Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2019 Jan;22(1):1-27. 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.1.1.
Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity: Recommendations from the Committee on Pediatric Obesity of the Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Chungju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Pediatrics, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 8Department of Pediatrics, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 9Department of Pediatrics, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 12Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Children's Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 13Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 15Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 16Department of Physical Education, College of Education, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 17Department of Psychiatry, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 18Department of Medical Nutrition, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 19Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. hryang@snubh.org
- 20Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2430912
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2019.22.1.1
Abstract
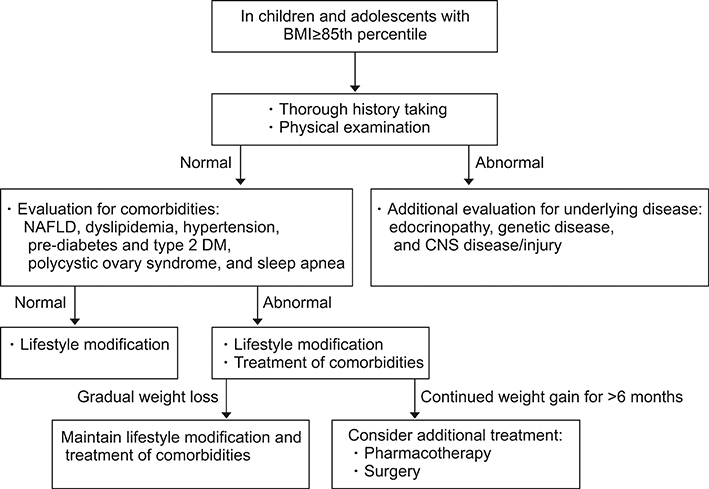
- The Committee on Pediatric Obesity of the Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition newly developed the first Korean Guideline on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Obesity in Children and Adolescents to deliver an evidence-based systematic approach to childhood obesity in South Korea. The following areas were systematically reviewed, especially on the basis of all available references published in South Korea and worldwide, and new guidelines were established in each area with the strength of recommendations based on the levels of evidence: 1) definition and diagnosis of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents; 2) principles of treatment of pediatric obesity; 3) behavioral interventions for children and adolescents with obesity, including diet, exercise, lifestyle, and mental health; 4) pharmacotherapy; and 5) bariatric surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kang KS. Nutritional counseling for obese children with obesity-related metabolic abnormalities in Korea. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2017; 20:71–78.
Article2. Yang HR, Yi DY, Choi HS. Comparison between a pediatric health promotion center and a pediatric obesity clinic in detecting metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:1672–1677.
Article3. Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, et al. GRADE Working Group. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2004; 328:1490.
Article4. Atkins D, Eccles M, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Henry D, Hill S, et al. GRADE Working Group. Systems for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations I: critical appraisal of existing approaches the GRADE Working Group. BMC Health Serv Res. 2004; 4:38.
Article5. Guarino A, Albano F, Ashkenazi S, Gendrel D, Hoekstra JH, Shamir R, et al. European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases. European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition/European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute gastroenteritis in children in Europe. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008; 46:Suppl 2. S81–S122.6. Kim JH, Yun S, Hwang SS, Shim JO, Chae HW, Lee YJ, the Korean, et al. Committee for the Development of Growth Standards for Korean Children and Adolescents. Committee for School Health and Public Health Statistics, the Korean Pediatric Society. Division of Health and Nutrition Survey, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The 2017 Korean National Growth Charts for children and adolescents: development, improvement, and prospects. Korean J Pediatr. 2018; 61:135–149.
Article7. Whitlock EP, O'Conner EA, Williams SB, Beil TL, Lutz KW. Effectiveness of primary care interventions for weight management in children and adolescents. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality;2010. 01. Report No.: 10-05144-EF-1.8. Barlow SE, Dietz WH. Obesity evaluation and treatment: Expert Committee recommendations. The Maternal and Child Health Bureau, Health Resources and Services Administration and the Department of Health and Human Services. Pediatrics. 1998; 102:E29.9. Ogden CL, Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Mei Z, Guo S, Wei R, et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2000 growth charts for the United States: improvements to the 1977 National Center for Health Statistics version. Pediatrics. 2002; 109:45–60.
Article10. Javed A, Jumean M, Murad MH, Okorodudu D, Kumar S, Somers VK, et al. Diagnostic performance of body mass index to identify obesity as defined by body adiposity in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Obes. 2015; 10:234–244.
