Anat Cell Biol.
2019 Dec;52(4):462-468. 10.5115/acb.19.210.
Neuregulin 1/ErbB4 signaling attenuates neuronal cell damage under oxygen-glucose deprivation in primary hippocampal neurons
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Neuroscience, Eulji University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. rswoo@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Department of Emergency Medical Technology, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea. jhlee@dju.kr
- KMID: 2466700
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.19.210
Abstract
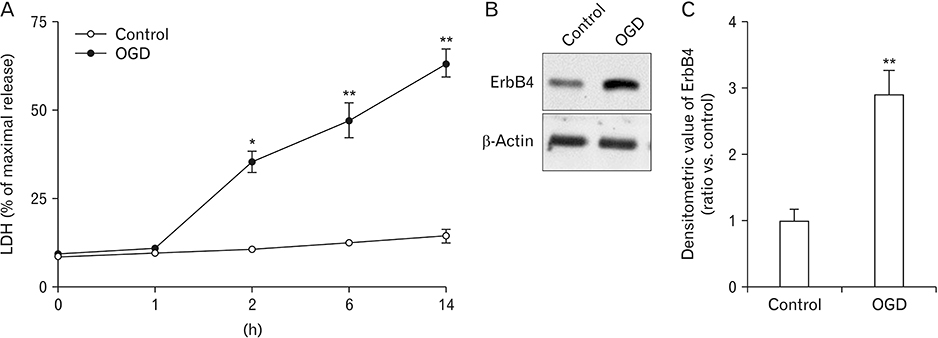
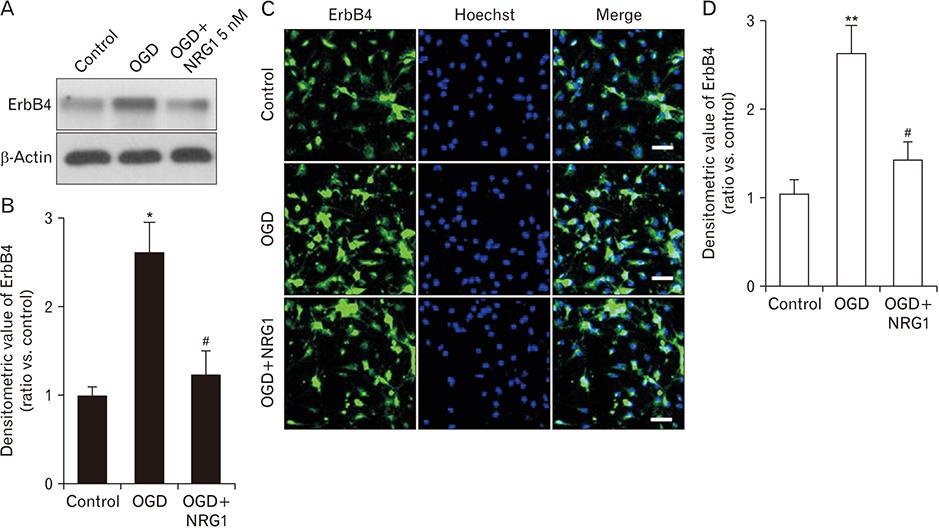
- The hippocampus is one of the most important brain areas of cognition. This region is particularly sensitive to hypoxia and ischemia. Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) has been shown to be able to protect against focal cerebral ischemia. The aim of the present study was to investigate the neuroprotective effect of NRG1 in primary hippocampal neurons and its underlying mechanism. Our data showed oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced cytotoxicity and overexpression of ErbB4 in primary hippocampal neurons. Moreover, pretreatment with NRG1 could inhibit OGD-induced overexpression of ErbB4. In addition, NRG1 significantly attenuated neuronal death induced by OGD. The neuroprotective effect of NRG1 was blocked in ischemic neurons after pretreatment with AG1478, an inhibitor of ErbB4, but not after pretreatment with AG879, an inhibitor of ErbB2. These results indicate an important role of ErbB4 in NRG1-mediated neuroprotection, suggesting that endogenous ErbB4 might serve as a valuable therapeutic target for treating global cerebral ischemia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Calle PA, Bogaert MG, Van Reempts JL, Buylaert WA. Neurological damage in a cardiopulmonary arrest model in the rat. J Pharmacol Methods. 1989; 22:185–195.2. Petito CK, Feldmann E, Pulsinelli WA, Plum F. Delayed hippocampal damage in humans following cardiorespiratory arrest. Neurology. 1987; 37:1281–1286.3. Kass IS, Lipton P. Protection of hippocampal slices from young rats against anoxic transmission damage is due to better maintenance of ATP. J Physiol. 1989; 413:1–11.4. Kobayashi T, Kuroda S, Tada M, Houkin K, Iwasaki Y, Abe H. Calcium-induced mitochondrial swelling and cytochrome c release in the brain: its biochemical characteristics and implication in ischemic neuronal injury. Brain Res. 2003; 960:62–70.5. Falls DL. Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res. 2003; 284:14–30.6. Buonanno A, Fischbach GD. Neuregulin and ErbB receptor signaling pathways in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001; 11:287–296.7. Mei L, Nave KA. Neuregulin-ERBB signaling in the nervous system and neuropsychiatric diseases. Neuron. 2014; 83:27–49.8. Corfas G, Roy K, Buxbaum JD. Neuregulin 1-erbB signaling and the molecular/cellular basis of schizophrenia. Nat Neurosci. 2004; 7:575–580.9. Lai C, Lemke G. An extended family of protein-tyrosine kinase genes differentially expressed in the vertebrate nervous system. Neuron. 1991; 6:691–704.10. Li B, Woo RS, Mei L, Malinow R. The neuregulin-1 receptor erbB4 controls glutamatergic synapse maturation and plasticity. Neuron. 