J Korean Med Assoc.
2009 Mar;52(3):287-298. 10.5124/jkma.2009.52.3.287.
Dietary Therapy for Prevention of Atherosclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1NongShim R&BD Center, Department of R&D, Korea. hkhee@nongshim.com
- KMID: 2187980
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2009.52.3.287
Abstract
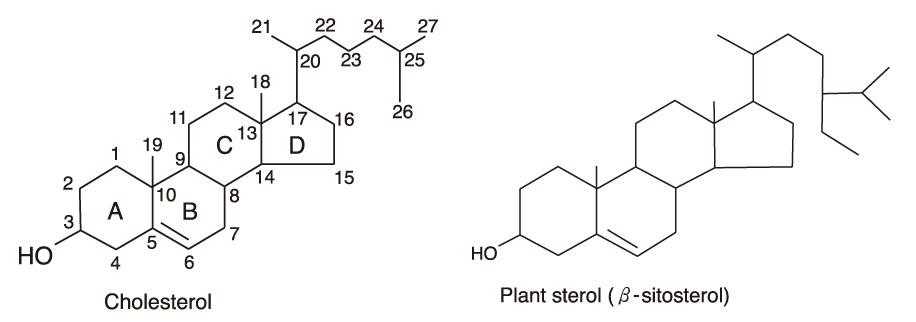
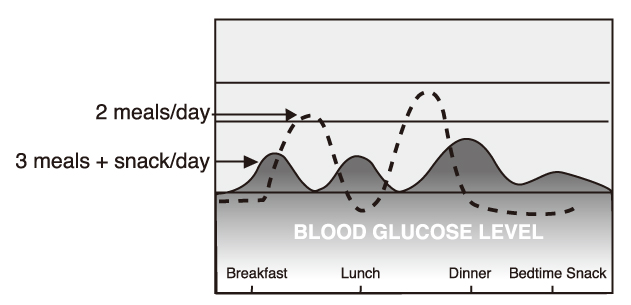
- Beside pharmacological therapy, therapeutic lifestyle changes (TLC) including diet therapy is essential for prevention of atherosclerosis. Dietary guidelines to reduce risk for atherosclerosis should be individualized considering the risk factors of atherosclerosis, i.e., obesity, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and hypertension. In obese patients, the primary goal should be weight reduction to improve overall health by reducing the calorie intake allowed for balanced essential nutrients, especially, adequate protein and micronutrients. Especially, alcohol has been the critical factor in calorie intake in Koreans. Nutritional recommendations of the TLC diet for hyperlipidemia are reduced intake of saturated fat, trans fat, and cholesterol, and increased intake of polyunsaturated fat, monounsaturated fat, soluble fiber, and phytosterols. Excessive intake of carbohydrate and simple sugar might be the risk factors for elevating VLDL in Korean women. For the management of diabetes, mealtime regularity, regular meal size, and balanced nutrients should be emphasized. Low GI diet can be beneficial to control blood glucose. Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is known to improve the health of hypertensive patients. Nutrient targets for the DASH diet are low fat, saturated fat, and cholesterol, and high fiber. Low sodium diet (2,300 mg/day) and foods rich in potassium, calcium, and magnesium are recommended. The Korean traditional diet considering the individual dietary pattern of patients could be the practical healthy diet to prevent atherosclerosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Di Buono M, Hannah JS, Katzel LI, Jones PJ. Weight loss due to energy restriction suppresses cholesterol biosynthesis in overweight, mildly hypercholesterolemic men. J Nutr. 1999. 129:1545–1548.
Article2. Poobalan A, Aucott L, Smith WC, Avenell A, Jung R, Broom J, Grant AM. Effects of weight loss in overweight/obese individuals and long-term lipid outcomes-a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2004. 5:43–50.
Article3. Aucott L, Poobalan A, Smith WC, Avenell A, Jung R, Broom J. Effects of weight loss in overweight/obese individuals and long-term hypertension outcomes: a systematic review. Hypertension. 2005. 45:1035–1041.
Article4. Howarth NC, Saltzman E, Roberts SB. Dietary fiber and weight regulation. Nutr Rev. 2001. 59:129–139.
Article5. Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001. 16(285):2486–2497.6. Mazier MJ, Jones PJ. Dietary fat quality and circulating cholesterol levels in humans: a review of actions and mechanisms. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1991. 15:21–41.7. Furtado JD, Campos H, Appel LJ, Miller ER, Laranjo N, Carey VJ, Sacks FM. Effect of protein, unsaturated fat, and carbohydrate intakes on plasma apolipoprotein B and VLDL and LDL containing apolipoprotein C-III: results from the Omni-Heart Trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008. 87:1623–1630.
Article8. Fernandez ML, West KL. Mechanisms by which dietary fatty acids modulate plasma lipids. J Nutr. 2005. 135:2075–2978.
Article9. Thijssen MA, Hornstra G, Mensink RP. Stearic, oleic, and linoleic acids have comparable effects on markers of thrombotic tendency in healthy human subjects. J Nutr. 2005. 135:2805–2011.
Article10. Simopoulos AP. The importance of the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008. 233:674–688.