Article11. Styne DM, Arslanian SA, Connor EL, Farooqi IS, Murad MH, Silverstein JH, et al. Pediatric obesity-assessment, treatment, and prevention: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:709–757.
Article12. WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO Child Growth Standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 2006; 450:76–85.13. Freedman DS, Mei Z, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS, Dietz WH. Cardiovascular risk factors and excess adiposity among overweight children and adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study. J Pediatr. 2007; 150:12–17.e2.
Article14. Barlow SE. Expert Committee. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: summary report. Pediatrics. 2007; 120:Suppl 4. S164–S192.
Article15. Valerio G, Maffeis C, Saggese G, Ambruzzi MA, Balsamo A, Bellone S, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of pediatric obesity: consensus position statement of the Italian Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology and the Italian Society of Pediatrics. Ital J Pediatr. 2018; 44:88.
Article16. de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ. 2007; 85:660–667.
Article17. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:Suppl 1. S81–S90.18. Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents: summary report. Pediatrics. 2011; 128:Suppl 5. S213–S256.19. Schwimmer JB, Dunn W, Norman GJ, Pardee PE, Middleton MS, Kerkar N, et al. alanine aminotransferase cutoff values are set too high for reliable detection of pediatric chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:1357–1364. 1364.e1–1364.e2.
Article20. Legro RS, Arslanian SA, Ehrmann DA, Hoeger KM, Murad MH, Pasquali R, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:4565–4592.
Article21. Wise MS, Nichols CD, Grigg-Damberger MM, Marcus CL, Witmans MB, Kirk VG, et al. Executive summary of respiratory indications for polysomnography in children: an evidence-based review. Sleep. 2011; 34:389–398AW.
Article22. Zametkin AJ, Zoon CK, Klein HW, Munson S. Psychiatric aspects of child and adolescent obesity: a review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2004; 43:134–150.
Article23. Spear BA, Barlow SE, Ervin C, Ludwig DS, Saelens BE, Schetzina KE, et al. Recommendations for treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity. Pediatrics. 2007; 120:Suppl 4. S254–S288.
Article24. Rhee KE, Lumeng JC, Appugliese DP, Kaciroti N, Bradley RH. Parenting styles and overweight status in first grade. Pediatrics. 2006; 117:2047–2054.
Article25. Zeller MH, Reiter-Purtill J, Ramey C. Negative peer perceptions of obese children in the classroom environment. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008; 16:755–762.
Article26. Fox CL, Farrow CV. Global and physical self-esteem and body dissatisfaction as mediators of the relationship between weight status and being a victim of bullying. J Adolesc. 2009; 32:1287–1301.
Article27. Koval JJ, Pederson LL, Zhang X, Mowery P, McKenna M. Can young adult smoking status be predicted from concern about body weight and self-reported BMI among adolescents? Results from a ten-year cohort study. Nicotine Tob Res. 2008; 10:1449–1455.
Article28. Pearce MJ, Boergers J, Prinstein MJ. Adolescent obesity, overt and relational peer victimization, and romantic relationships. Obes Res. 2002; 10:386–393.
Article29. Rajjo T, Mohammed K, Alsawas M, Ahmed AT, Farah W, Asi N, et al. Treatment of pediatric obesity: an umbrella systematic review. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:763–775.
Article30. Mcmurray RG, Harrell JS, Bangdiwala SI, Bradley CB, Deng S, Levine A. A school-based intervention can reduce body fat and blood pressure in young adolescents. J Adolesc Health. 2002; 31:125–132.
Article31. Sallis JF, Conway TL, Prochaska JJ, McKenzie TL, Marshall SJ, Brown M. The association of school environments with youth physical activity. Am J Public Health. 2001; 91:618–620.
Article32. te Velde SJ, van Nassau F, Uijtdewilligen L, van Stralen MM, Cardon G, De Craemer M, et al. Energy balance-related behaviours associated with overweight and obesity in preschool children: a systematic review of prospective studies. Obes Rev. 2012; 13:Suppl 1. 56–74.
Article33. Epstein LH, Roemmich JN, Robinson JL, Paluch RA, Winiewicz DD, Fuerch JH, et al. A randomized trial of the effects of reducing television viewing and computer use on body mass index in young children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2008; 162:239–245.
Article34. Steffen LM, Sinaiko AR, Zhou X, Moran A, Jacobs DR Jr, Korenfeld Y, et al. Relation of adiposity, television and screen time in offspring to their parents. BMC Pediatr. 2013; 13:133.
Article35. Edwards C, Nicholls D, Croker H, Van Zyl S, Viner R, Wardle J. Family-based behavioural treatment of obesity: acceptability and effectiveness in the UK. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006; 60:587–592.
Article36. Schalkwijk AA, Bot SD, de Vries L, Westerman MJ, Nijpels G, Elders PJ. Perspectives of obese children and their parents on lifestyle behavior change: a qualitative study. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015; 12:102.
Article37. Munding E, Ponniah K, Stephen G, Weedn A. The Oklahoma Chapter AAP obesity provider and parent handouts: tools to encourage lifestyle changes to manage and prevent pediatric obesity. Pediatrics. 2018; 141:MeetingAbstract. Available from: http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/141/1_MeetingAbstract/00.2..info.
Article38. US Preventive Services Task Force. Grossman DC, Bibbins-Domingo K, Curry SJ, Barry MJ, Davidson KW, et al. Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2017; 317:2417–2426.39. Speiser PW, Rudolf MC, Anhalt H, Camacho-Hubner C, Chiarelli F, Eliakim A, et al. Childhood obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90:1871–1887.
Article40. Sherafat-Kazemzadeh R, Yanovski SZ, Yanovski JA. Pharmacotherapy for childhood obesity: present and future prospects. Int J Obes (Lond). 2013; 37:1–15.
Article41. Nobili V, Vajro P, Dezsofi A, Fischler B, Hadzic N, Jahnel J, et al. Indications and limitations of bariatric intervention in severely obese children and adolescents with and without nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: ESPGHAN Hepatology Committee Position Statement. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015; 60:550–561.
Article42. Michalsky M, Reichard K, Inge T, Pratt J, Lenders C. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. ASMBS pediatric committee best practice guidelines. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2012; 8:1–7.
Article43. Lee HS, Kwon SO, Lee Y. Weight status and dietary factors associated with sugar-sweetened beverage intake among Korean children and adolescents - Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008–2011. Clin Nutr Res. 2013; 2:135–142.
Article44. Ebbeling CB, Feldman HA, Osganian SK, Chomitz VR, Ellenbogen SJ, Ludwig DS. Effects of decreasing sugar-sweetened beverage consumption on body weight in adolescents: a randomized, controlled pilot study. Pediatrics. 2006; 117:673–680.
Article45. Ebbeling CB, Feldman HA, Chomitz VR, Antonelli TA, Gortmaker SL, Osganian SK, et al. A randomized trial of sugar-sweetened beverages and adolescent body weight. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:1407–1416.
Article46. DeBoer MD, Scharf RJ, Demmer RT. Sugar-sweetened beverages and weight gain in 2- to 5-year-old children. Pediatrics. 2013; 132:413–420.
Article47. Frantsve-Hawley J, Bader JD, Welsh JA, Wright JT. A systematic review of the association between consumption of sugar-containing beverages and excess weight gain among children under age 12. J Public Health Dent. 2017; 77:Suppl 1. S43–S66.
Article48. Kosova EC, Auinger P, Bremer AA. The relationships between sugar-sweetened beverage intake and cardiometabolic markers in young children. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2013; 113:219–227.
Article49. Gow ML, Ho M, Burrows TL, Baur LA, Stewart L, Hutchesson MJ, et al. Impact of dietary macronutrient distribution on BMI and cardiometabolic outcomes in overweight and obese children and adolescents: a systematic review. Nutr Rev. 2014; 72:453–470.
Article50. Thomas DE, Elliott EJ, Baur L. Low glycaemic index or low glycaemic load diets for overweight and obesity. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; (3):CD005105.
Article51. Schwingshackl L, Hobl LP, Hoffmann G. Effects of low glycaemic index/low glycaemic load vs. high glycaemic index/ high glycaemic load diets on overweight/obesity and associated risk factors in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr J. 2015; 14:87.
Article52. Ochiai H, Shirasawa T, Nanri H, Nishimura R, Hoshino H, Kokaze A. Relationship between eating quickly and overweight: a cohort study of schoolchildren in Japan. Acta Med Okayama. 2018; 72:121–128.53. Ochiai H, Shirasawa T, Ohtsu T, Nishimura R, Morimoto A, Hoshino H, et al. The impact of eating quickly on anthropometric variables among schoolgirls: a prospective cohort study in Japan. Eur J Public Health. 2014; 24:691–695.
Article54. Costa S, Pinto A, Santos AC, Oliveira A. The association of problematic eating behaviours with food quality and body mass index at 7 years of age. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2018; DOI: 10.1038/s41430-018-0169-z. [Epub ahead of print].
Article55. Timlin MT, Pereira MA, Story M, Neumark-Sztainer D. Breakfast eating and weight change in a 5-year prospective analysis of adolescents: project EAT (Eating Among Teens). Pediatrics. 2008; 121:e638–e645.
Article56. Croezen S, Visscher TL, Ter Bogt NC, Veling ML, Haveman-Nies A. Skipping breakfast, alcohol consumption and physical inactivity as risk factors for overweight and obesity in adolescents: results of the E-MOVO project. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2009; 63:405–412.
Article57. Brown AW, Bohan Brown MM, Allison DB. Belief beyond the evidence: using the proposed effect of breakfast on obesity to show 2 practices that distort scientific evidence. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013; 98:1298–1308.
Article58. Arora M, Nazar GP, Gupta VK, Perry CL, Reddy KS, Stigler MH. Association of breakfast intake with obesity, dietary and physical activity behavior among urban school-aged adolescents in Delhi, India: results of a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2012; 12:881.
Article59. Bayer O, Nehring I, Bolte G, von Kries R. Fruit and vegetable consumption and BMI change in primary school-age children: a cohort study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014; 68:265–270.
Article60. Bontrager Yoder AB, Schoeller DA. Fruits and vegetables displace, but do not decrease, total energy in school lunches. Child Obes. 2014; 10:357–364.
Article61. Kral TV, Rolls BJ. Energy density and portion size: their independent and combined effects on energy intake. Physiol Behav. 2004; 82:131–138.
Article62. Hollands GJ, Shemilt I, Marteau TM, Jebb SA, Lewis HB, Wei Y, et al. Portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; (9):CD011045.
Article63. Fisher JO, Liu Y, Birch LL, Rolls BJ. Effects of portion size and energy density on young children's intake at a meal. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007; 86:174–179.
Article64. McConahy KL, Smiciklas-Wright H, Mitchell DC, Picciano MF. Portion size of common foods predicts energy intake among preschool-aged children. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004; 104:975–979.
Article65. Torbahn G, Gellhaus I, Koch B, von Kries R, Obermeier V, Holl RW, et al. Reduction of portion size and eating rate is associated with BMI-SDS reduction in overweight and obese children and adolescents: results on eating and nutrition behaviour from the Observational KgAS Study. Obes Facts. 2017; 10:503–516.
Article66. Braithwaite I, Stewart AW, Hancox RJ, Beasley R, Murphy R, Mitchell EA. ISAAC Phase Three Study Group. ISAAC Phase Three Study Group. Fast-food consumption and body mass index in children and adolescents: an international cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2014; 4:e005813.
Article67. Niemeier HM, Raynor HA, Lloyd-Richardson EE, Rogers ML, Wing RR. Fast food consumption and breakfast skipping: predictors of weight gain from adolescence to adulthood in a nationally representative sample. J Adolesc Health. 2006; 39:842–849.
Article68. Lee JW, Hwang J, Cho HS. Dietary patterns of children and adolescents analyzed from 2001 Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey. Nutr Res Pract. 2007; 1:84–88.
Article69. Park EH, Oh MS, Kim S, Lee J, Kang KS. The analysis of factors causing the high prevalence of child obesity in Jeju Island. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2018; 21:127–133.
Article70. Martin A, Booth JN, Laird Y, Sproule J, Reilly JJ, Saunders DH. Physical activity, diet and other behavioural interventions for improving cognition and school achievement in children and adolescents with obesity or overweight. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018; 3:CD009728.
Article71. Pate RR, Davis MG, Robinson TN, Stone EJ, McKenzie TL, Young JC. American Heart Association Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism (Physical Activity Committee). Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Council on Cardiovascular Nursing. Promoting physical activity in children and youth: a leadership role for schools: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism (Physical Activity Committee) in collaboration with the Councils on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young and Cardiovascular Nursing. Circulation. 2006; 114:1214–1224.72. Kim KB, Lim KI, So WY, Park SK, Song W. A meta-analysis of the effects of exercise therapy applied in obesity studies. Korean J Obes. 2007; 16:177–185.73. Lee DC, Pate RR, Lavie CJ, Sui X, Church TS, Blair SN. Leisure-time running reduces all-cause and cardiovascular mortality risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 64:472–481.
Article74. Bidzan-Bluma I, Lipowska M. Physical activity and cognitive functioning of children: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018; 15:pii: E800.
