Nat Prod Sci.
2017 Sep;23(3):175-182. 10.20307/nps.2017.23.3.175.
Anti-Helicobacter and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Sohamhyungtang in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Human Gastric Epithelial AGS cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Sahmyook University, 815, Hwarang-ro, Nowon-gu, Seoul 01795, Republic of Korea. sschoi@syu.ac.kr
- 2Qu-best consulting, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Gwanak-ro, Gwanak-gu, Seoul 08826, Republic of Korea.
- 3Re-creation Institute of Phytochemicals, College of Pharmacy, Sahmyook University, 815, Hwarang-ro, Nowon-gu, Seoul 01795, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2393798
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2017.23.3.175
Abstract
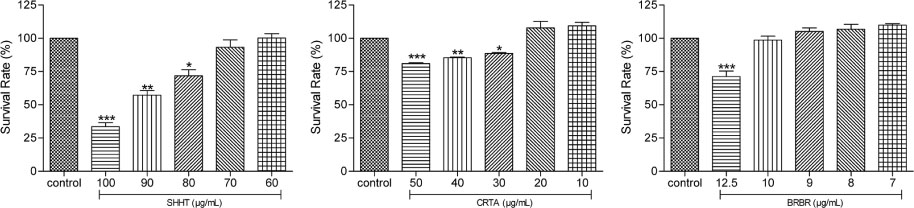
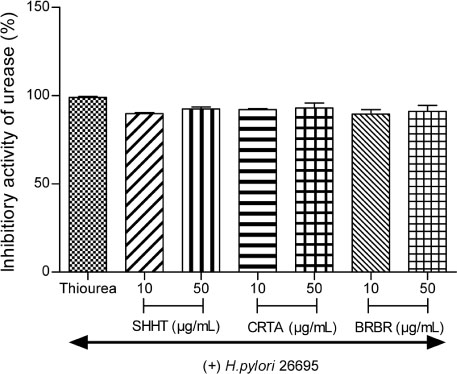
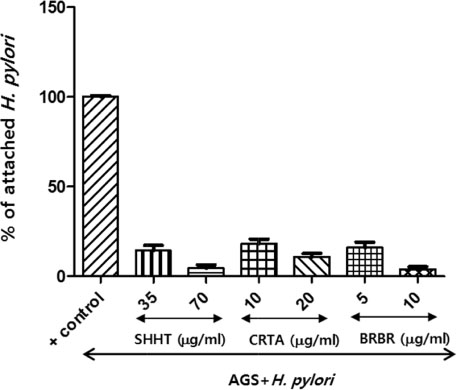
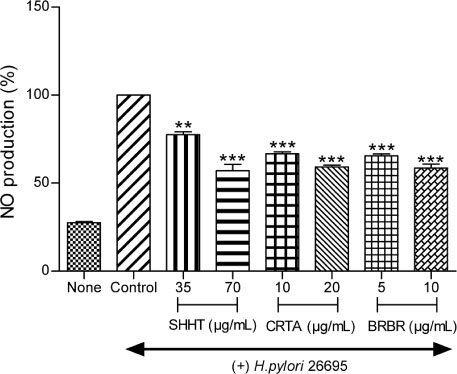
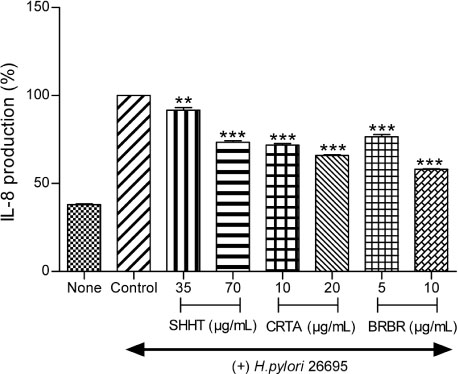
- This study evaluated the anti-Helicobacter and anti-inflammatory effects of Sohamhyungtang (SHHT). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of SHHT against Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) was determined by the agar dilution method. Expression of the H. pylori cagA gene in the presence of SHHT was determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Inhibition of H. pylori urease by SHHT was determined by the phenol-hypochlorite assay. Antiadhesion activity of SHHT was measured by ureaphenol red reagent. Inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production in AGS cells was measured with Griess reagent. Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and IL-8 mRNA expression in AGS cells which were infected with H. pylori was determined by qRT-PCR. IL-8 level was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The MIC of SHHT was 100 µg/mL and the expression of cagA gene was decreased about 25 folds in the presence of SHHT. H. pylori urease was inhibited 90% by SHHT. SHHT inhibited H. pylori adhesion on AGS cell in a concentration dependent manner. mRNA expression of iNOS and IL-8 and the production of NO and IL-8 were significantly decreased in the presence of SHHT. In conclusion, SHHT showed anti-Helicobacter activity and has potent anti-inflammatory effect on H. pylori-induced inflammation in human gastric epithelial AGS cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Agar
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter*
Humans*
Inflammation
Interleukin-8
Methods
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
RNA, Messenger
Urease
Agar
Interleukin-8
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II
RNA, Messenger
Urease
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim JH, Kim HY, Kim NY, Kim SW, Kim JG, Kim JJ, Seo JK, Sim JG, Roe IH, Ahn H, Yoon BC, Lee SW, Lee YC, Chung IS, Jung HY, Hong WS, Choi KW. Korean J Med. 2000; 59:388–397.2. Peek RM Jr, Blaser MJ. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002; 2:28–37.3. Grahma DY, Yamaoka Y. Heliocbacter. 2000; 5:S3–S9.4. Odenbreit S, Püls J, Sedlmaier B, Gerland E, Fischer W, Haas R. Science. 2000; 287:1497–1500.5. Tegtmeyer N, Wessler S, Backert S. FEBS J. 2011; 278:1190–1202.6. Blaser MJ, Perez-Perez GI, Kleanthous H, Cover TL, Peek RM, Chyou PH, Stemmermann GN, Nomura A. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:2111–2115.7. Crabtree JE, Wyatt JI, Trejdosiewicz LK, Peichl P, Nichols PH, Ramsay N, Primrose JN, Lindley IJ. J Clin Pathol. 