Ann Dermatol.
2017 Apr;29(2):173-179. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.173.
Transcription Factors Regulating Inflammatory Cytokine Production Are Differentially Expressed in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Behçet Disease Depending on Disease Activity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. sinsun@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedical Sciences, The Graduate School, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. esl@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2394840
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.173
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
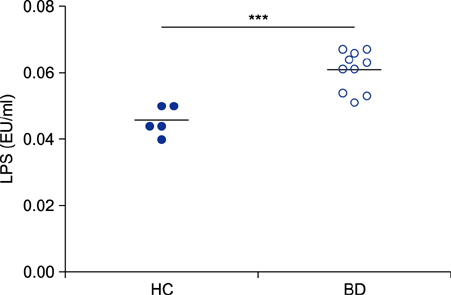
Behçet disease (BD) is a relapsing inflammatory disease with increased production of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs); however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not well known.
OBJECTIVE
To analyze whether the differential expression of transcription factors is involved in the increased tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6 production by PBMCs of BD patients compared to healthy controls (HCs).
METHODS
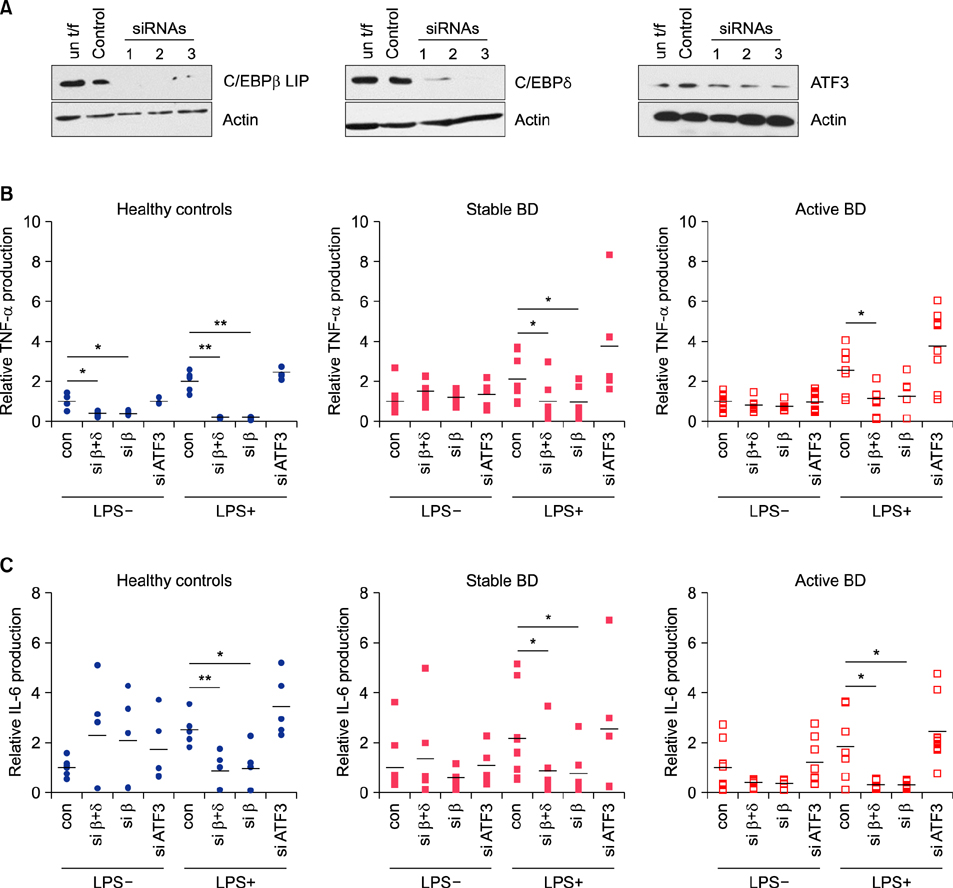
Expression of transcription factors was examined by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. Cytokine production by CD11b+ cells transfected with siRNAs against transcription factors was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
RESULTS
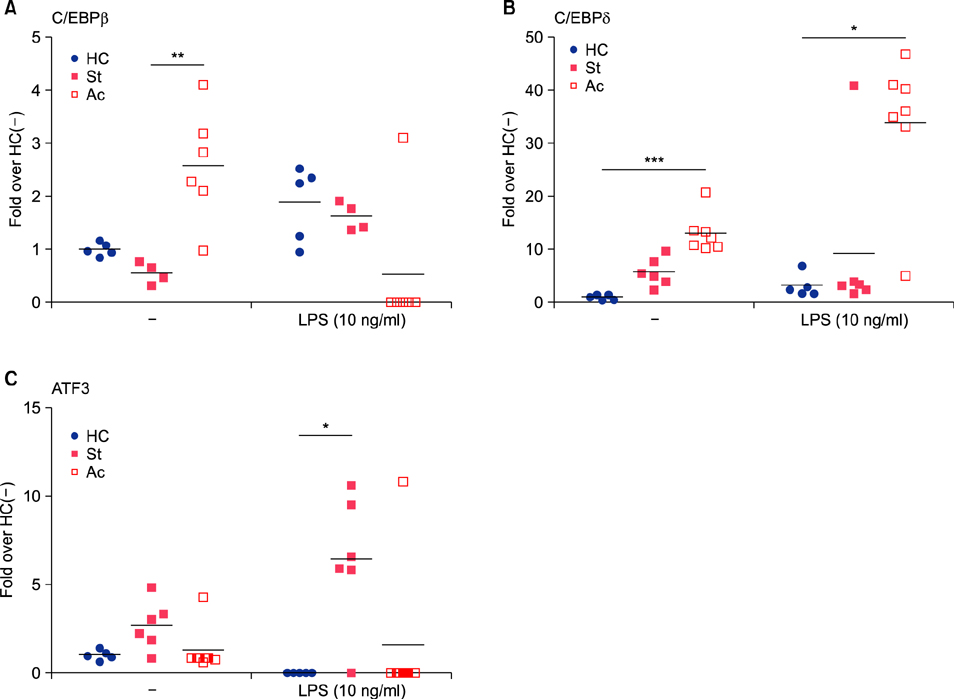
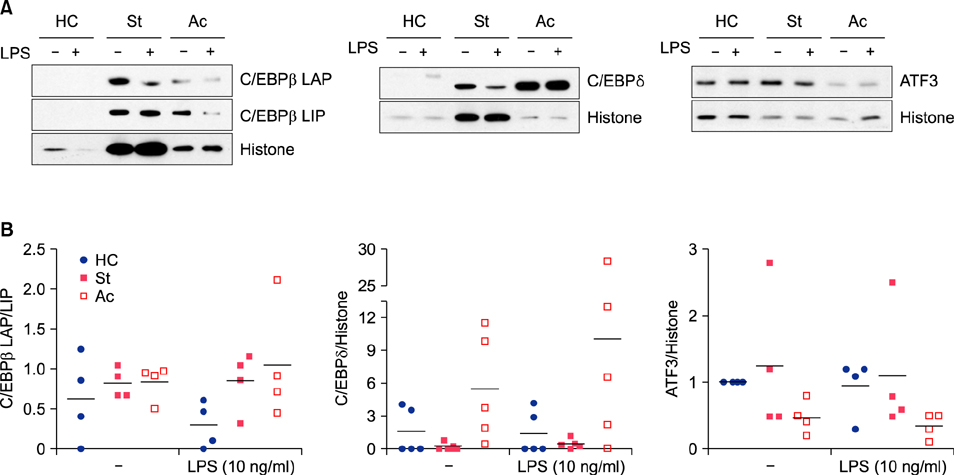
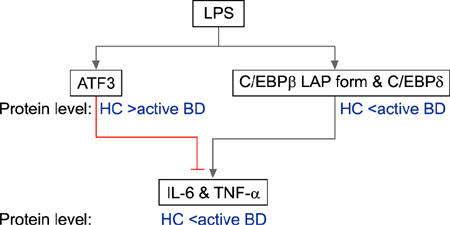
In the absence of lipopolysaccharide stimulation, the transcript level of CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP) β was increased in PBMCs from patients with active BD compared to that in PBMCs from patients with stable BD. The C/EBPδ transcript level was higher in PBMCs from patients with active BD than in those from HCs. The activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) transcript level was increased in PBMCs from patients with stable BD compared to that in PBMCs from HCs. siRNAs targeting C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ significantly reduced the production of IL-6 and TNF-α in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated CD11b+ cells from patients with BD as well as from HCs.