Article75. Davis CL, Tomporowski PD, McDowell JE, Austin BP, Miller PH, Yanasak NE, et al. Exercise improves executive function and achievement and alters brain activation in overweight children: a randomized, controlled trial. Health Psychol. 2011; 30:91–98.
Article76. Mead E, Brown T, Rees K, Azevedo LB, Whittaker V, Jones D, et al. Diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese children from the age of 6 to 11 years. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 6:CD012651.
Article77. Oude Luttikhuis H, Baur L, Jansen H, Shrewsbury VA, O'Malley C, Stolk RP, et al. Interventions for treating obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009; (1):CD001872.
Article78. Strahan BE, Ahn H, Shuster J. Meta-analysis of the effects of exercise interventions on obese adolescents. J Nurs Interprof Leadersh Qual Saf. 2018; 2:Available from: https://digitalcommons.library.tmc.edu/uthoustonjqualsafe/vol2/iss1/1.79. Katzmarzyk PT, Denstel KD, Beals K, Bolling C, Wright C, Crouter SE, et al. Results from the United States of America's 2016 report card on physical activity for children and youth. J Phys Act Health. 2016; 13:11 Suppl 2. S307–S313.
Article80. Piekarz E, Schermbeck R, Young SK, Leider J, Ziemann M, Chriqui JF. School district wellness policies: evaluating progress and potential for improving children's health eight years after the federal mandate. School years 2006-07 through 2013-14. Chicago, IL: Bridging the Gap Program and the National Wellness Policy Study;2016.81. Ismail I, Keating SE, Baker MK, Johnson NA. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of aerobic vs. resistance exercise training on visceral fat. Obes Rev. 2012; 13:68–91.
Article82. Peirson L, Fitzpatrick-Lewis D, Morrison K, Warren R, Usman Ali M, Raina P. Treatment of overweight and obesity in children and youth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ Open. 2015; 3:E35–E46.
Article83. Farias Edos S, Gonçalves EM, Morcillo AM, Guerra-Júnior G, Amancio OM. Effects of programmed physical activity on body composition in post-pubertal schoolchildren. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2015; 91:122–129.
Article84. Baek S. The effect of physical activity on children's obesity. Korean J Obes. 2008; 17:55–64.85. Kim HG, Nam HK. A survey of life style habits of obese school children. J Korean Soc Sch Health. 1998; 11:99–110.86. Lee YJ, Chang KJ. A comparative study of obese children and normal children on dietary intake and environmental factors at an elementary school in Inchon. Korean J Community Nutr. 1999; 4:504–511.87. Kim BS, Lee KA. Comparisons of the daily activities and energy expenditures of normally-weighted and obese elementary school children. Korean J Nutr. 2005; 38:847–855.88. Park DK, Kang EH. A comparative study on the attitudes toward physical education as related to a degree of obesity in elementary students. J Korean Soc Study Phys Educ. 1996; 1:109–124.89. Kim MS, Choi JH, Shin HC, Joo KJ, Yoo YJ, Ko HJ, et al. Association of TV viewing and computer using habits with obesity and obesity related lifestyles. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2008; 29:182–188.90. Jung MH, Song JH, Chun JY, Cho YG, Kim YH, Kim MJ, et al. Relationship between physical activity, dietary habits and overweight of 7-year-old Korean children. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2007; 28:195–203.91. Park JB, Choi TI, Kim JS, Jung DS, Kim KN, Lee SY, et al. The prevalence of childhood obesity, risk factors, and obesity related disease in elementary students. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2006; 27:104–112.92. Rey-López JP, Vicente-Rodríguez G, Biosca M, Moreno LA. Sedentary behaviour and obesity development in children and adolescents. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008; 18:242–251.
Article93. Salmon J, Campbell KJ, Crawford DA. Television viewing habits associated with obesity risk factors: a survey of Melbourne schoolchildren. Med J Aust. 2006; 184:64–67.
Article94. Coon KA, Goldberg J, Rogers BL, Tucker KL. Relationships between use of television during meals and children's food consumption patterns. Pediatrics. 2001; 107:E7.
Article95. Zabinski MF, Norman GJ, Sallis JF, Calfas KJ, Patrick K. Patterns of sedentary behavior among adolescents. Health Psychol. 2007; 26:113–120.
Article96. Grimm GC, Harnack L, Story M. Factors associated with soft drink consumption in school-aged children. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004; 104:1244–1249.
Article97. Lee BH, Kang SG, Choi JW, Lee YJ. The association between self-reported sleep duration and body mass index among Korean adolescents. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:1996–2001.
