Immune Netw.
2014 Oct;14(5):255-259. 10.4110/in.2014.14.5.255.
Effects of Endurance Training on the Serum Levels of Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha and Interferon-gamma in Sedentary Men
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Center for Non.communicable Diseases, Immunology Department, Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran.
- 2Department of Physical Education & Sport Science,University of Jahrom, Jahrom, Iran.
- 3Department of Physical Education & Sport Sciences, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran.
- 4Sport and Health Sciences, College of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK.
- 5Department of Exercise Physiology, G.C. Shahid Beheshti University, Tehran, Iran.
- 6Department of Immunology, Medical School, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. amanid@sums.ac.ir
- KMID: 2391722
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.5.255
Abstract
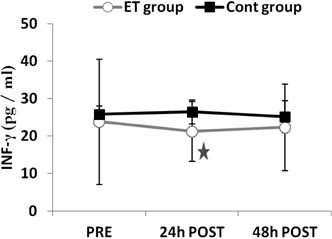
- Physical activity could be considered one of the factors that affect the immune system status and function. To find the relation between exercise and cytokines, we examined the possible effects of an 8-week endurance training program on the serum levels of cytokines, including tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in sedentary men. A total of 30 healthy young male volunteers were randomly divided into an endurance training group and a control group. The training group followed a specific exercise protocol (running on a treadmill for 15~30 min at 50~70% maximal heart rate) for 8 weeks and the control group did not participate in any exercise program. Venous blood samples were collected from both the groups 24 h before and 24 h and 48 h after the exercise. Repeated ANOVA was used for statistical purposes. The serum levels of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma were determined by ELISA. Significant (p<0.05) and non-significant (p>0.05) decreases were observed in the serum levels of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, respectively, after the 8-week endurance training program. Our findings indicated that an 8-week endurance exercise may affect the serum levels of some inflammatory cytokines, suggesting the beneficial role of this training protocol in elderly population and people with certain conditions (inflammation of the vertebrae or other inflammatory diseases).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cytokine Pattern is Affected by Training Intensity in Women Futsal Players
Abdossaleh Zar, Fatemeh Ahmadi, Maryamosadat Miri, Hassan Ali Abedi, Mohsen Salesi
Immune Netw. 2016;16(2):109-115. doi: 10.4110/in.2016.16.2.109.
Reference
-
1. Koch AJ. Immune Response to Exercise. Braz J Biomotricity. 2010; 4:92–103.2. Abbas AK, Pillai S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. 6th Edition. Publisher: Elsevier Science;2007. p. 212–229.3. Nieman DC, Davis JM, Henson DA, Walberg-Rankin J, Shute M, Dumke CL, Utter AC, Vinci DM, Carson JA, Brown A, Lee WJ, McAnulty SR, McAnulty LS. Carbohydrate ingestion influences skeletal muscle cytokine mRNA and plasma cytokine levels after a 3-h run. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2003; 94:1917–1925.
Article4. Peake JM, Suzuki K, Hordern M, Wilson G, Nosaka K, Coombes JS. Plasma cytokine changes in relation to exercise intensity and muscle damage. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2005; 95:514–521.
Article5. Ostrowski K, Rohde T, Asp S, Schjerling P, Pedersen BK. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine balance in strenuous exercise in humans. J Physiol. 1999; 515:287–291.
Article6. Bruunsgaard H, Pedersen BK. Special feature for the Olympics: effects of exercise on the immune system: effects of exercise on the immune system in the elderly population. Immunol Cell Biol. 2000; 78:523–531.
Article7. Radom-Aizik S, Zaldivar F Jr, Leu SY, Galassetti P, Cooper DM. Effects of 30 min of aerobic exercise on gene expression in human neutrophils. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008; 104:236–243.
Article8. Pedersen BK, Febbraio M. Muscle-derived interleukin-6--a possible link between skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, liver, and brain. Brain Behav Immun. 2005; 19:371–376.
Article9. Heesen C, Gold SM, Hartmann S, Mladek M, Reer R, Braumann KM, Wiedemann K, Schulz KH. Endocrine and cytokine responses to standardized physical stress in multiple sclerosis. Brain Behav Immun. 2003; 17:473–481.
Article10. Hovanloo FK, Zar A. The effect of exercise with low and high intensity on respiratory burst activities and neutrophils counts. Hormozgan Med J. 2009; 13:253–259.11. Conraads VM, Beckers P, Bosmans J, De Clerck LS, Stevens WJ, Vrints CJ, Brutsaert DL. Combined endurance/resistance training reduces plasma TNF-alpha receptor levels in patients with chronic heart failure and coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 2002; 23:1854–1860.
Article12. Ryan AS, Nicklas BJ. Reductions in plasma cytokine levels with weight loss improve insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese postmenopausal women. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1699–1705.
Article13. Moldoveanu AI, Shephard RJ, Shek PN. The cytokine response to physical activity and training. Sports Med. 2001; 31:115–144.
Article14. Suzuki K, Yamada M, Kurakake S, Okamura N, Yamaya K, Liu Q, Kudoh S, Kowatari K, Nakaji S, Sugawara K. Circulating cytokines and hormones with immunosuppressive but neutrophil-priming potentials rise after endurance exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000; 81:281–287.
Article15. Ross ML, Halson SL, Suzuki K, Garnham A, Hawley JA, Cameron-Smith D, Peake JM. Cytokine responses to carbohydrate ingestion during recovery from exercise-induced muscle injury. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010; 30:329–337.
Article16. Sugama K, Suzuki K, Yoshitani K, Shiraishi K, Kometani T. Urinary excretion of cytokines versus their plasma levels after endurance exercise. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2013; 19:29–48.17. Rosa JS, Heydari S, Oliver SR, Flores RL, Pontello AM, Ibardolaza M, Galassetti PR. Inflammatory cytokine profiles during exercise in obese, diabetic, and healthy children. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2011; 3:115–121.
Article18. Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Routsi C, Plachouras D, Markaki V, Raftogiannis M, Zervakis D, Koussoulas V, Orfanos S, Kotanidou A, Armaganidis A, Roussos C, Giamarellou H. Early apoptosis of blood monocytes in the septic host: is it a mechanism of protection in the event of septic shock. Crit Care. 2006; 10:R76.19. Lowe GD. Circulating inflammatory markers and risks of cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular disease. J Thromb Haemost. 2005; 3:1618–1627.
Article20. Smith JK, Dykes R, Douglas JE, Krishnaswamy G, Berk S. Long-term exercise and atherogenic activity of blood mononuclear cells in persons at risk of developing ischemic heart disease. JAMA. 1999; 281:1722–1727.
Article21. Lancaster GI, Khan Q, Drysdale PT, Wallace F, Jeukendrup AE, Drayson MT, Gleeson M. Effect of prolonged exercise and carbohydrate ingestion on type 1 and type 2 T lymphocyte distribution and intracellular cytokine production in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005; 98:565–571.
Article22. Franchimont D, Galon J, Gadina M, Visconti R, Zhou Y, Aringer M, Frucht DM, Chrousos GP, O'Shea JJ. Inhibition of Th1 immune response by glucocorticoids: dexamethasone selectively inhibits IL-12-induced Stat4 phosphorylation in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2000; 164:1768–1774.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Human Recombinant Interferon-Gamma and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha on Expressions of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Activity Human Bladder Cancer Cell Lines
- Modification effects of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor and recombinant human interferon-gamma intrinsic and acquired resistance to cisplatin in human stomach and lung cancer cell lines
- The Changes of Serum Level of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha, Gamma-Interferon and Soluble-Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Relating to the Progression and Treatment of Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Determination and Significance of Serum Interleukin-18 Levels in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Effects of L-carnitine supplementation on anemia in patients undergoing hemodialysis