1994; 47:61–66.8. Marshall BJ, Barrett LJ, Prakash C, McCallum RW, Guerrant RL. Gastroenterology. 1990; 99:697–702.9. Lee YC. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 46:159–165.10. Bell GD, Bate CM, Axon AT, Tildesley G, Kerr GD, Green JR, Emmas CE, Taylor MD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995; 9:513–520.11. Misiewicz JJ, Harris AW, Bardhan KD, Levi S, O'Morain C, Cooper BT, Kerr GD, Dixon MF, Langworthy H, Piper D. Gut. 1997; 41:735–739.12. Spinzi GC, Boni F, Bortoli A, Colombo E, Ballardini G, Venturelli R, Minoli G. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000; 14:325–330.13. Egan BJ, Marzio L, O'Connor H, O'Morain C. Helicobacter. 2008; 13:35–40.14. Romano M, Iovene MR, Russo MI, Rocco A, Salerno R, Cozzolino D, Pilloni AP, Tufano MA, Vaira D, Nardone G. J Clin Pathol. 2008; 61:1112–1115.15. Brown JC, Huang G, Haley-Zitlin V, Jiang X. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009; 75:848–852.16. Cha WS, Kim JH, Lee KH, Kwon HJ, Yoon SJ, Choi UK, Cho YJ. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2006; 35:315–320.17. Choi SS, Lee HK, Chae HS. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2010; 101:206–209.18. Hong YH, Peacher WG. SHANG HAN LUN: The great classic of Chinese medicine. California: Oriental healing arts institute;1981. p22.19. Kook YB. Bangjekak. Seoul: Younglimsa;1999. p. 535–536.20. Xie PS. Characteristic chemical fingerprints of traditional Chinese medicine. Beijing: People's Publishing House;2005. p. 314–322.21. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Document M100-S19. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 19th Informational Supplement. Pennsylvania: CLSI;2009.22. Weatherburn MW. Anal Chem. 1967; 39:971–974.23. Lee JH, Shim JS, Chung MS, Lim ST, Kim KH. Phytother Res. 2009; 23:460–466.24. Choi YS, Cheon JH, Lee JY, Kim SG, Kim JS, Kim N, Lee DH, Kim JM, Jung HC, Song IS. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006; 48:156–161.25. Kim JE, Yun HJ, Choi DY, Park SD. Kor J Ori Med Physiol Pathol. 2010; 24:61–66.26. Yum DY, Baek DG, Song YS. Kor J Ori Med Physiol Pathol. 2012; 26:886–893.27. Bae EA, Han MJ, Kim DH, Kim NJ. Biol Pharm Bull. 1998; 21:990–992.28. Khan KM, Iqbal S, Lodhi MA, Maharvi GM, Ullah Z, Choudhary MI, Rahman AU, Perveen S. Bioorg Med Chem. 2004; 12:1963–1968.29. Lodhi MA, Shams S, Choudhary MI, Lodhi A, UI-Haq Z, Jalil S, Nawaz SA, Khan KM, Iqbal S, Rahman AU. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:935039.30. Guruge JL, Falk PG, Lorenz RG, Dans M, Wirth HP, Blasér MJ, Berg DE, Gordon JI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:3925–3930.31. Harris PR, Mobley HL, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ, Smith PD. Gastroenterology. 1996; 111:419–425.32. Huang J, O'Toole PW, Doig P, Trust TJ. Infect Immun. 1995; 63:1732–1738.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Rosiglitazone on the Cell Proliferation and the Expressions of p27 and Skp2 in Helicobacter pylori Infected Human Gastric Epithelial Cells
- Steamed Ginger Extract Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells through Inhibition of NF-κB
- Caspase-3 Activation Leads to Apoptosis of Human Gastric Epithelial Cells Infected with Helicobacter pylori
- Astaxanthin Prevents Decreases in Superoxide Dismutase 2 Level and Superoxide Dismutase Activity in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells
- In vitro and in vivo inhibition of Helicobacter pylori by Lactobacilllus paracasei HP7