17. Lee JM, Kim SR, Yoo SJ, Hong OK, Son HS, Chang SA. The relationship between adipokines, metabolic parameters and insulin resistance in patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. J Int Med Res. 2009. 37:1803–1812.18. Grundy SM. Metabolic syndrome scientific statement by the American Heart Association and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. 25:2243–2244.19. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985. 28:412–419.20. Oda N, Imamura S, Fujita T, Uchida Y, Inagaki K, Kakizawa H, Hayakawa N, Suzuki A, Takeda J, Horikawa Y, Itoh M. The ratio of leptin to adiponectin can be used as an index of insulin resistance. Metabolism. 2008. 57:268–273.21. Mente A, Razak F, Blankenberg S, Vuksan V, Davis AD, Miller R, Teo K, Gerstein H, Sharma AM, Yusuf S, Anand SS, Anand SS. Study of the Health Assessment And Risk Evaluation. Study of the Health Assessment And Risk Evaluation in Aboriginal Peoples Investigators. Ethnic variation in adiponectin and leptin levels and their association with adiposity and insulin resistance. Diabetes Care. 2010. 33:1629–1634.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The relationship between leptin adiponectin ratio and insulin resistance in healthy children
- Serum leptin, adiponectin and resistin levels in obese children and their correlations with insulin resistance
- Impact of Serum Leptin to Adiponectin Ratio on Regression of Metabolic Syndrome in High-Risk Individuals: The ARIRANG Study
- Correlations of Leptin, Adiponectin and Leptin/Adiponectin Ratio with Metabolic Disorders in the Childhood Obesity
- Leptin and adiponectin levels in girls with central precocious puberty before and during GnRH agonist treatment