Korean J Crit Care Med.
2015 Aug;30(3):171-175. 10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.3.171.
Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in Pneumonic Septic Shock Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sbhong@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2227644
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.3.171
Abstract
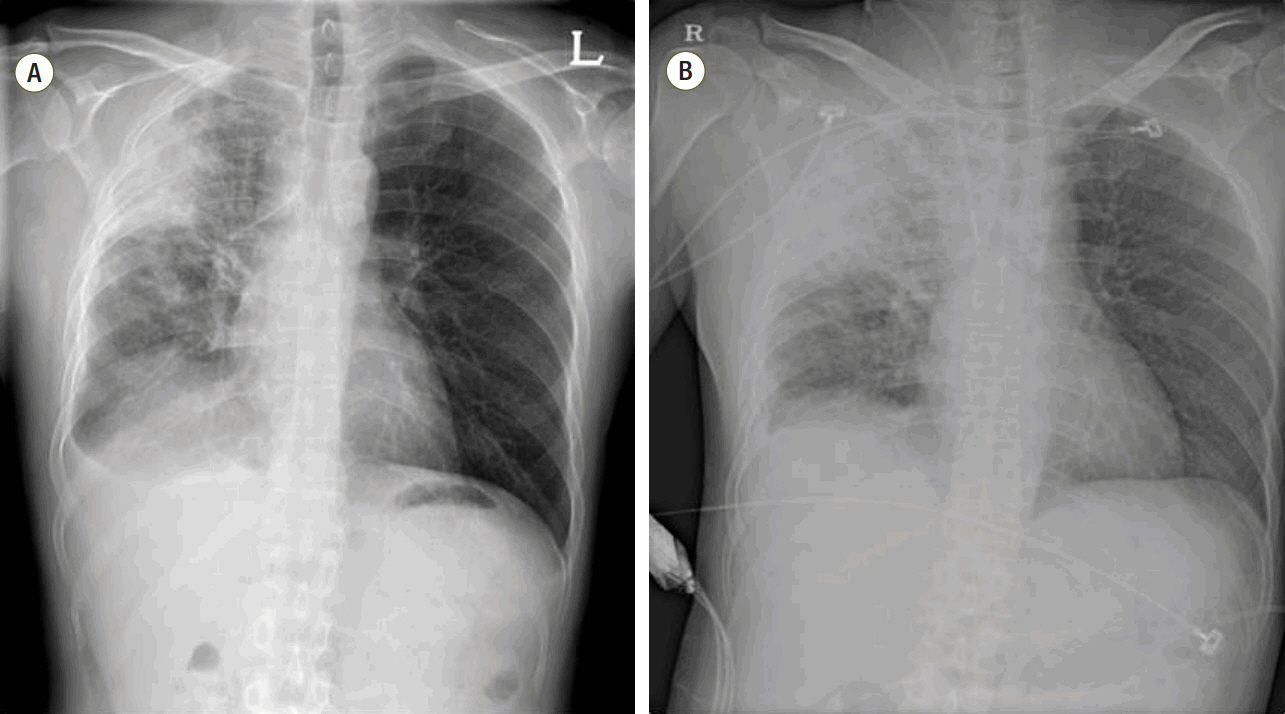
- Severe sepsis and septic shock are the main causes of death in critically ill patients. Early detection and appropriate treatment according to guidelines are crucial for achieving favorable outcomes. Endotoxin is considered to be a main element in the pathogenic induction of gram-negative bacterial sepsis. Polymyxin B hemoperfusion can remove endotoxin and is reported to improve clinical outcomes in patients with intra-abdominal septic shock, but its clinical efficacy for pneumonic septic shock remains unclear. Here, we report a case of a 51-year-old man with pneumonic septic shock caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, who recovered through polymyxin B hemoperfusion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Eng J Med. 2003; 348:1546–54.
Article2. Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J, Paz HL. Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: a trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Crit Care Med. 2007; 35:1244–50.
Article3. Danner RL, Elin RJ, Hosseini JM, Wesley RA, Reilly JM, Parillo JE. Endotoxemia in human septic shock. Chest. 1991; 99:169–75.
Article4. Marshall JC, Foster D, Vincent JL, Cook DJ, Cohen J, Dellinger RP, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of endotoxemia in critical illness: results of the MEDIC study. J Infect Dis. 2004; 190:527–34.
Article5. Opal SM, Glück T. Endotoxin as a drug target. Crit Care Med. 2003; 31(1 Suppl):S57–64.
Article6. Zavascki AP, Goldani LZ, Li J, Nation RL. Polymyxin B for the treatment of multidrug-resistant pathogens: a critical review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007; 60:1206–15.
Article7. Shoji H, Tani T, Hanasawa K, Kodama M. Extracorporeal endotoxin removal by polymyxin B immobilized fiber cartridge: designing and antiendotoxin efficacy in the clinical application. Ther apher. 1998; 2:3–12.
Article8. Cruz DN, Antonelli M, Fumagalli R, Foltran F, Brienza N, Donati A, et al. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: the EUPHAS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009; 301:2445–52.9. Mitaka C, Fujiwara N, Yamamoto M, Toyofuku T, Haraguchi G, Tomita M. Polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column hemoperfusion removes endotoxin throughout a 24-hour treatment period. J Crit Care. 2014; 29:728–32.
Article10. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013; 41:580–637.
Article11. Shoji H. Extracorporeal endotoxin removal for the treatment of sepsis: endotoxin adsorption cartridge (Toraymyxin). Ther Apher Dial. 2003; 7:108–14.12. Ronco C, Klein DJ. Polymyxin B hemoperfusion: a mechanistic perspective. Crit Care. 2014; 18:309.
Article13. Cruz DN, Perazella MA, Bellomo R, de Cal M, Polanco N, Corradi V, et al. Effectiveness of polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care. 2007; 11:R47.
Article14. Mitaka C, Tomita M. Polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column hemoperfusion therapy for septic shock. Shock. 2011; 36:332–8.
Article15. Zhou F, Peng Z, Murugan R, Kellum JA. Blood purification and mortality in sepsis: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Crit Care Med. 2013; 41:2209–20.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Initial Experience of Using Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in Abdominal Septic Shock: Things to Consider for Better Outcome
- A successful application of adult polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column hemoperfusion to a neonate with septic shock
- Refractory Septic Shock Treated with Nephrectomy under the Support of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
- Up-to-date information on polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column direct hemoperfusion for septic shock
- Use of Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion in a Patient with Septic Shock and Septic Cardiomyopathy Who Was Placed on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygen Support