2007; 54:583–597.11. Garcia RA, Vasudevan K, Buonanno A. The neuregulin receptor ErbB-4 interacts with PDZ-containing proteins at neuronal synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97:3596–3601.12. Huang YZ, Won S, Ali DW, Wang Q, Tanowitz M, Du QS, Pelkey KA, Yang DJ, Xiong WC, Salter MW, Mei L. Regulation of neuregulin signaling by PSD-95 interacting with ErbB4 at CNS synapses. Neuron. 2000; 26:443–455.13. Woo RS, Li XM, Tao Y, Carpenter-Hyland E, Huang YZ, Weber J, Neiswender H, Dong XP, Wu J, Gassmann M, Lai C, Xiong WC, Gao TM, Mei L. Neuregulin-1 enhances depolarization-induced GABA release. Neuron. 2007; 54:599–610.14. Akasofu S, Kosasa T, Kimura M, Kubota A. Protective effect of donepezil in a primary culture of rat cortical neurons exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003; 472:57–63.15. Goldshmit Y, Erlich S, Pinkas-Kramarski R. Neuregulin rescues PC12-ErbB4 cells from cell death induced by H2O2. Regulation of reactive oxygen species levels by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:46379–46385.16. Erlich S, Goldshmit Y, Lupowitz Z, Pinkas-Kramarski R. ErbB-4 activation inhibits apoptosis in PC12 cells. Neuroscience. 2001; 107:353–362.17. Lee JH, Yoo JY, Kim HB, Yoo HI, Song DY, Min SS, Baik TK, Woo RS. Neuregulin1 attenuates H2O2-induced reductions in EAAC1 protein levels and reduces H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Neurotox Res. 2019; 35:401–409.18. Croslan DR, Schoell MC, Ford GD, Pulliam JV, Gates A, Clement CM, Harris AE, Ford BD. Neuroprotective effects of neuregulin-1 on B35 neuronal cells following ischemia. Brain Res. 2008; 1210:39–47.19. Guan YF, Wu CY, Fang YY, Zeng YN, Luo ZY, Li SJ, Li XW, Zhu XH, Mei L, Gao TM. Neuregulin 1 protects against ischemic brain injury via ErbB4 receptors by increasing GABAergic transmission. Neuroscience. 2015; 307:151–159.20. Lu YM, Gao YP, Tao RR, Liao MH, Huang JY, Wu G, Han F, Li XM. Calpain-Dependent ErbB4 Cleavage Is Involved in Brain Ischemia-Induced Neuronal Death. Mol Neurobiol. 2016; 53:2600–2609.21. Guo WP, Wang J, Li RX, Peng YW. Neuroprotective effects of neuregulin-1 in rat models of focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2006; 1087:180–185.22. Li Y, Xu Z, Ford GD, Croslan DR, Cairobe T, Li Z, Ford BD. Neuroprotection by neuregulin-1 in a rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2007; 1184:277–283.23. Xu Z, Jiang J, Ford G, Ford BD. Neuregulin-1 is neuroprotective and attenuates inflammatory responses induced by ischemic stroke. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 322:440–446.24. Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Chiang MF, Yang HI, Thajeb P, Li H. Neuregulin-1 reduces ischemia-induced brain damage in rats. Neurobiol Aging. 2004; 25:935–944.25. Yu HN, Park WK, Nam KH, Song DY, Kim HS, Baik TK, Woo RS. Neuregulin 1 controls glutamate uptake by up-regulating excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1). J Biol Chem. 2015; 290:20233–20244.26. Fernandes J, Vieira M, Carreto L, Santos MA, Duarte CB, Carvalho AL, Santos AE. In vitro ischemia triggers a transcriptional response to down-regulate synaptic proteins in hippocampal neurons. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e99958.27. Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006; 7:505–516.28. Law AJ, Shannon Weickert C, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Harrison PJ. Neuregulin-1 (NRG-1) mRNA and protein in the adult human brain. Neuroscience. 2004; 127:125–136.29. Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell. 1997; 91:231–241.30. Baik TK, Kim YJ, Kang SM, Song DY, Min SS, Woo RS. Blocking the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway inhibits neuregulin-1-mediated rescue of neurotoxicity induced by Aβ1-42. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016; 68:1021–1029.31. Chen YJ, Johnson MA, Lieberman MD, Goodchild RE, Schobel S, Lewandowski N, Rosoklija G, Liu RC, Gingrich JA, Small S, Moore H, Dwork AJ, Talmage DA, Role LW. Type III neuregulin-1 is required for normal sensorimotor gating, memory-related behaviors, and corticostriatal circuit components. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:6872–6883.32. Silberberg G, Darvasi A, Pinkas-Kramarski R, Navon R. The involvement of ErbB4 with schizophrenia: association and expression studies. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2006; 141B:142–148.33. Joshi D, Fullerton JM, Weickert CS. Elevated ErbB4 mRNA is related to interneuron deficit in prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 2014; 53:125–132.34. Erlich S, Shohami E, Pinkas-Kramarski R. Closed head injury induces up-regulation of ErbB-4 receptor at the site of injury. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000; 16:597–608.35. Xu Z, Ford BD. Upregulation of erbB receptors in rat brain after middle cerebral arterial occlusion. Neurosci Lett. 2005; 375:181–186.36. Zhu JM, Li KX, Cao SX, Chen XJ, Shen CJ, Zhang Y, Geng HY, Chen BQ, Lian H, Zhang JM, Li XM. Increased NRG1-ErbB4 signaling in human symptomatic epilepsy. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:141.37. Depboylu C, Rösler TW, de Andrade A, Oertel WH, Höglinger GU. Systemically administered neuregulin-1β1 rescues nigral dopaminergic neurons via the ErbB4 receptor tyrosine kinase in MPTP mouse models of Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2015; 133:590–597.38. Ryu J, Yu HN, Cho H, Kim HS, Baik TK, Lee SJ, Woo RS. Neuregulin-1 exerts protective effects against neurotoxicities induced by C-terminal fragments of APP via ErbB4 receptor. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 119:73–81.39. Woo RS, Lee JH, Kim HS, Baek CH, Song DY, Suh YH, Baik TK. Neuregulin-1 protects against neurotoxicities induced by Swedish amyloid precursor protein via the ErbB4 receptor. Neuroscience. 2012; 202:413–423.40. Ryu J, Hong BH, Kim YJ, Yang EJ, Choi M, Kim H, Ahn S, Baik TK, Woo RS, Kim HS. Neuregulin-1 attenuates cognitive function impairments in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 7:e2117.41. Min SS, An J, Lee JH, Seol GH, Im JH, Kim HS, Baik TK, Woo RS. Neuregulin-1 prevents amyloid β-induced impairment of long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices via ErbB4. Neurosci Lett. 2011; 505:6–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of ErbB4 in the apoptotic neurons of Alzheimer's disease brain
- Expression of ErbB4 in the neurons of Alzheimer's disease brain and APP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease
- Expressional Change of Nitric Oxide Synthase and erbB4 in Rat Hippocampus after Seizure
- An Immunohistochemical Study of ErbB4 Receptor in Alzheimer's Disease Hippocampus
- The Neuroprotective Potential of Cyanidin-3-glucoside Fraction Extracted from Mulberry Following Oxygen-glucose Deprivation