J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Sep;54(9):1365-1370.
Reproducibility of Choroidal Thickness in Normal Korean Eyes Using Two Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sklee219@yuhs.ac
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the reproducibility of choroidal thickness measurements in healthy Koreans using two spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) instruments: Zeiss Cirrus HD-OCT (Carl Zeiss Meditec Inc., Dublin, CA, USA) and Heidelberg Spectralis (Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany).
METHODS
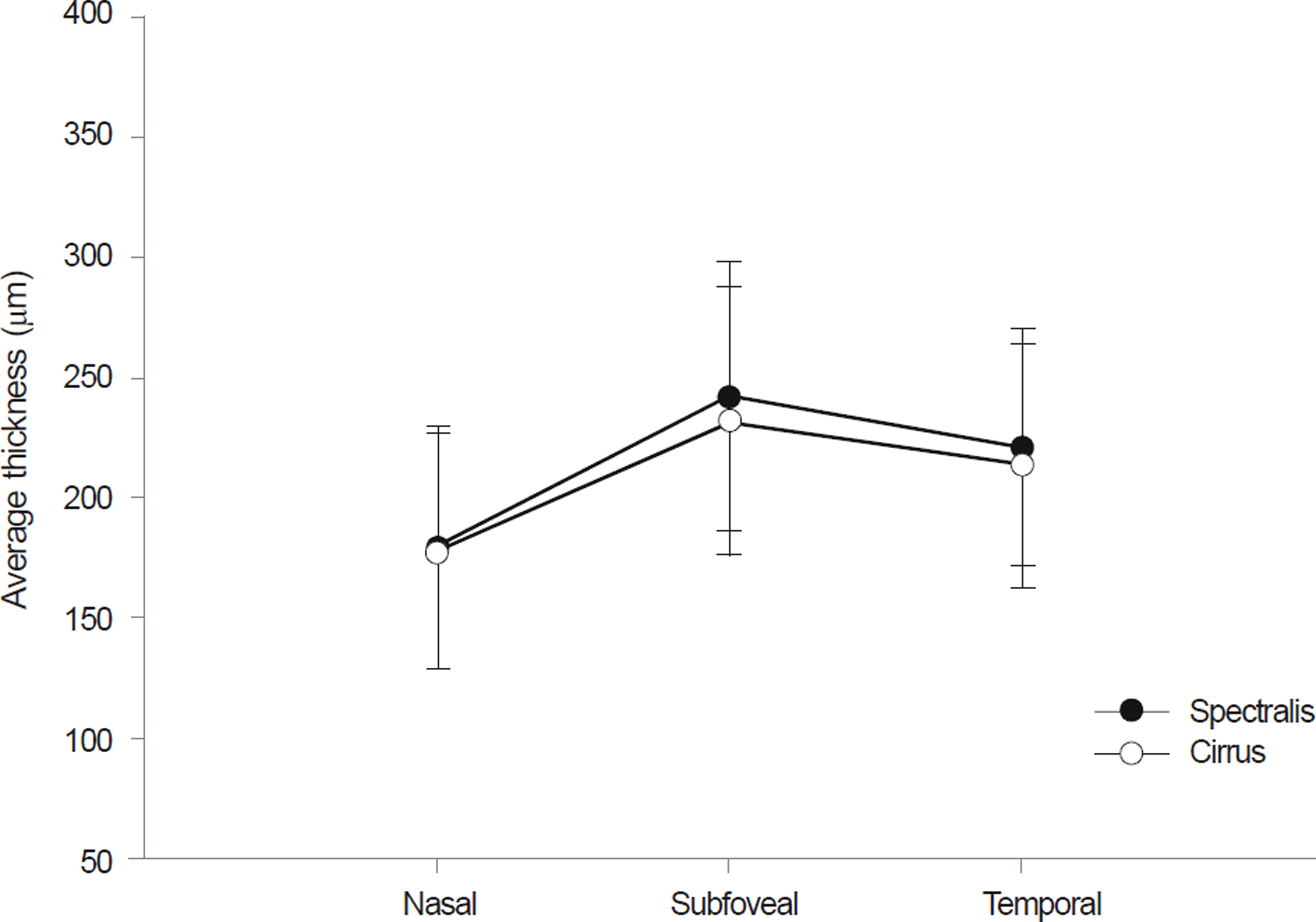
Images were obtained in 60 eyes of 30 healthy undilated volunteers without ocular pathology in a clinical setting. The choroid was imaged in all subjects using Cirrus HD 1-line raster and Spectralis enhanced depth imaging (EDI). The choroid was measured subfoveally, 1500 microm temporal, and 1500 microm nasal to the fovea. All measurements were performed by two independent observers. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Pearson correlation, and Bland-Altman analysis were used to compare measurements.
