Korean J Hematol.
2009 Jun;44(2):122-126. 10.5045/kjh.2009.44.2.122.
Plasmablastic Lymphoma in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus-negative Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea. moonhlmd@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Inha University Hospital, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2252159
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2009.44.2.122
Abstract
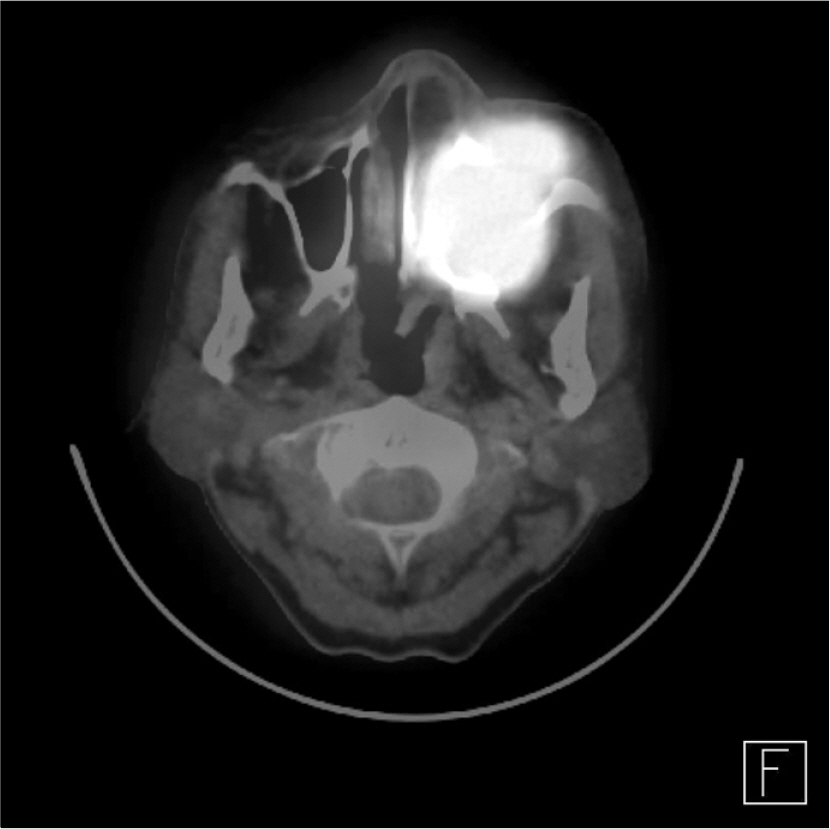
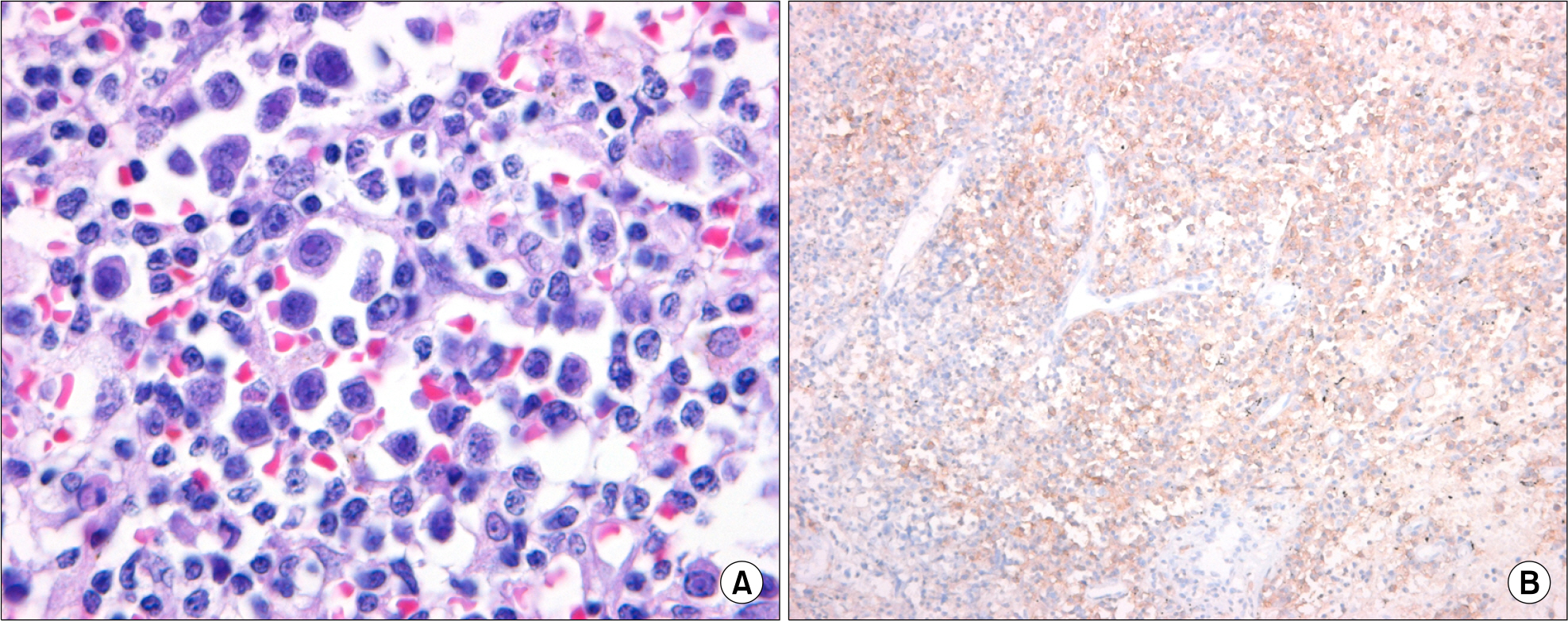
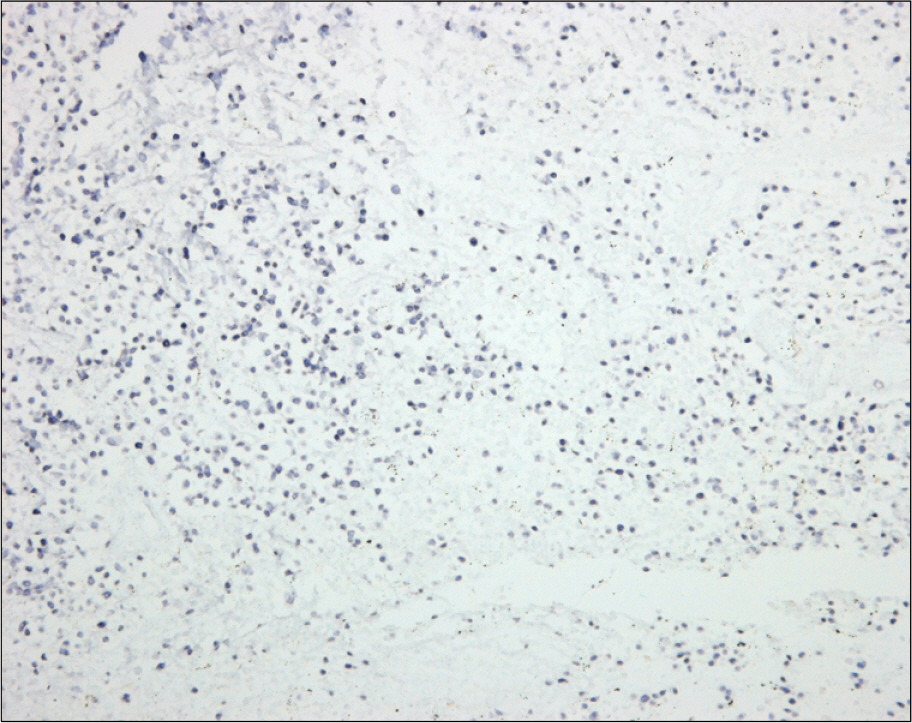
- The plasmablastic lymphomas (PBLs) are an aggressive group of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas occurring primarily in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals with absolute CD4 counts less than 200 per microliter. It was considered to be a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with a unique immunophenotype and occurred primarily in the oral cavity. Recent studies report that PBLs also occur in patients without HIV infection. Herein we report an unusual case of plasmablastic lymphoma presenting in nasal cavity in a 74-year-old, HIV-negative woman. Cytologic and histologic examinations demonstrated a large cell lymphoma with plasmacytic differentiation. The tumor cells were positive for CD79a, CD38, however lacked expression of leukocyte common antigen, T-cell, and B-cell markers. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNA transcripts were identified by in situ hybridization. To our best knowledge, this is the second case of plasmablastic lymphoma in HIV-negative patient in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Delecluse HJ, Anagnostopoulos I, Dallenbach F, et al. Plasmablastic lymphomas of the oral cavity: a new entity associated with the human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood. 1997; 89:1413–20.
Article2. Teruya-Feldstein J, Chiao E, Filippa DA, et al. CD20-negative large-cell lymphoma with plasmablastic features: a clinically heterogenous spectrum in both HIV-positive and -negative patients. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:1673–9.
Article3. Tavora F, Gonzalez-Cuyar LF, Sun CC, Burke A, Zhao XF. Extra-oral plasmablastic lymphoma: report of a case and review of literature. Hum Pathol. 2006; 37:1233–6.
Article4. Lin Y, Rodrigues GD, Turner JF, Vasef MA. Plasmablastic lymphoma of the lung: report of a unique case and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2001; 125:282–5.5. Kim TS, Kang JM, Kim HW, et al. A case of plasma-blastic lymphoma in the nasal cavity in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient. Korean J Med. 2005; 69:446–50.6. Riedel DJ, Gonzalez-Cuyar LF, Zhao XF, Redfield RR, Gilliam BL. Plasmablastic lymphoma of the oral cavity: a rapidly progressive lymphoma associated with HIV infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008; 8:261–7.
Article7. Flaitz CM, Nichols CM, Walling DM, Hicks MJ. Plasmablastic lymphoma: an HIV-associated entity with primary oral manifestations. Oral Oncol. 2002; 38:96–102.
Article8. Castillo J, Pantanowitz L, Dezube BJ. HIV-associated plasmablastic lymphoma: lessons learned from 112 published cases. Am J Hematol. 2008; 83:804–9.
Article9. Scheper MA, Nikitakis NG, Fernandes R, Gocke CD, Ord RA, Sauk JJ. Oral plasmablastic lymphoma in an HIV-negative patient: a case report and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005; 100:198–206.
Article10. Lin F, Zhang K, Quiery AT Jr, Prichard J, Schuerch C. Plasmablastic lymphoma of the cervical lymph nodes in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004; 128:581–4.
Article11. Colomo L, Loong F, Rives S, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with plasmablastic differentiation represent a heterogeneous group of disease entities. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004; 28:736–47.
Article12. Dong HY, Scadden DT, de Leval L, Tang Z, Isaacson PG, Harris NL. Plasmablastic lymphoma in HIV-positive patients: an aggressive Epstein-Barr virus-associated extramedullary plasmacytic neoplasm. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005; 29:1633–41.13. Lester R, Li C, Phillips P, et al. Improved outcome of human immunodeficiency virus-associated plas-mablastic lymphoma of the oral cavity in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy: a report of two cases. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:1881–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of plasmablastic lymphoma in the nasal cavity in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient
- Plasmablastic Lymphoma in the Anal Canal
- Primary Effusion Lymphoma in a Non-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Patient: A Case Report
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Plasmablastic Lymphoma in Human Immunodeficiency Virus(HIV) Negative Patient: A Case Report
- A Case Report with Plasmablastic Lymphoma of the Jejunum