Article11. Wang S, Wu D, Matthan NR, Lamon-Fava S, Lecker JL, Lichtenstein AH. Reduction in dietary omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Eicosapentaenoic acid plus docosahexaenoic acid ratio minimizes atherosclerotic lesion formation and inflammatory response in the LDL receptor null mouse. Atherosclerosis. 2008. 09. 02. [Epub ahead of print].
Article12. Micallef MA, Garg ML. Anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and plant sterols in hyperlipidemic individuals. Atherosclerosis. 2008. 09. 27. [Epub ahead of print].
Article13. Breslow JL. n-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006. 83:6S. 1477S–1482S.
Article14. Lindqvist H, Langkilde AM, Undeland I, Rådendal T, Sandberg AS. Herring (Clupea harengus) supplemented diet influences risk factors for CVD in overweight subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007. 61:1106–1113.
Article15. Elvevoll EO, Eilertsen KE, Brox J, Dragnes BT, Falkenberg P, Olsen JO, Kirkhus B, Lamglait A, Østerud B. Seafood diets: hypolipidemic and antiatherogenic effects of taurine and n-3 fatty acids. Atherosclerosis. 2008. 200:396–402.
Article16. Ruxton CH, Calder PC, Reed SC, Simpson MJ. The impact of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on human health. Nutr Res Rev. 2005. 18:1129–1131.17. Pérez-Jiménez F, López-Miranda J, Mata P. Protective effect of dietary monounsaturated fat on arteriosclerosis: beyond cholesterol. Atherosclerosis. 2002. 163:385–398.
Article18. Ascherio A. Trans fatty acids and blood lipids. Atheroscler Suppl. 2006. 7:25–27.
Article19. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Trans fat Q&A. 2008. 8–19.20. Lichtenstein AH. Dietary fat, carbohydrate, and protein:effects on plasma lipoprotei patterns. J Lipid Res. 2006. 47:1661–1667.
Article21. McNamara DJ. Dietary cholesterol and atherosclerosis. Biocheimica et Biophysica Acta. 2000. 1529:310–320.
Article22. Djoussé L, Gaziano JM. Egg consumption in relation to cardiovascular disease and mortality: the Physicians' Health Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008. 87:964–969.
Article23. Tanaka K, Sakai T, Ikeda I, Imaizumi K, Sugano M. Effects of dietary shrimp, squid and octopus on serum and liver lipid levels in mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998. 62:1369–1375.
Article24. Vahouoy GV, Connor WE, Roy T, Lin DS, Gallo LL. Lymphatic absorption of shellfish sterols and their effects on cholesterol absorption. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981. 34:507–513.
Article25. Theuwissen E, Mensink RP. Water-soluble dietary fibers and cardiovascular disease. Physiol Behav. 2008. 94:285–292.
Article26. Hallikainen MA, Sxarkkinen ES, Uusitupa MI. Plant stanol esters affect serum cholesterol concentrations of hypercholesterolemic men and women in a dose-dependent manner. J Nutr. 2000. 130:767–776.
Article27. Brufau G, Canela MA, Rafecas M. Phytosterol: physiologic and metabolic aspects related to cholesterol-lowering properties. Nutr Res. 2008. 28:217–225.
Article28. Parks EJ. Effect of dietary carbohydrate on triglyceride metabolism in humans. J Nutr. 2001. 131:2772S–2774S.
Article29. Thom SL. Nutritional management of diabetes. Nurs Clin North Am. 1993. 28:97–112.30. Mann JI. Nutrition recommendations for the treatment and prevention of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: an evidenced-based review. Nutr Rev. 2006. 64:422–427.
Article31. Foster-Powell K, Holt SH, Brand-Miller JC. International table of glycemic index and glycemic load values: 2002. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002. 76:5–56.
Article32. National Institute of health. The 7th report of the joint Nationa Committee on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. 2003. NIH publication;No 03-5233.33. Champagne CM. Dietary interventions on blood pressure: the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) trials. Nutr Rev. 2006. 64(2 Pt 2):S53–S56.
Article34. Haddy F, Pamnari M. Role of dietary salt in hypertensin. J Am Coll Nutr. 1995. 14:428–438.35. Cutler J, Follmann D, Allender P. Randomized trials of sodium reduction: an overview. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997. 65:643S–651S.
Article36. Barri Y, Wingo C. The effects of potassium depletion and supplementation on blood pressure: a clinical review. Am J Med Sci. 1997. 314:37–40.
Article37. Bucher H, Cook R, Guyatt G, Lang J, Cook D, Hatala R, Hunt D. Effects of dietary calcium supplementation on blood pressure:a meta- analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 1996. 275:1016–1022.
Article38. Allender P, Cutler J, Follmann D, Cappuccio F, Pryer J, Elliott P. Dietary calcium and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Ann Intern Med. 1996. 124:825–831.39. Suter PM, Sierro C, Vetter W. Nutritional factors in the control of blood pressure and hypertension. Nutr Clin Care. 2002. 5:9–19.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hormone Replacement Therapy for Prevention or Treatment of Atherosclerosis in Postmenopausal Women
- Diet management for dyslipidemia
- Prevention of cardiovascular complications in high risk patients of atherosclerosis
- Dietary Behavior Score and Serum Lipid Profiles of Old Men with Atherosclerosis Operated by Angiography
- Risk Factors and Primary and Secondary Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease