J Lipid Atheroscler.
2019 Sep;8(2):221-231. 10.12997/jla.2019.8.2.221.
Efficacy and Safety of Prescription Omega-3 Fatty Acids Added to Stable Statin Therapy in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertriglyceridemia: a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. sjyoo@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Endocrinology, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2458387
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12997/jla.2019.8.2.221
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of omega-3 fatty acids added to statin monotherapy in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes who have persistent hypertriglyceridemia despite statin therapy.
METHODS
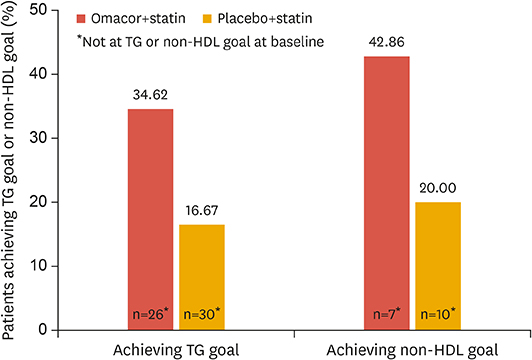
This study was a randomized controlled trial conducted in 4 clinical sites between February 2009 and February 2011. The inclusion criteria were patients with type 2 diabetes who had received ≥6 weeks of statin therapy and had fasting triglyceride (TG) levels ≥1.7mmol/L and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels <2.6 mmol/L. The study regimen consisted of 16 weeks of randomized treatment with omega-3 fatty acids (4 g/day) plus a statin (n=26) or statin only (n=30). The primary endpoint was the change from baseline to final visit in mean TG level.
RESULTS
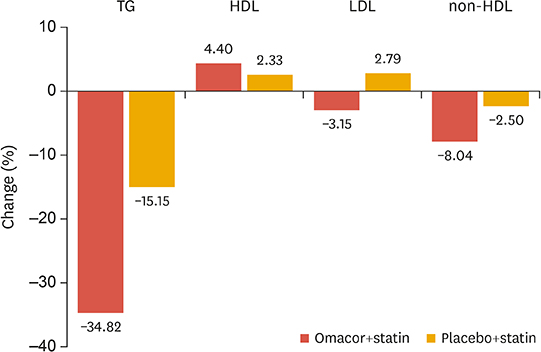
A total of 56 participants were analyzed. At week 16, the change in the TG level in the combination therapy group differed significantly from the change in the statin monotherapy group (−34.8% vs. −15.2%, p=0.0176). Treatment with omega-3 fatty acids plus a statin was also associated with a significant decrease in non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol compared with baseline, but the difference was not significant compared with the statin monotherapy group (−8.0% vs. −2.5%, p=0.165). The changes in LDL cholesterol and HbA1c levels did not differ significantly between groups. The study medications were well tolerated, and adverse events were comparable between two groups.
CONCLUSION
Adding omega-3 fatty acids to statin treatment reduced TG levels more effectively than statin monotherapy without undesirable effects in Korean type 2 diabetic patients who had hypertriglyceridemia despite well-controlled LDL cholesterol on stable statin therapy. TRIAL REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02305355
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Haffner SM, Lehto S, Rönnemaa T, Pyörälä K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:229–234.
Article2. de Vegt F, Dekker JM, Stehouwer CD, Nijpels G, Bouter LM, Heine RJ. Similar 9-year mortality risks and reproducibility for the World Health Organization and American Diabetes Association glucose tolerance categories: the Hoorn study. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:40–44.
Article3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2012. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:Suppl 1. S11–S63.4. National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002; 106:3143–3421.5. Nordestgaard BG, Benn M, Schnohr P, Tybjaerg-Hansen A. Nonfasting triglycerides and risk of myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, and death in men and women. JAMA. 2007; 298:299–308.
Article6. Teno S, Uto Y, Nagashima H, Endoh Y, Iwamoto Y, Omori Y, et al. Association of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:1401–1406.
Article7. Brunzell JD. Clinical practice. Hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:1009–1017.8. Din JN, Newby DE, Flapan AD. Omega 3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease--fishing for a natural treatment. BMJ. 2004; 328:30–35.
Article9. Dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E after myocardial infarction: results of the GISSI-Prevenzione trial. Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nell'Infarto miocardico. Lancet. 1999; 354:447–455.10. Yokoyama M, Origasa H, Matsuzaki M, Matsuzawa Y, Saito Y, Ishikawa Y, et al. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid on major coronary events in hypercholesterolaemic patients (JELIS): a randomised open-label, blinded endpoint analysis. Lancet. 2007; 369:1090–1098.
Article11. Hartweg J, Farmer AJ, Perera R, Holman RR, Neil HA. Meta-analysis of the effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on lipoproteins and other emerging lipid cardiovascular risk markers in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:1593–1602.
Article12. Hartweg J, Perera R, Montori V, Dinneen S, Neil HA, Farmer A. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008; CD003205.
Article13. Nordøy A, Bønaa KH, Nilsen H, Berge RK, Hansen JB, Ingebretsen OC. Effects of Simvastatin and omega-3 fatty acids on plasma lipoproteins and lipid peroxidation in patients with combined hyperlipidaemia. J Intern Med. 1998; 243:163–170.
Article14. Durrington PN, Bhatnagar D, Mackness MI, Morgan J, Julier K, Khan MA, et al. An omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrate administered for one year decreased triglycerides in simvastatin treated patients with coronary heart disease and persisting hypertriglyceridaemia. Heart. 2001; 85:544–548.
Article15. Davidson MH, Stein EA, Bays HE, Maki KC, Doyle RT, Shalwitz RA, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of adding prescription omega-3 fatty acids 4 g/d to simvastatin 40 mg/d in hypertriglyceridemic patients: an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Ther. 2007; 29:1354–1367.
Article16. Keech A, Simes RJ, Barter P, Best J, Scott R, Taskinen MR, et al. Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in 9795 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005; 366:1849–1861.
Article17. Balk EM, Lichtenstein AH, Chung M, Kupelnick B, Chew P, Lau J. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on serum markers of cardiovascular disease risk: a systematic review. Atherosclerosis. 2006; 189:19–30.
Article18. Mori TA, Burke V, Puddey IB, Watts GF, O'Neal DN, Best JD, et al. Purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids have differential effects on serum lipids and lipoproteins, LDL particle size, glucose, and insulin in mildly hyperlipidemic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000; 71:1085–1094.
Article19. Preiss D, Seshasai SR, Welsh P, Murphy SA, Ho JE, Waters DD, et al. Risk of incident diabetes with intensive-dose compared with moderate-dose statin therapy: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011; 305:2556–2564.
Article20. Sattar N, Preiss D, Murray HM, Welsh P, Buckley BM, de Craen AJ, et al. Statins and risk of incident diabetes: a collaborative meta-analysis of randomised statin trials. Lancet. 2010; 375:735–742.
Article21. Hartweg J, Farmer AJ, Holman RR, Neil A. Potential impact of omega-3 treatment on cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009; 20:30–38.
Article22. Contacos C, Barter PJ, Sullivan DR. Effect of pravastatin and omega-3 fatty acids on plasma lipids and lipoproteins in patients with combined hyperlipidemia. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993; 13:1755–1762.
Article23. Friday KE, Childs MT, Tsunehara CH, Fujimoto WY, Bierman EL, Ensinck JW. Elevated plasma glucose and lowered triglyceride levels from omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in type II diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1989; 12:276–281.
Article24. Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC. PAI-1, obesity, insulin resistance and risk of cardiovascular events. Thromb Haemost. 1997; 78:656–660.
Article25. Boberg M, Pollare T, Siegbahn A, Vessby B. Supplementation with n-3 fatty acids reduces triglycerides but increases PAI-1 in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992; 22:645–650.
Article26. Kabir M, Skurnik G, Naour N, Pechtner V, Meugnier E, Rome S, et al. Treatment for 2 mo with n 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces adiposity and some atherogenic factors but does not improve insulin sensitivity in women with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007; 86:1670–1679.
Article27. Nomura S, Inami N, Shouzu A, Omoto S, Kimura Y, Takahashi N, et al. The effects of pitavastatin, eicosapentaenoic acid and combined therapy on platelet-derived microparticles and adiponectin in hyperlipidemic, diabetic patients. Platelets. 2009; 20:16–22.
Article28. Cefalu WT, Schneider DJ, Carlson HE, Migdal P, Gan Lim L, Izon MP, et al. Effect of combination glipizide GITS/metformin on fibrinolytic and metabolic parameters in poorly controlled type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:2123–2128.
Article29. Manson JE, Cook NR, Lee IM, Christen W, Bassuk SS, Mora S, et al. Marine n-3 fatty acids and prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:23–32.
Article30. Bhatt DL, Steg PG, Miller M, Brinton EA, Jacobson TA, Ketchum SB, et al. Cardiovascular risk reduction with icosapent ethyl for hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:11–22.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Beneficial Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Low Density Lipoprotein Particle Size in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Already under Statin Therapy
- Combination pharmacotherapy in lipid management
- Update on the Pharmacologic Agents for Dyslipidemia
- Effects of Adding omega-3 Fatty Acids to Simvastatin on Lipids, Lipoprotein Size and Subspecies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Hypertriglyceridemia
- An Update on Hypertriglyceridemia-Induced Acute Pancreatitis