RESULTS
The study group consisted of 15 males and 15 females. The mean age was 50.73 +/- 15.09 years (range, 24-75 years). There was no significant difference in the mean choroidal thickness (p > 0.05) between systems for any location. The choroidal thickness measurements using two instruments (Cirrus vs. Spectralis) were also strongly correlated (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
In the present study of healthy Korean adults, good reproducibility was observed between choroidal thickness measurements of images obtained from Cirrus and Spectralis.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Torres VL, Brugnoni N, Kaiser PK, Singh AD. Optical coherence tomography enhanced depth imaging of choroidal tumors. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151:586–93.e2.
Article2. Spaide RF. Age-related choroidal atrophy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:801–10.
Article3. Gemenetzi M, De Salvo G, Lotery AJ. Central serous chorioretin-opathy: an update on pathogenesis and treatment. Eye (Lond). 2010; 24:1743–56.
Article4. Spaide RF, Koizumi H, Pozzoni MC. Enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008; 146:496–500.
Article5. Branchini L, Regatieri CV, Flores-Moreno I. . Reproducibility of choroidal thickness measurements across three spectral domain optical coherence tomography systems. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:119–23.
Article6. Manjunath V, Fujimoto JG, Duker JS. Cirrus HD-OCT high defi-nition imaging is another tool available for visualization of the cho-roid and provides agreement with the finding that the choroidal thickness is increased in central serous chorioretinopathy in com-parison to normal eyes. Retina. 2010; 30:1320–1.7. Manjunath V, Taha M, Fujimoto JG, Duker JS. Choroidal thickness in normal eyes measured using Cirrus HD optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2010; 150:325–9.
Article8. Yamashita T, Yamashita T, Shirasawa M. . Repeatability and reproducibility of subfoveal choroidal thickness in normal eyes of Japanese using different SD-OCT devices. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:1102–7.
Article9. Benavente-Pérez A, Hosking SL, Logan NS, Bansal D. Reproducibility- repeatability of choroidal thickness calculation using optical co-herence tomography. Optom Vis Sci. 2010; 87:867–72.10. Carrasco S, Torres JP, Torner L. . Enhancing the axial reso-lution of quantum optical coherence tomography by chirped qua-si-phase matching. Opt Lett. 2004; 29:2429–31.
Article11. Fujiwara T, Imamura Y, Margolis R. . Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in highly myopic eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 148:445–50.
Article12. Ikuno Y, Maruko I, Yasuno Y. . Reproducibility of retinal and choroidal thickness measurements in enhanced depth imaging and high-penetration optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:5536–40.
Article13. Imamura Y, Fujiwara T, Margolis R, Spaide RF. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in central se-rous chorioretinopathy. Retina. 2009; 29:1469–73.
Article14. Imamura Y, Iida T, Maruko I. . Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the sclera in dome-shaped macula. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151:297–302.
Article15. Ikuno Y, Kawaguchi K, Nouchi T, Yasuno Y. Choroidal thickness in healthy Japanese subjects. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:2173–6.
Article16. Manjunath V, Goren J, Fujimoto JG, Duker JS. Analysis of choroi-dal thickness in age-related macular degeneration using spec-tral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 152:663–8.
Article17. Hirata M, Tsujikawa A, Matsumoto A. . Macular choroidal thickness and volume in normal subjects measured by swept- source optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:4971–8.18. Margolis R, Spaide RF. A pilot study of enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in normal eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 147:811–5.
Article19. Kim SW, Oh J, Kwon SS. . Comparison of choroidal thickness among patients with healthy eyes, early age-related maculopathy, neovascular age-related macular degeneration, central serous cho-rioretinopathy, and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina. 2011; 31:1904–11.
Article20. Esmaeelpour M, Povazay B, Hermann B. . Three-dimensional 1060-nm OCT: choroidal thickness maps in normal subjects and improved posterior segment visualization in cataract patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:5260–6.
Article21. Ding X, Li J, Zeng J. . Choroidal thickness in healthy Chinese subjects. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:9555–60.
Article22. Li XQ, Larsen M, Munch IC. Subfoveal choroidal thickness in re-lation to sex and axial length in 93 Danish university students. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:8438–41.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Choroidal Thickness in Patients with Diabetes by Spectral-domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- Choroidal Thickness at the Outside of Fovea in Diabetic Retinopathy Using Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- Subfoveal Choroidal Thickness in Fellow Eyes of Patients with Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
- Choroidal Thickness in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Using Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
- Measurement of Choroidal Thickness in Normal Eyes Using 3D OCT-1000 Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography