Yonsei Med J.
2017 May;58(3):552-556. 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.3.552.
Entecavir to Telbivudine Switch Therapy in Entecavir-Treated Patients with Undetectable Hepatitis B Viral DNA
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. cklee33@nhimc.or.kr
- KMID: 2419112
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2017.58.3.552
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study examined 2-year outcome of consecutive therapy using entecavir (ETV) followed by telbivudine (LdT) in subjects with undetectable hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA level and normal alanine aminotransferase level after the initial 6 months of ETV treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
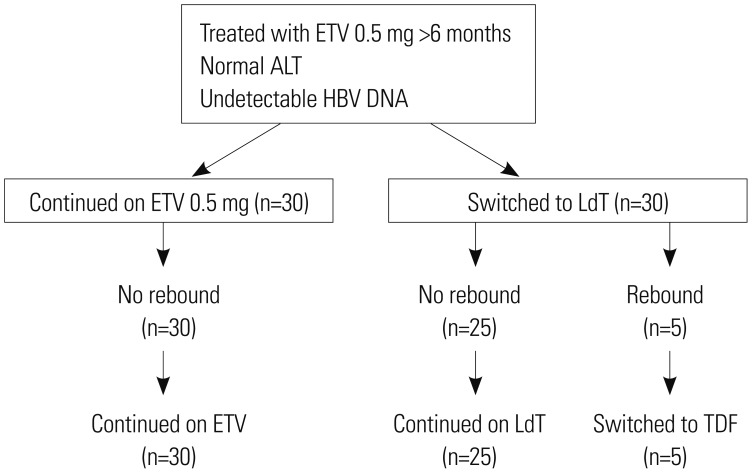
Sixty subjects were randomized to continue with ETV or switch to LdT. Significant difference in baseline characteristics was not found between the two groups. Persistent HBV DNA level of 20-60 IU/mL in three consecutive samples collected three months apart or singly measured HBV DNA level of >60 IU/mL was defined as virological rebound.
RESULTS
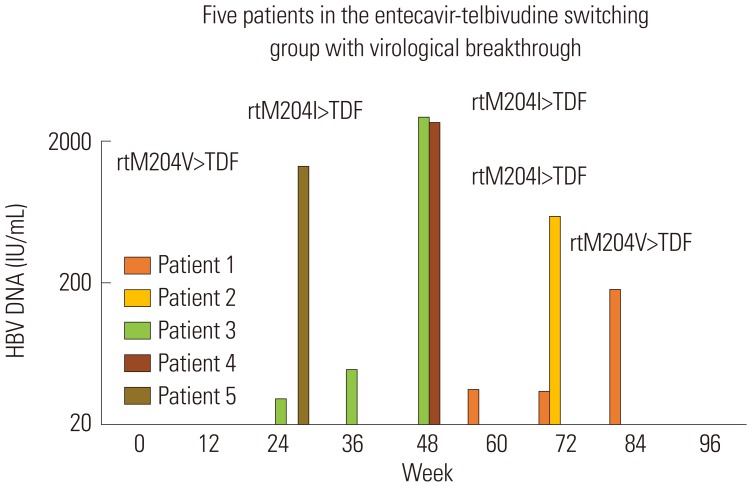
During 96 weeks of follow-up, all subjects of the ETV-only group (n=30) resulted in undetectable HBV DNA level. On the other hand, 83.3% (n=25) of the LdT-switched group showed treatment success. Virological rebound time varied from week 24 to 84 after switching to LdT. HBV DNA level was 180 to 2940 IU/mL at rebound time. All subjects with virological rebound (n=5) showed drug-resistant mutation: three had mutation rtM204I, and two had mutation rtM204V. Consecutive treatment using ETV followed by LdT showed virological rebound in 16.7% of subjects during 96 weeks of follow-up. HBV DNA negativity during initial ETV therapy could not be achieved in patients who switched to LdT.
CONCLUSION
Consecutive treatment using ETV followed by lamivudine was ineffective for treating chronic hepatitis B. LdT was found as a more potent antiviral agent than lamivudine. However, this conclusion requires larger-scale, long-term prospective reviews of the treatment effects of ETV-LdT switch therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Alanine Transaminase/blood
Antiviral Agents/*therapeutic use
DNA, Viral/blood/genetics
Drug Resistance, Viral/genetics
Drug Substitution
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Guanine/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Hepatitis B virus/*drug effects/genetics/isolation & purification
Hepatitis B, Chronic/*drug therapy/*virology
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Mutation
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Prospective Studies
Thymidine/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Treatment Outcome
Viral Load
Antiviral Agents
DNA, Viral
Guanine
Alanine Transaminase
Thymidine
Figure
Reference
-
2. Pol S, Lampertico P. First-line treatment of chronic hepatitis B with entecavir or tenofovir in ‘real-life’ settings: from clinical trials to clinical practice. J Viral Hepat. 2012; 19:377–386. PMID: 22571899.
