Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Jan;77(1):22-29. 10.4166/kjg.2020.144.
Maintaining Antiviral Efficacy after Switching to Generic Entecavir 1 mg for Antiviral-resistant Chronic Hepatitis B
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2510772
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.144
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Clinical equivalence of generic antiviral agents for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) has not been demonstrated, particularly in cases with previous antiviral resistance. Entecavir 1 mg is prescribed frequently as a mono- or combination therapy in antiviral-resistant CHB patients. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of switching to generic entecavir 1 mg (Baracle ® ) in CHB patients taking brand-name entecavir 1 mg (Baraclude ® ) alone or in combination with other nucleotide analogs after the development of antiviral resistance.
Methods
This study was a single-arm prospective study. The primary endpoint was undetectable HBV DNA (<20 IU/mL) at 12 months after switching treatment. The biochemical and serologic responses, virologic breakthrough, and antiviral resistance rates were also evaluated.
Results
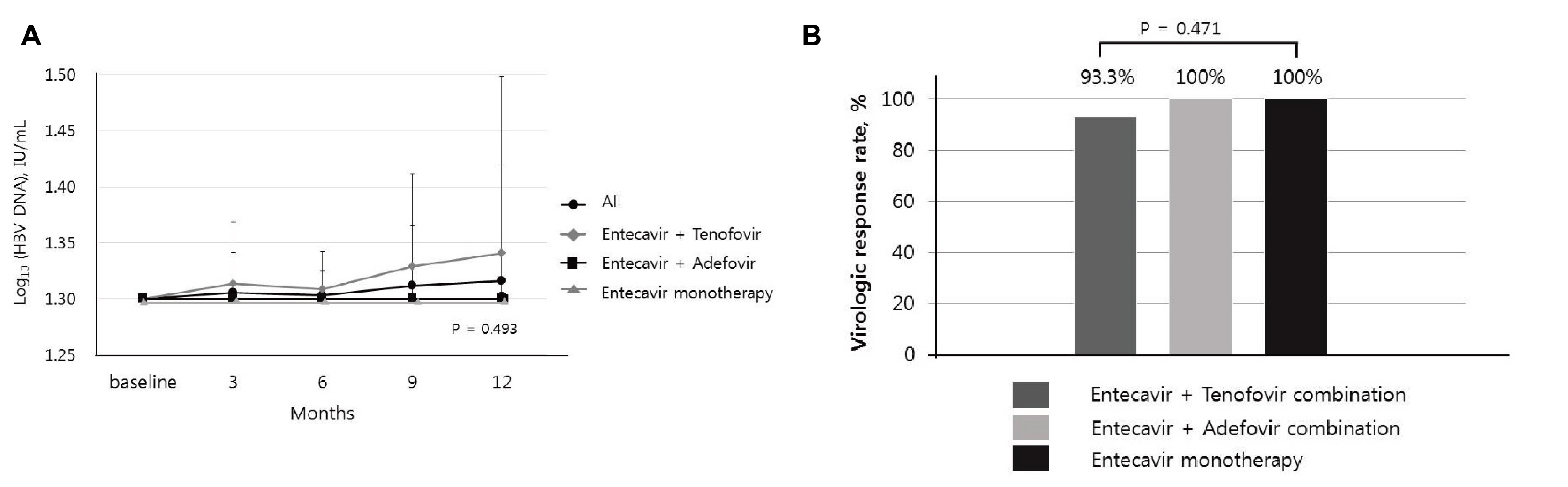
Forty CHB patients with undetectable HBV DNA through the brand-name entecavir 1 mg treatment as a mono- or combination therapy after developing antiviral resistance to nucleos(t)ide analogs were enrolled in this study. No significant difference in the HBV DNA non-detection rate was observed between the baseline and 12 months after switching therapy (p=0.324).Furthermore, non-inferiority of the generic entecavir 1 mg to the brand-name entecavir 1 mg with 10% margin in maintaining undetectable HBV DNA was demonstrated (95% CI -2.80 to 8.20%). Similarly, no difference in the biochemical response rate was observed after switching therapy. Serum hepatitis B e antigen loss was observed in 12.5%. No virologic breakthrough was reported.
Conclusions
Generic entecavir 1 mg is a reasonable alternative to the brand-name entecavir 1 mg in antiviral-resistant CHB patients with viral suppression.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. European Association for the Study of the Liver. 2017; EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 67:370–398.2. Lok AS, McMahon BJ. 2009; Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology. 50:661–662. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23190. PMID: 19714720.
Article3. Terrault NA, Lok ASF, McMahon BJ, et al. 2018; Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology. 67:1560–1599. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29800. PMID: 29405329. PMCID: PMC5975958.
Article4. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). 2019; KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Mol Hepatol. 25:93–159. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2019.1002. PMID: 31185710. PMCID: PMC6589848.5. Yim HJ, Hwang SG. 2013; Options for the management of antiviral resistance during hepatitis B therapy: reflections on battles over a decade. Clin Mol Hepatol. 19:195–209. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2013.19.3.195. PMID: 24133659. PMCID: PMC3796671.
Article6. Lok AS, Lai CL, Leung N, et al. 2003; Long-term safety of Lamivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 125:1714–1722. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2003.09.033. PMID: 14724824.
Article7. European Association For The Study Of The Liver. 2012; EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 57:167–185. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.02.010. PMID: 22436845.8. Yim HJ, Seo YS, Yoon EL, et al. 2013; Adding adefovir vs. switching to entecavir for Lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B (ACE study): a 2-year follow-up randomized controlled trial. Liver Int. 33:244–254. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12036. PMID: 23295056.
Article9. Cho EY, Yim HJ, Jung YK, et al. 2017; Management of clevudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B: a multicenter cohort study. Gut Liver. 11:129–135. DOI: 10.5009/gnl15597. PMID: 27538443. PMCID: PMC5221870.
Article10. Kang SH, Yim HJ, Kim HR, et al. 2014; Comparison of Lamivudine plus adefovir therapy versus entecavir with or without adefovir therapy for adefovir-resistant chronic hepatitis B. J Clin Gastroenterol. 48:889–895. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000066. PMID: 24440937.
Article11. Kim HS, Yim HJ, Jang MK, et al. 2015; Management of entecavirresistant chronic hepatitis B with adefovir-based combination therapies. World J Gastroenterol. 21:10874–10882. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10874. PMID: 26478678. PMCID: PMC4600588.
Article12. Lee S, Ahn SH, Jung KS, et al. 2017; Tenofovir versus tenofovir plus entecavir for chronic hepatitis B with Lamivudine resistance and entecavir resistance. J Viral Hepat. 24:141–147. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12623. PMID: 27766731.
Article13. Park JY, Kim CW, Bae SH, et al. 2016; Entecavir plus tenofovir combination therapy in patients with multidrug-resistant chronic hepatitis B: results of a multicentre, prospective study. Liver Int. 36:1108–1115. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13059. PMID: 26781724.
Article14. Lee YB, Lee JH, Lee DH, et al. 2014; Efficacy of entecavir-tenofovir combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients with multidrug-resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 58:6710–6716. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.03845-14. PMID: 25155601. PMCID: PMC4249402.
Article15. Petersen J, Ratziu V, Buti M, et al. 2012; Entecavir plus tenofovir combination as rescue therapy in pre-treated chronic hepatitis B patients: an international multicenter cohort study. J Hepatol. 56:520–526. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.09.018. PMID: 22037226.
Article16. Huang ZB, Zhao SS, Huang Y, et al. 2013; Comparison of the efficacy of Lamivudine plus adefovir versus entecavir in the treatment of Lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Ther. 35:1997–2006. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.10.002. PMID: 24238791.
Article17. Hutin Y, Nasrullah M, Easterbrook P, et al. 2018; Access to treatment for hepatitis B virus infection - worldwide, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 67:773–777. DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6728a2. PMID: 30025413. PMCID: PMC6054001.
Article18. 2014. Global price reporting mechanism for HIV, tuberculosis and malaria. [Internet]. World Health Organization (WHO);Geneva (CH): Available from: www.who.int/hiv/amds/gprm/en/. cited 2020 Dec 1.19. Kersnik J, Peklar J. 2006; Attitudes of Slovene general practitioners towards generic drug prescribing and comparison with international studies. J Clin Pharm Ther. 31:577–583. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2006.00776.x. PMID: 17176362.
Article20. Hill A, Gotham D, Cooke G, et al. 2015; Analysis of minimum target prices for production of entecavir to treat hepatitis B in high- and low-income countries. J Virus Erad. 1:103–110. DOI: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30484-2.
Article21. Kim DY, Kim JH, Tak WY, et al. 2017; Baracle® vs Baraclude® for 48 weeks in patients with treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B: a comparison of efficacy and safety. Drug Des Devel Ther. 11:3145–3152. DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S149199. PMID: 29184389. PMCID: PMC5673034.22. Oh MJ, Lee HJ. 2016; Antiviral efficacy of entecavir versus entecavir plus adefovir for hepatitis B virus rtA181V/T mutants alone. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 22:37–42. DOI: 10.4103/1319-3767.173757. PMID: 26831605. PMCID: PMC4763527.
Article23. Heo NY, Lim YS, Lee HC, Chung YH, Lee YS, Suh DJ. 2010; Lamivudine plus adefovir or entecavir for patients with chronic hepatitis B resistant to lamivudine and adefovir. J Hepatol. 53:449–454. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.03.020. PMID: 20646776.
Article24. Kitrinos KM, Corsa A, Liu Y, et al. 2014; No detectable resistance to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate after 6 years of therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 59:434–442. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26686. PMID: 23939953.
Article25. Tenney DJ, Rose RE, Baldick CJ, et al. 2009; Long-term monitoring shows hepatitis B virus resistance to entecavir in nucleoside-naïve patients is rare through 5 years of therapy. Hepatology. 49:1503–1514. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22841. PMID: 19280622.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of New Anti-viral Agent in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B
- Management of Antiviral-Resistant Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Antiviral Effect of Entecavir Switching Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Clevudine-associated Myopathy
- New antiviral agents for treatment of chronic hepatitis B
- Efficacy of Entecavir Switching Therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Clevudine-induced Myopathy