Nat Prod Sci.
2016 Mar;22(1):46-52. 10.20307/nps.2016.22.1.46.
Ginsenoside Re Enriched Fraction (GS-F3K1) from Ginseng Berries Ameliorates Ethanol-Induced Erectile Dysfunction via Nitric Oxide-cGMP Pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1International Ginseng and Herb Research Institute, Geumsan 312-804, Korea. pmk67@ginherb.re.kr
- 2Department of Oriental Pharmaceutical Development, Nambu University, Gwangju, 506-706, Korea.
- 3Huvet Co., Ltd., Iksan, 570-749, Korea.
- 4Braintropia Co.Ltd., Anyang, 431-060, Korea.
- 5Department of Microbiology, College of Natural Science, Dankook University, Cheonan, 330-714, Korea.
- KMID: 2312921
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2016.22.1.46
Abstract
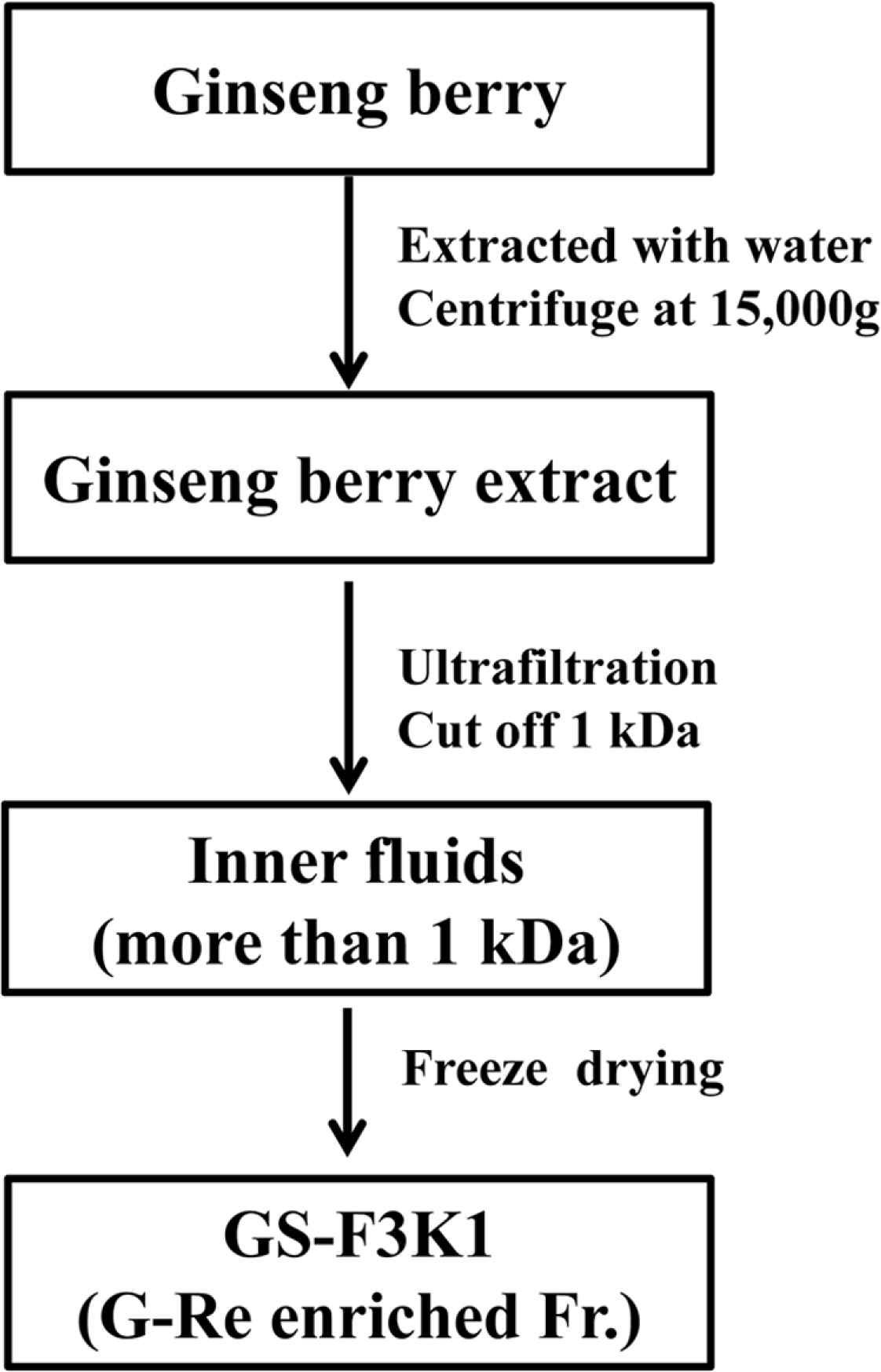
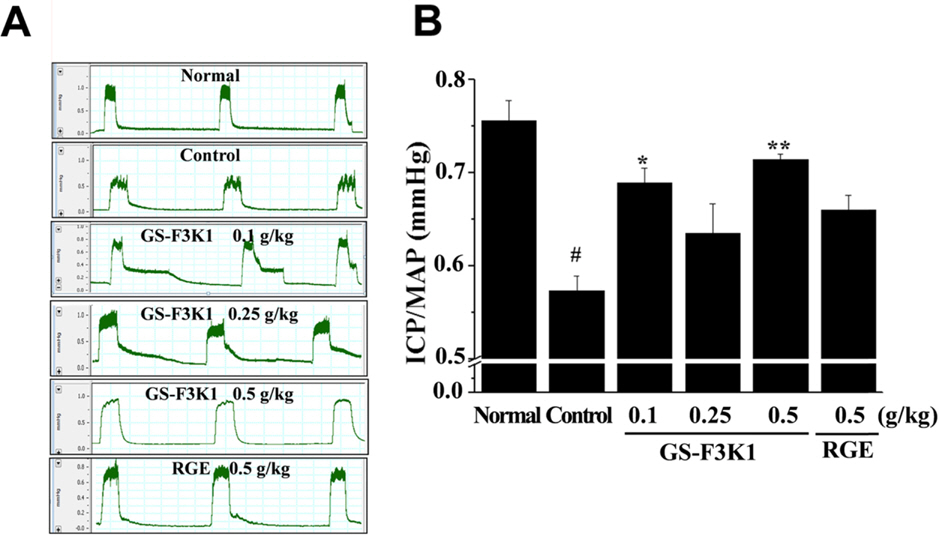
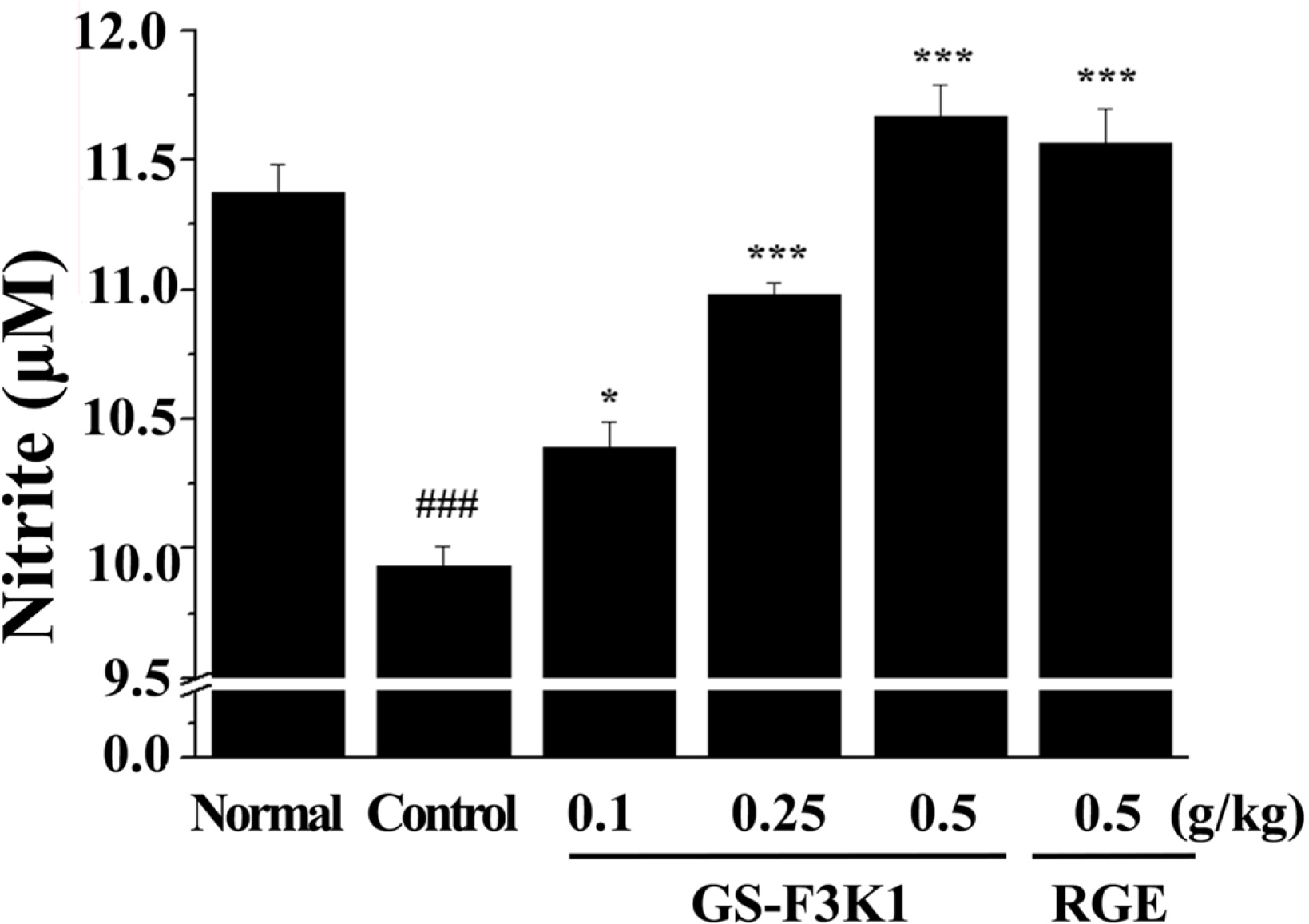
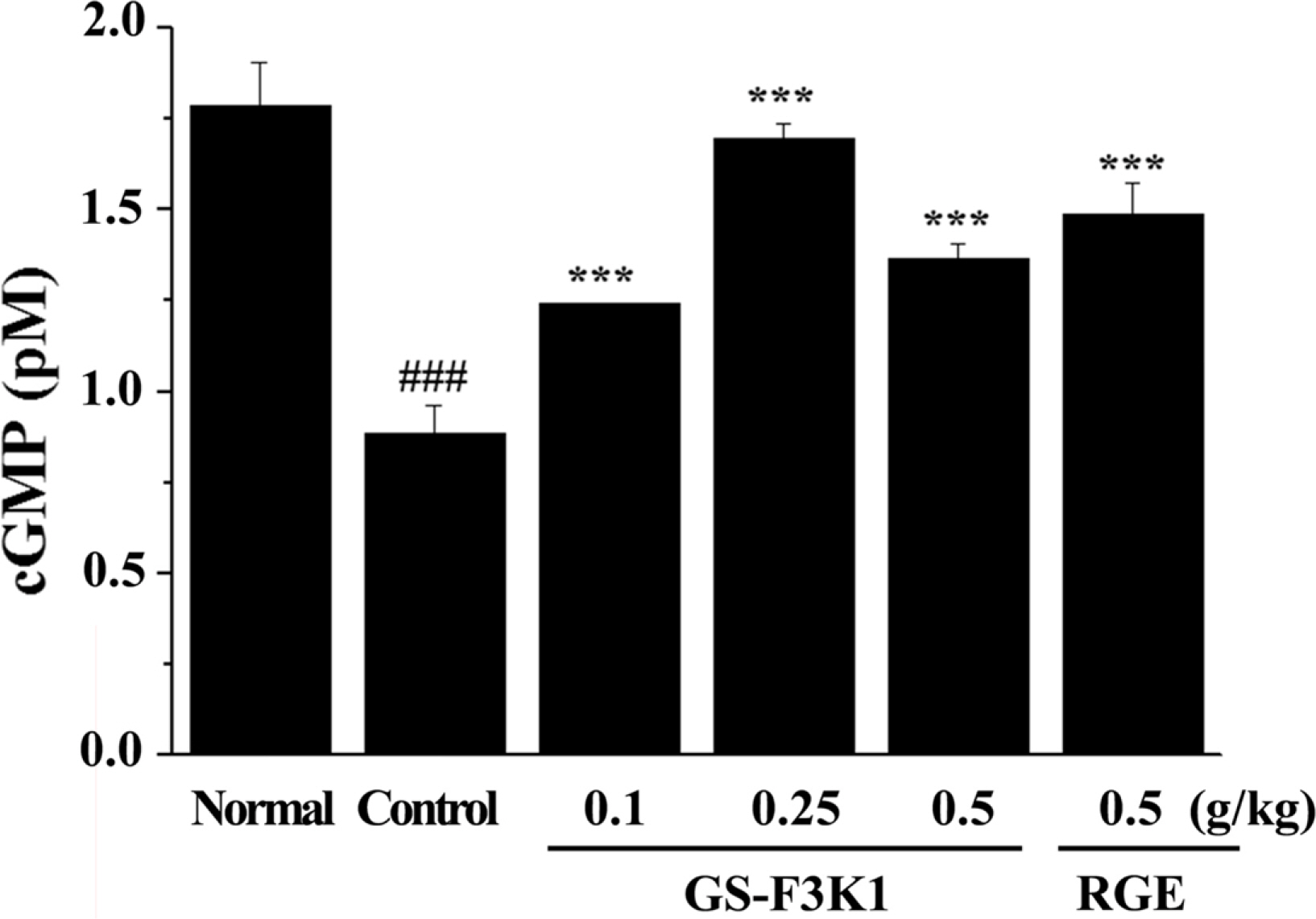
- Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a highly prevalent disorder that affects millions of men and considered to be an early symptom of atherosclerosis and a precursor of various systemic vascular disorders. The aim of the present study was to prepare ginsenoside Re enriched fraction (GS-F3K1, ginsenoside Re 10%, w/w) from ginseng berries flesh and to investigate the enhanced activities of GS-F3K1 on alcohol-induced ED. GS-F3K1 was prepared by the continuous liquid and solid separating centrifugation and circulatory ultrafiltration from ginseng berries flesh. GS-F3K1 was administered for 5 weeks in ethanol-induced ED rat by oral administration of 20% ethanol. To investigate the effects of GS-F3K1 on ED model, the levels of nitrite expression, cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and erectile response of the penile corpus cavernosum of rat were measured. The erectile response of the corpus cavernosum was restored after GS-F3K1 administration, to a level similar to the normal group. The level of nitrite and cGMP expression in the corpus cavernosum of GS-F3K1-administered male rats was increased significantly compared to positive control group. GS-F3K1 from ginseng berries should effectively restore ethanol-induced ED in male rats and could be developed as a new functional food for the elderly men.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
(1). Huang K. C.The Pharmacology of Chinese Herbs: Boca Raton; CRC Press; USA. 1999; 17–45.(2). Attele A. S., Wu J. A., Yuan C. S.Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999; 58:1685–1693.(3). Jang H. J., Han I. H., Kim Y. J., Yamabe N., Lee D., Hwang G. S., Oh M., Choi K. C., Kim S. N., Ham J., Eom D. W., Kang K. S. J.Agric. Food Chem. 2014; 62:2830–2836.(4). Shergis J. L., Zhang A. L., Zhou W., Xue C. C.Phytother. Res. 2013; 27:949–965.
Article(5). Cho K. S., Park C. W., Kim C. K., Jeon H. Y., Kim W. G., Lee S. J., Kim Y. M., Lee J. Y., Choi Y. D.Asian J. Androl. 2013; 15:503–507.(6). Zhang H., Zhou Q. M., Li X. D., Xie Y., Duan X., Min F. L., Liu B., Yuan Z. G.Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006; 29:145–151.(7). Zhang H., Zhou Q., Li X., Zhao W., Wang Y., Liu H., Li N.Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2007; 74:497–501.(8). Nakaya Y., Mawatari K., Takahashi A., Harada N., Hata A., Yasui S. J.Med. Invest. 2007; 54:381–384.(9). Seol S. Y., Kim B. R., Hong S. C., Yoo J. H., Lee K. H., Lee H. J., Park J. D., Pyo M. K.Nat. Prod. Sci. 2014; 20:58–64.(10). Feldman H. A., Goldstein I., Hatzichristou D. G., Krane R. J., McKinlay J. B. J.Urol. 1994; 151:54–61.(11). Sommer F., Goldstein I., Korda J. B. J.Sex. Med. 2010; 7:2346–2358.(12). Bancroft J. H., Jones H. G., Pullan B. R.Behav. Res. Ther. 1996; 4:239–241.(13). Sandroni P.Clin. Auton. Res. 2001; 11:303–307.(14). Choi Y. D., Xin Z. C., Choi H. K.Int. J. Impot. Res. 1998; 10:37–43.(15). Choi H. K, Seong D. H., Rha K. H.Int. J. Impot. Res. 1995; 7:181–186.(16). Choi H. K., Choi Y. D.Proc.'99 Korea-Japan Ginseng Symp. 1999; 97–106.(17). Kim S.W., Paick J. S. Kor. J.Androl. 1999; 17:23–28.(18). Choi Y. D., Park C. W., Jang J., Kim S. H., Jeon H. Y., Kim W. G., Lee S. J., Chung W. S.Int. J. Impot. Res. 2012; 25:45–50.(19). Boolell M., Allen M. J., Ballard S. A., Gepi-Attee S., Muirhead G. J., Naylor A. M., Osterloh I. H.Int. J. Impot. Res. 1996; 8:47–52.(20). Lue T. F., Tanagho E. A. J.Urol. 1987; 137:829–836.(21). Sullivan M. E., Thompson C. S., Dashwood M. R., Khan M. A., Jeremy J. Y., Morgan R. J., Mikhailidis D. P.Cardiovasc. Res. 1999; 43:658–665.(22). Moncada S., Higgs A. N. Engl. J.Med. 1993; 329:2002–2012.(23). Park K. H., Kim J. S., Noh E. M., Yu H. N., Kim S. Y., Kim S. Z., Kim S. M., Chung E. Y.Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2013; 9:235–241.(24). Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1989; 86:3375–3378.(25). Ponizovsky A. M. J.Sex. Med. 2008; 5:2347–2358.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Nitric Oxide Donor on Penile Erection in Rats
- Effects of Ginseng Saponin on the Stress-Induced Plasma Corticosterone Levels in Mice
- Effects of Ginsenosides on Relaxation of Rabbit Vaginal Smooth Muscle
- Production of Ginsenoside-Rg3 from Lipomyces starkeyi Grown on Ginseng-Steaming Effluent
- Penile Erection Induced by Scoparone from Artemisia capillaris through the Nitric Oxide-Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate Signaling Pathway