Article3. Zeuzem S, Gane E, Liaw YF, Lim SG, DiBisceglie A, Buti M, et al. Baseline characteristics and early on-treatment response predict the outcomes of 2 years of telbivudine treatment of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2009; 51:11–20. PMID: 19345439.4. Yuen MF, Fong DY, Wong DK, Yuen JC, Fung J, Lai CL. Hepatitis B virus DNA levels at week 4 of lamivudine treatment predict the 5-year ideal response. Hepatology. 2007; 46:1695–1703. PMID: 18027877.
Article5. Fung J, Lai CL, Yuen J, Cheng C, Wu R, Wong DK, et al. Randomized trial of lamivudine versus entecavir in entecavir-treated patients with undetectable hepatitis B virus DNA: outcome at 2 Years. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1148–1153. PMID: 21480321.
Article6. Lee HW, Lee HJ, Hwang JS, Sohn JH, Jang JY, Han KJ, et al. Lamivudine maintenance beyond one year after HBeAg seroconversion is a major factor for sustained virologic response in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010; 51:415–421. PMID: 19902424.
Article7. Yuen MF, Sablon E, Hui CK, Yuan HJ, Decraemer H, Lai CL. Factors associated with hepatitis B virus DNA breakthrough in patients receiving prolonged lamivudine therapy. Hepatology. 2001; 34(4 Pt 1):785–791. PMID: 11584376.
Article8. Lai CL, Leung N, Teo EK, Tong M, Wong F, Hann HW, et al. A 1-year trial of telbivudine, lamivudine, and the combination in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:528–536. PMID: 16083710.
Article9. Lui YY, Tsoi KK, Wong VW, Kao JH, Hou JL, Teo EK, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of roadmap models in chronic hepatitis B using tenofovir as the rescue therapy. Antivir Ther. 2010; 15:145–155. PMID: 20386069.
Article10. Lee JM, Kim HJ, Park JY, Lee CK, Kim DY, Kim JK, et al. Rescue monotherapy in lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B: adefovir versus entecavir. Antivir Ther. 2009; 14:705–712. PMID: 19704174.11. Leemans WF, Janssen HL, Niesters HG, de Man RA. Switching patients with lamivudine resistant chronic hepatitis B virus from tenofovir to adefovir results in less potent HBV-DNA suppression. J Viral Hepat. 2008; 15:108–114. PMID: 18184193.
Article12. Seo YS, Kim JH, Yeon JE, Park JJ, Kim JS, Byun KS, et al. Antiviral efficacy of adefovir dipivoxil versus lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B sequentially treated with lamivudine and adefovir due to lamivudine resistance. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:4072–4079. PMID: 17696224.13. Fung J, Lai CL, Yuen JC, Wong DK, Tanaka Y, Mizokami M, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy and combination therapy with lamivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in an Asian population. Antivir Ther. 2007; 12:41–46. PMID: 17503746.14. Lampertico P, Viganò M, Manenti E, Iavarone M, Sablon E, Colombo M. Low resistance to adefovir combined with lamivudine: a 3-year study of 145 lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B patients. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:1445–1451. PMID: 17983801.
Article15. Sherman M, Yurdaydin C, Sollano J, Silva M, Liaw YF, Cianciara J, et al. Entecavir for treatment of lamivudine-refractory, HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130:2039–2049. PMID: 16762627.
Article16. Niro GA, Fontana R, Gioffreda D, Fiorella S, Accadia L, Iacobellis A, et al. Sequential treatment with lamivudine and alpha-interferon in anti-HBe-positive chronic hepatitis B patients: a pilot study. Dig Liver Dis. 2007; 39:857–863. PMID: 17652045.
Article17. Shi M, Wang RS, Zhang H, Zhu YF, Han B, Zhang Y, et al. Sequential treatment with lamivudine and interferon-alpha monotherapies in hepatitis B e antigen-negative Chinese patients and its suppression of lamivudine-resistant mutations. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006; 58:1031–1035. PMID: 16987866.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Maintaining Antiviral Efficacy after Switching to Generic Entecavir 1 mg for Antiviral-resistant Chronic Hepatitis B
- Real World Experience of Telbivudine Versus Entecavir in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B, Including Long-Term Outcomes after Treatment Modification
- Experience with Entecavir Therapy for Lamivudine-Resistant Chronic Hepatitis B in Korean Children and Adolescents
- The Short Term Efficacy of Entecavir Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B
- Efficacy of Entecavir Switching Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Clevudine-induced Myopathy