CONCLUSION
We found differential expression of C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ, and ATF3 in PBMCs from patients with BD depending on disease activity, indicating the involvement of these molecules in BD pathogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Activating Transcription Factor 3
Behcet Syndrome*
Blotting, Western
CCAAT-Enhancer-Binding Proteins
Cytokines
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Gene Expression
Humans
Interleukin-6
Interleukins
RNA, Small Interfering
Transcription Factors*
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Activating Transcription Factor 3
CCAAT-Enhancer-Binding Proteins
Cytokines
Interleukin-6
Interleukins
RNA, Small Interfering
Transcription Factors
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pineton de Chambrun M, Wechsler B, Geri G, Cacoub P, Saadoun D. New insights into the pathogenesis of Behçet's disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2012; 11:687–698.
Article2. Sim JH, Park MJ, Park S, Lee ES. Altered expression of costimulatory molecules in Behçet's disease according to clinical activity. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 164:1285–1291.
Article3. Mege JL, Dilsen N, Sanguedolce V, Gul A, Bongrand P, Roux H, et al. Overproduction of monocyte derived tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin (IL) 6, IL-8 and increased neutrophil superoxide generation in Behçet's disease. A comparative study with familial Mediterranean fever and healthy subjects. J Rheumatol. 1993; 20:1544–1549.4. Akman A, Sallakci N, Coskun M, Bacanli A, Yavuzer U, Alpsoy E, et al. TNF-alpha gene 1031 T/C polymorphism in Turkish patients with Behçet's disease. Br J Dermatol. 2006; 155:350–356.5. Medzhitov R, Horng T. Transcriptional control of the inflammatory response. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9:692–703.
Article6. Lu YC, Kim I, Lye E, Shen F, Suzuki N, Suzuki S, et al. Differential role for c-Rel and C/EBPbeta/delta in TLR-mediated induction of proinflammatory cytokines. J Immunol. 2009; 182:7212–7221.
Article7. Whitmore MM, Iparraguirre A, Kubelka L, Weninger W, Hai T, Williams BR. Negative regulation of TLR-signaling pathways by activating transcription factor-3. J Immunol. 2007; 179:3622–3630.
Article8. Cangemi R, Pignatelli P, Carnevale R, Bartimoccia S, Nocella C, Falcone M, et al. Low-grade endotoxemia, gut permeability and platelet activation in community-acquired pneumonia. J Infect. 2016; 73:107–114.
Article9. Calkhoven CF, Müller C, Leutz A. Translational control of C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta isoform expression. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:1920–1932.10. Tsai VW, Mohammad MG, Tolhurst O, Breit SN, Sawchenko PE, Brown DA. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-δ expression by dendritic cells regulates CNS autoimmune inflammatory disease. J Neurosci. 2011; 31:17612–17621.
Article11. Dasgupta S, Jana M, Liu X, Pahan K. Role of very-late antigen-4 (VLA-4) in myelin basic protein-primed T cell contact-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines in microglial cells. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:22424–22431.
Article12. Tsushima H, Okazaki K, Hayashida M, Ushijima T, Iwamoto Y. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β regulates expression of matrix metalloproteinase-3 in arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71:99–107.
Article13. Lu D, Chen J, Hai T. The regulation of ATF3 gene expression by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Biochem J. 2007; 401:559–567.
Article14. Pan YX, Chen H, Kilberg MS. Interaction of RNA-binding proteins HuR and AUF1 with the human ATF3 mRNA 3'-untranslated region regulates its amino acid limitation-induced stabilization. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:34609–34616.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Suppressive Effect of Butyrate and Bromopyruvate on Inflammatory Cytokine Production and Short Chain Fatty Acid Receptor Expression by Blood Mononuclear Cells in Patients with Behçet's Disease
- Analysis of Cytokine Gene Expression in Thyroid Aspirates and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell and in vitro Production of Interferon - Gamma by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Culture
- Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor,Interleukin-1β and Interleukin-6 Levels in Behçet's Disease
- Cytokine production of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from atopic asthmatics
- Expression of mRNA of GATA-3 and T-bet in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of atopic asthmatics