Article98. Kam H, Kagn M, Youn J, Park J, Cha Y, Yu Y, et al. Association between sleep duration and obesity in Korean adolescents: the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2014). Korean J Fam Pract. 2017; 7:625–632.
Article99. Sekine M, Yamagami T, Handa K, Saito T, Nanri S, Kawaminami K, et al. A dose-response relationship between short sleeping hours and childhood obesity: results of the Toyama Birth Cohort Study. Child Care Health Dev. 2002; 28:163–170.
Article100. Jiang F, Zhu S, Yan C, Jin X, Bandla H, Shen X. Sleep and obesity in preschool children. J Pediatr. 2009; 154:814–818.
Article101. Chaput JP, Brunet M, Tremblay A. Relationship between short sleeping hours and childhood overweight/ obesity: results from the ‘Québec en Forme’ Project. Int J Obes (Lond). 2006; 30:1080–1085.
Article102. Felső R, Lohner S, Hollódy K, Erhardt É, Molnár D. Relationship between sleep duration and childhood obesity: systematic review including the potential underlying mechanisms. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2017; 27:751–761.
Article103. Hart CN, Carskadon MA, Considine RV, Fava JL, Lawton J, Raynor HA, et al. Changes in children's sleep duration on food intake, weight, and leptin. Pediatrics. 2013; 132:e1473–e1480.
Article104. Chaput JP, Katzmarzyk PT, LeBlanc AG, Tremblay MS, Barreira TV, Broyles ST, et al. Associations between sleep patterns and lifestyle behaviors in children: an international comparison. Int J Obes Suppl. 2015; 5:Suppl 2. S59–S65.
Article105. Kjeldsen JS, Hjorth MF, Andersen R, Michaelsen KF, Tetens I, Astrup A, et al. Short sleep duration and large variability in sleep duration are independently associated with dietary risk factors for obesity in Danish school children. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014; 38:32–39.
Article106. Berge JM, Everts JC. Family-based interventions targeting childhood obesity: a meta-analysis. Child Obes. 2011; 7:110–121.
Article107. Kim SW, Cho YG, Kang JH, Lee SH, Lee JE, Park HA, et al. The relationships between parental lifestyle habits and children's overweight. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2008; 29:395–404.108. Lee HS, Duffey KJ, Kim CI, Popkin BM. The relationship between family and child weight status by household structure in South Korea: 2007-2010. Nutr Diabetes. 2013; 3:e73.
Article109. Wu S, Ding Y, Wu F, Li R, Hu Y, Hou J, et al. Socio-economic position as an intervention against overweight and obesity in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:11354.
Article110. Barriuso L, Miqueleiz E, Albaladejo R, Villanueva R, Santos JM, Regidor E. Socioeconomic position and childhood-adolescent weight status in rich countries: a systematic review, 1990–2013. BMC Pediatr. 2015; 15:129.
Article111. Jang HB, Park JY, Lee HJ, Kang JH, Park KH, Song J. Association between parental socioeconomic level, overweight, and eating habits with diet quality in Korean sixth grade school children. Korean J Nutr. 2011; 44:416–427.
Article112. Höglund D, Samuelson G, Mark A. Food habits in Swedish adolescents in relation to socioeconomic conditions. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998; 52:784–789.
Article113. Abudayya AH, Stigum H, Shi Z, Abed Y, Holmboe-Ottesen G. Sociodemographic correlates of food habits among school adolescents (12–15 year) in North Gaza Strip. BMC Public Health. 2009; 9:185.
Article114. Samuelson G. Dietary habits and nutritional status in adolescents over Europe. An overview of current studies in the Nordic countries. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000; 54:Suppl 1. S21–S28.
Article115. Park J, Ma H, Lee YN, Oh H. Trends in intervention study for childhood obesity in Korea. Child Health Nurs Res. 2017; 23:81–90.
Article116. Waters E, de Silva-Sanigorski A, Hall BJ, Brown T, Campbell KJ, Gao Y, et al. Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (12):CD001871.
Article117. Samuels SE, Craypo L, Boyle M, Crawford PB, Yancey A, Flores G. The California Endowment's Healthy Eating, Active Communities program: a midpoint review. Am J Public Health. 2010; 100:2114–2123.
Article118. Power TG, Bindler RC, Goetz S, Daratha KB. Obesity prevention in early adolescence: student, parent, and teacher views. J Sch Health. 2010; 80:13–19.
Article119. Griffiths LJ, Parsons TJ, Hill AJ. Self-esteem and quality of life in obese children and adolescents: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2010; 5:282–304.
Article120. Rankin J, Matthews L, Cobley S, Han A, Sanders R, Wiltshire HD, et al. Psychological consequences of childhood obesity: psychiatric comorbidity and prevention. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2016; 7:125–146.121. Kwak YS, Shin JH, Kang KS, Jung YE, Kim MD. Prevalence of high risk for eating disorder and its correlates in children and adolescents: focus on body image distortion. Mood Emot. 2013; 11:195–201.122. Kang NR, Lee JS, Kang KS, Kwack YS. Mental health problems in child and adolescent obesity. J Korean Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2016; 27:119–129.
Article123. Van Vlierberghe L, Braet C, Goossens L, Mels S. Psychiatric disorders and symptom severity in referred versus non-referred overweight children and adolescents. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2009; 18:164–173.
Article124. McClure AC, Tanski SE, Kingsbury J, Gerrard M, Sargent JD. Characteristics associated with low self-esteem among US adolescents. Acad Pediatr. 2010; 10:238–244.e2.
Article125. Nowicka P, Höglund P, Birgerstam P, Lissau I, Pietrobelli A, Flodmark CE. Self-esteem in a clinical sample of morbidly obese children and adolescents. Acta Paediatr. 2009; 98:153–158.
Article126. Varni JW, Limbers CA, Burwinkle TM. Impaired health-related quality of life in children and adolescents with chronic conditions: a comparative analysis of 10 disease clusters and 33 disease categories/severities utilizing the PedsQL 4.0 Generic Core Scales. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2007; 5:43.
Article127. Schwimmer JB, Burwinkle TM, Varni JW. Health-related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. JAMA. 2003; 289:1813–1819.
Article128. Britz B, Siegfried W, Ziegler A, Lamertz C, Herpertz-Dahlmann BM, Remschmidt H, et al. Rates of psychiatric disorders in a clinical study group of adolescents with extreme obesity and in obese adolescents ascertained via a population based study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000; 24:1707–1714.
Article129. McLean N, Griffin S, Toney K, Hardeman W. Family involvement in weight control, weight maintenance and weight-loss interventions: a systematic review of randomised trials. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003; 27:987–1005.
Article130. Halliday JA, Palma CL, Mellor D, Green J, Renzaho AM. The relationship between family functioning and child and adolescent overweight and obesity: a systematic review. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014; 38:480–493.
Article131. Shin JA, Bae SP, Kim HS, Park HS. Psychosocial factors and familial environments in adolescent obesity. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2002; 23:1024–1032.132. Gibson LY, Byrne SM, Davis EA, Blair E, Jacoby P, Zubrick SR. The role of family and maternal factors in childhood obesity. Med J Aust. 2007; 186:591–595.
Article133. Oh MS, Kim S, Jang JH, Park JY, Kang HS, Lee MS, et al. Associations among the degree of Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, metabolic syndrome, degree of obesity in children, and parental obesity. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2016; 19:199–206.
Article134. Braet C, Van Winckel M, Van Leeuwen K. Follow-up results of different treatment programs for obese children. Acta Paediatr. 1997; 86:397–402.
Article135. Braet C, Van Winckel M. Long-term follow-up of a cognitive behavioral treatment program for obese children. Behav Ther. 2000; 31:55–74.
Article136. Flodmark CE, Lissau I, Moreno LA, Pietrobelli A, Widhalm K. New insights into the field of children and adolescents' obesity: the European perspective. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004; 28:1189–1196.
Article137. Wadden TA, Butryn ML, Wilson C. Lifestyle modification for the management of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:2226–2238.
Article138. Rosen JC, Orosan P, Reiter J. Cognitive behavior therapy for negative body image in obese women. Behav Ther. 1995; 26:25–42.
Article139. Mead E, Atkinson G, Richter B, Metzendorf MI, Baur L, Finer N, et al. Drug interventions for the treatment of obesity in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; 11:CD012436.140. Parkin P, Connor Gorber S, Shaw E, Bell N, Jaramillo A, Tonelli M, et al. Recommendations for growth monitoring, and prevention and management of overweight and obesity in children and youth in primary care. CMAJ. 2015; 187:411–421.
Article141. Shettar V, Patel S, Kidambi S. Epidemiology of obesity and pharmacologic treatment options. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017; 32:441–462.
Article142. Kelly AS, Rudser KD, Nathan BM, Fox CK, Metzig AM, Coombes BJ, et al. The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist therapy on body mass index in adolescents with severe obesity: a randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2013; 167:355–360.
