Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jul;48(3):948-954. 10.4143/crt.2015.360.
Polymorphic Variants in Oxidative Stress Genes and Acute Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physics, School of Exact Sciences, National University of La Plata, Argentina. elisaecordoba@gmail.com
- 2IGEVET-Veterinary Genetics Institute (National Scientific and Technical Research Council-National University of La Plata) School of Veterinary Sciences, La Plata, Argentina.
- 3Basic and Applied Immunological Research Center, School of Medicine, National University of La Plata, Argentina.
- 421st Century Oncology, Naples, FL, USA.
- KMID: 2344067
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.360
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated as an indirect product of radiation therapy (RT). Genetic variation in genes related to ROS metabolism may influence the level of RT-induced adverse effects. We evaluated the potential association of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-related response to radiotherapy injury in breast cancer patients undergoing RT.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighty patients receiving conventional RT were included. Acute effects were evaluated according to the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) scores. DNA was extracted from blood and buccal swab samples. SNPs were genotyped for GSTP1, GSTA1, SOD2, and NOS3 genes by polymerase chain reaction-based restriction fragment length polymorphism. Univariate analysis (odds ratios [ORs] and 95% confidence interval [CI]) and principal component analysis were used for correlation of SNPs and factors related to risk of developing ≥ grade 2 acute effects.
RESULTS
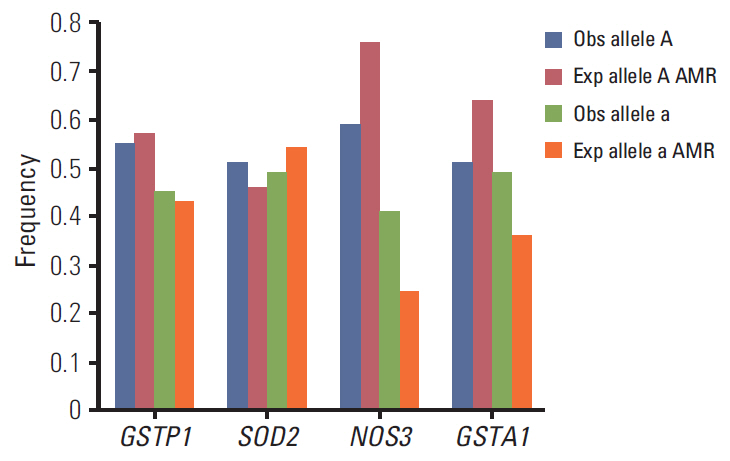
Sixty-five patients (81.2%) showed side effects, 32 (40%) presented moderate to severe acute skin toxicity, and 33 (41.2%) manifested minimal acute skin reactions by the end of treatment. In both univariate and multivariate analyses, nominally significant associations were found among body mass index (OR, 3.14; 95% CI, 8.5338 to 1.1274; p=0.022), breast size (OR, 5.11; 95% CI, 17.04 to 1.54; p=0.004), and grade ≥ 2 acute radiation skin toxicity. A significant association was also observed between NOS3 G894T polymorphism (OR, 9.8; 95% CI, 211.6 to 0.45; p=0.041) and grade ≥ 2 acute radiation skin toxicity in patients with neo-adjuvant chemotherapy treatment.
CONCLUSION
The analysis of the factors involved in individual radiosensitivity contributed to the understanding of the mechanisms underlying this trait.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Body Mass Index
Breast Neoplasms*
Breast*
DNA
Drug Therapy
Genetic Variation
Humans
Metabolism
Multivariate Analysis
Oxidative Stress*
Polymorphism, Restriction Fragment Length
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Principal Component Analysis
Radiation Tolerance
Radiotherapy*
Reactive Oxygen Species
Skin
DNA
Reactive Oxygen Species
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Seibold P, Hall P, Schoof N, Nevanlinna H, Heikkinen T, Benner A, et al. Polymorphisms in oxidative stress-related genes and mortality in breast cancer patients: potential differential effects by radiotherapy? Breast. 2013; 22:817–23.2. Pan American Health Organization. Breast Cancer in the Americas. GLOBOCAN 2012 [Internet]. Washington, DC: Regional Office for the Americas of the World Health Organization;2015. [cited 2015 Dec 1]. Available from http://www.paho.org/.3. Henriquez-Hernandez LA, Bordon E, Pinar B, Lloret M, Rodriguez-Gallego C, Lara PC. Prediction of normal tissue toxicity as part of the individualized treatment with radiotherapy in oncology patients. Surg Oncol. 2012; 21:201–6.4. West CM, Barnett GC. Genetics and genomics of radiotherapy toxicity: towards prediction. Genome Med. 2011; 3:52.
Article5. Terrazzino S, La Mattina P, Gambaro G, Masini L, Franco P, Canonico PL, et al. Common variants of GSTP1, GSTA1, and TGFbeta1 are associated with the risk of radiation-induced fibrosis in breast cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 83:504–11.6. Bentzen SM, Dorr W, Anscher MS, Denham JW, Hauer-Jensen M, Marks LB, et al. Normal tissue effects: reporting and analysis. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2003; 13:189–202.
Article7. Barnett GC, West CM, Dunning AM, Elliott RM, Coles CE, Pharoah PD, et al. Normal tissue reactions to radiotherapy: towards tailoring treatment dose by genotype. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009; 9:134–42.
Article8. Popanda O, Marquardt JU, Chang-Claude J, Schmezer P. Genetic variation in normal tissue toxicity induced by ionizing radiation. Mutat Res. 2009; 667:58–69.
Article9. Terrazzino S, La Mattina P, Masini L, Caltavuturo T, Gambaro G, Canonico PL, et al. Common variants of eNOS and XRCC1 genes may predict acute skin toxicity in breast cancer patients receiving radiotherapy after breast conserving surgery. Radiother Oncol. 2012; 103:199–205.
Article10. Andreassen CN, Alsner J, Overgaard M, Overgaard J. Prediction of normal tissue radiosensitivity from polymorphisms in candidate genes. Radiother Oncol. 2003; 69:127–35.
Article11. Funke S, Risch A, Nieters A, Hoffmeister M, Stegmaier C, Seiler CM, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in genes related to oxidative stress (GSTP1, GSTM1, GSTT1, CAT, MnSOD, MPO, eNOS) and survival of rectal cancer patients after radiotherapy. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2009; 2009:302047.
Article12. Ahn J, Ambrosone CB, Kanetsky PA, Tian C, Lehman TA, Kropp S, et al. Polymorphisms in genes related to oxidative stress (CAT, MnSOD, MPO, and eNOS) and acute toxicities from radiation therapy following lumpectomy for breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:7063–70.13. Schnur JB, Love B, Scheckner BL, Green S, Wernicke AG, Montgomery GH. A systematic review of patient-rated measures of radiodermatitis in breast cancer radiotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 2011; 34:529–36.
Article14. Kim JH, Jenrow KA, Brown SL. Mechanisms of radiationinduced normal tissue toxicity and implications for future clinical trials. Radiat Oncol J. 2014; 32:103–15.
Article15. Ambrosone CB, Tian C, Ahn J, Kropp S, Helmbold I, von Fournier D, et al. Genetic predictors of acute toxicities related to radiation therapy following lumpectomy for breast cancer: a case-series study. Breast Cancer Res. 2006; 8:R40.
Article16. Falvo E, Strigari L, Citro G, Giordano C, Arcangeli S, Soriani A, et al. Dose and polymorphic genes xrcc1, xrcc3, gst play a role in the risk of articledeveloping erythema in breast cancer patients following single shot partial breast irradiation after conservative surgery. BMC Cancer. 2011; 11:291.
Article17. Tan XL, Popanda O, Ambrosone CB, Kropp S, Helmbold I, von Fournier D, et al. Association between TP53 and p21 genetic polymorphisms and acute side effects of radiotherapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006; 97:255–62.
Article18. Ambrosone CB, Ahn J, Singh KK, Rezaishiraz H, Furberg H, Sweeney C, et al. Polymorphisms in genes related to oxidative stress (MPO, MnSOD, CAT) and survival after treatment for breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:1105–11.19. Veldman BA, Spiering W, Doevendans PA, Vervoort G, Kroon AA, de Leeuw PW, et al. The Glu298Asp polymorphism of the NOS 3 gene as a determinant of the baseline production of nitric oxide. J Hypertens. 2002; 20:2023–7.
Article20. Andreassen CN, Alsner J. Genetic variants and normal tissue toxicity after radiotherapy: a systematic review. Radiother Oncol. 2009; 92:299–309.
Article21. Pires AM, Segreto RA, Segreto HR. RTOG criteria to evaluate acute skin reaction and its risk factors in patients with breast cancer submitted to radiotherapy. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2008; 16:844–9.
Article22. Porock D, Kristjanson L, Nikoletti S, Cameron F, Pedler P. Predicting the severity of radiation skin reactions in women with breast cancer. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1998; 25:1019–29.23. Turesson I, Nyman J, Holmberg E, Oden A. Prognostic factors for acute and late skin reactions in radiotherapy patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996; 36:1065–75.24. Back M, Guerrieri M, Wratten C, Steigler A. Impact of radiation therapy on acute toxicity in breast conservation therapy for early breast cancer. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2004; 16:12–6.
Article25. Twardella D, Popanda O, Helmbold I, Ebbeler R, Benner A, von Fournier D, et al. Personal characteristics, therapy modalities and individual DNA repair capacity as predictive factors of acute skin toxicity in an unselected cohort of breast cancer patients receiving radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2003; 69:145–53.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Eosinophilic, Polymorphic, and Pruritic Eruption Associated with Radiotherapy in a Patient with Breast Cancer
- Eosinophilic, Polymorphic, and Pruritic Eruption Associated with Radiotherapy in a Patient with Parotid Gland Cancer
- Lecithin: Cholesterol Acyltransferase and Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase Activity in Patients with Breast Cancer
- Utility of Next-Generation Sequencing Panel Including Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer-Related Genes for Pathogenic Variant Detection
- Body Image and Physical suffering during Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients Following Breast Conserving Operations