Article143. Ryder JR, Kaizer A, Rudser KD, Gross A, Kelly AS, Fox CK. Effect of phentermine on weight reduction in a pediatric weight management clinic. Int J Obes (Lond). 2017; 41:90–93.
Article144. Fox CK, Kaizer AM, Rudser KD, Nathan BM, Gross AC, Sunni M, et al. Meal replacements followed by topiramate for the treatment of adolescent severe obesity: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016; 24:2553–2561.
Article145. Chanoine JP, Hampl S, Jensen C, Boldrin M, Hauptman J. Effect of orlistat on weight and body composition in obese adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005; 293:2873–2883.
Article146. Yanovski JA, Krakoff J, Salaita CG, McDuffie JR, Kozlosky M, Sebring NG, et al. Effects of metformin on body weight and body composition in obese insulin-resistant children: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes. 2011; 60:477–485.
Article147. Maahs D, de Serna DG, Kolotkin RL, Ralston S, Sandate J, Qualls C, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss in adolescents. Endocr Pract. 2006; 12:18–28.
Article148. Kim MK, Lee WY, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim BT, Kim SM, et al. 2014 clinical practice guidelines for overweight and obesity in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2014; 29:405–409.
Article149. O'Connor EA, Evans CV, Burda BU, Walsh ES, Eder M, Lozano P. Screening for obesity and intervention for weight management in children and adolescents: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2017; 317:2427–2444.150. Heck AM, Yanovski JA, Calis KA. Orlistat, a new lipase inhibitor for the management of obesity. Pharmacotherapy. 2000; 20:270–279.
Article151. Czernichow S, Lee CM, Barzi F, Greenfield JR, Baur LA, Chalmers J, et al. Efficacy of weight loss drugs on obesity and cardiovascular risk factors in obese adolescents: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2010; 11:150–158.
Article152. Chao AM, Wadden TA, Berkowitz RI. The safety of pharmacologic treatment for pediatric obesity. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2018; 17:379–385.
Article153. Boland CL, Harris JB, Harris KB. Pharmacological management of obesity in pediatric patients. Ann Pharmacother. 2015; 49:220–232.
Article154. Lenders CM, Gorman K, Lim-Miller A, Puklin S, Pratt J. Practical approaches to the treatment of severe pediatric obesity. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2011; 58:1425–1438. x–xi.
Article155. Atabek ME, Pirgon O. Use of metformin in obese adolescents with hyperinsulinemia: a 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 21:339–348.
Article156. Kendall D, Vail A, Amin R, Barrett T, Dimitri P, Ivison F, et al. Metformin in obese children and adolescents: the MOCA trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:322–329.
Article157. Adeyemo MA, McDuffie JR, Kozlosky M, Krakoff J, Calis KA, Brady SM, et al. Effects of metformin on energy intake and satiety in obese children. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015; 17:363–370.
Article158. Wiegand S, l'Allemand D, Hübel H, Krude H, Bürmann M, Martus P, et al. Metformin and placebo therapy both improve weight management and fasting insulin in obese insulin-resistant adolescents: a prospective, placebo-controlled, randomized study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2010; 163:585–592.
Article159. Danne T, Biester T, Kapitzke K, Jacobsen SH, Jacobsen LV, Petri KCC, et al. Liraglutide in an adolescent population with obesity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 5-week trial to assess safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of liraglutide in adolescents aged 12–17 years. J Pediatr. 2017; 181:146–153.e3.
Article160. Davidson MH, Hauptman J, DiGirolamo M, Foreyt JP, Halsted CH, Heber D, et al. Weight control and risk factor reduction in obese subjects treated for 2 years with orlistat: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999; 281:235–242.
Article161. O'Brien PE, Sawyer SM, Laurie C, Brown WA, Skinner S, Veit F, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in severely obese adolescents: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2010; 303:519–526.162. Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, Ard JD, Comuzzie AG, Donato KA, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63:2985–3023.
Article163. Kushner RF, Ryan DH. Assessment and lifestyle management of patients with obesity: clinical recommendations from systematic reviews. JAMA. 2014; 312:943–952.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric obesity: recommendations from the Committee on Pediatric Obesity of the Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Childhood Obesity
- Treatment of Obesity in Childhood
- Dedication: The Korean Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Celebrates the Retirement of Professor Jeong Kee Seo
- An overview and the future of pediatric subspecialty board certification of the Korean Pediatric Society