Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Aug;35(4):514-523. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.4.514.
Effects of Transforaminal Injection for Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis Combined with Spinal Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul 134-701, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul 139-707, Korea. swc328@naver.com
- KMID: 1971717
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.4.514
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The objectives of this study were to clarify the short-term effects of transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) for degenerative lumbar scoliosis combined with spinal stenosis (DLSS), and to extrapolate factors relating to the prognosis of treatment. METHOD: Thirty-six patients with lumbar radicular pain from DLSS were enrolled. Subjects were randomly assigned to one of two groups (steroid or lidocaine group). We compared the effect of pain suppression at 2, 4 and 12 weeks after the procedure between the two groups. Radiographic analysis included measurement of the Cobb's angle, the upper endplate obliquities of L3 and L4, and maximal lateral olisthy between two adjacent lumbar vertebrae. Sagittal plane measurement included lumbar lordosis, and thoracolumbar kyphosis. Statistical analysis of both radiographic and clinical parameters along with treatment outcome was performed to determine any significant correlations between the two.
RESULTS
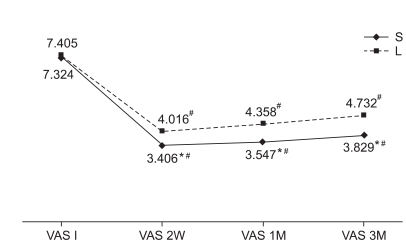
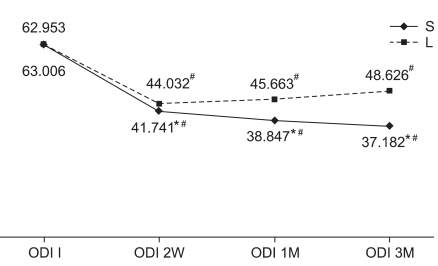
There were no significant differences in the demographic data, initial visual analogue scale (VAS) or Oswestry disability index (ODI) between the steroid group (n=17) and the lidocaine group (n=19). Two, 4, and 12 weeks after injection VAS, ODI showed a significantly greater improvement in the steroid group compared to the lidocaine group (p<0.05). The radiographic and clinical parameters were not significantly correlated with treatment outcome.
CONCLUSION
Our findings suggest that fluoroscopic transforaminal epidural steroid injections appear to be an effective non-surgical treatment option for patients with degenerative lumbar scoliosis combined with spinal stenosis (DLSS) and radicular pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Medial Branch Block in Chronic Facet Joint Pain for Osteoporotic Compression Fracture: One Year Retrospective Study
Ki Deok Park, Haemi Jee, Hee Seung Nam, Soo Kyoung Cho, Hyoung Seop Kim, Yongbum Park, Oh Kyung Lim
Ann Rehabil Med. 2013;37(2):191-201. doi: 10.5535/arm.2013.37.2.191.
Reference
-
1. Nygaard OP, Mellgren SI, Osterud B. The inflammatory properties of contained and noncontained lumbar disc herniation. Spine. 1997; 22:2484–2488. PMID: 9383853.
Article2. Franson RC, Saal JS, Saal JA. Human disc phospholipase A2 is inflammatory. Spine. 1992; 17(6 Suppl):S129–S132. PMID: 1631712.
Article3. Olmarker K, Blomquist J, Stromberg J, Nannmark U, Thomsen P, Rydevik B. Inflammatogenic properties of nucleus pulposus. Spine. 1995; 20:665–669. PMID: 7604342.
Article4. Rydevik B, Brown MD, Lundborg G. Pathoanatomy and pathophysiology of nerve root compression. Spine. 1984; 9:7–15. PMID: 6372124.
Article5. Olmarker K, Redevik B, Holm S. Edema formation in spinal nerve roots induced by experimental, graded compression. An experimental study on the pig cauda equina with special reference to differences in effects between rapid and slow onset of compression. Spine. 1989; 14:569–573. PMID: 2546258.6. Lutz GE, Vad VB, Wisneski RJ. Fluoroscopic transforaminal lumbar epidural steroids: an outcome study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998; 79:1362–1366. PMID: 9821894.
Article7. Cooper G, Lutz GE, Boachie-Adjei O, Lin J. Effectiveness of transforaminal epidural steroid injections in patients with degenerative lumbar scoliotic stenosis and radiculopathy. Pain Physician. 2004; 7:311–317. PMID: 16858467.8. Vad VB, Bhat AL, Lutz GE, Cammisa F. Transforaminal epidural steroid injections in lumbosacral radiculopathy: a prospective randomized study. Spine. 2002; 27:11–16. PMID: 11805628.9. Kostuik JP, Bentivoglio J. The incidence of low backpain in adult scoliosis. Spine. 1981; 6:268–273. PMID: 6455747.10. Robin GC, Span Y, Steinberg R, Makin M, Menczel J. Scoliosis in the elderly: a follow- up study. Spine. 1982; 7:355–359. PMID: 6215719.11. Dawson E, Bernbeck J. The surgical treatment of low back pain. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 1998; 9:489–495. PMID: 9894129.
Article12. Nasca RJ. Rationale for spinal fusion in lumbar sipnal stenosis. Spine. 1989; 14:451–454. PMID: 2718051.13. Simotas AC, Dorey FJ, Hansraj KK, Cammisa F Jr. Nonoperative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis. Clinical and outcome results and a 3-year survivorship analysis. Spine. 2000; 25:197–203. PMID: 10685483.14. Nash CL Jr, Moe JH. A study of vertebral rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969; 51:223–229. PMID: 5767315.
Article15. Schwab FJ, Smith VA, Biserni M, Gamez L, Farcy JP, Pagala M. Adult scoliosis: a quantitative radiographic and clinical analysis. Spine. 2002; 27:387–392. PMID: 11840105.16. Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ. Diagnostic findings in painful adult scoliosis. Spine. 1992; 17:518–527. PMID: 1621151.
Article17. Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Coonrad RW. Degenerative adult onset scoliosis. Spine. 1988; 13:241–245. PMID: 2968664.
Article18. Grubb SA, Lipscomb HJ, Suh PB. Results of surgical treatment of painful adult scoliosis. Spine. 1994; 19:1619–1627. PMID: 7939999.
Article19. Jackson RP, McManus AC. Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size. A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine. 1994; 19:1611–1618. PMID: 7939998.20. Kantrowitz F, Robinson DR, McGuire MB, Levine L. Corticosteroids inhibit prostaglandin production by rheumatoid synovia. Nature. 1975; 258:737–739. PMID: 1207758.
Article21. Fukusaki M, Kobayashi I, Hara T, Sumikawa K. Symptoms of spinal stenosis do not improve after epidural steroid injection. Clin J Pain. 1998; 14:148–151. PMID: 9647457.
Article22. Johansson A, Hao J, Sjolund B. Local corticosteroid application blocks transmission in normal nociceptor C-fibres. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1990; 34:335–338. PMID: 2167604.23. Hoogmartens M, Morelle P. Epidural injection in the treatment of spinal stenosis. Acta Orthop Belg. 1987; 53:409–411. PMID: 3442227.24. Rosen CD, Kahanovitz N, Bernstein R, Viola K. A retrospective analysis of the efficacy of epidural steroid injections. Clin Orthop. 1988; 228:270–272. PMID: 2963720.
Article25. Delport EG, Cucuzzella AR, Marley JK, Pruitt CM, Fisher JR. Treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with epidural steroid injections: a retrospective outcome study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 85:479–484. PMID: 15031837.
Article26. Riew KD, Yin Y, Gilula L, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Lauryssen C, Goette K. The effect of nerve-root injections on the need for operative treatment of lumbar radicular pain. A prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82:1589–1593. PMID: 11097449.27. Cannon DT, Aprill CN. Lumbosacral epidural steroid injections. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000; 81(3 Suppl 1):S87–S98. PMID: 10721765.
Article28. Miyamoto H, Sumi M, Uno K, Tadokoro K, Mizuno K. Clinical outcome of nonoperative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis, and predictive factors relating to prognosis, in a 5-year minimum follow-up. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008; 21:563–568. PMID: 19057249.
Article29. van Dam BE. Nonoperative treatment of adult scoliosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1988; 19:347–351. PMID: 3282202.
Article30. Pritchett JW, Bortel DT. Degenerative symptomatic lumbar scoliosis. Spine. 1993; 18:700–703. PMID: 8516697.
Article31. Ng L, Chaudhary N, Sell P. The efficacy of corticosteroids in periradicular infiltration for chronic radicular pain: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Spine. 2005; 30:857–862. PMID: 15834326.32. Kluba T, Dikmenli G, Dietz K, Giehl JP, Niemeyer T. Comparison of surgical and conservative treatment for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129:1–5. PMID: 18560848.
Article33. Irwin ZN, Hilibrand A, Gustavel M, McLain R, ShaVer W, Myers M, Glaser J, Hart RA. Variations in surgical decision making for degenerative spinal disorders. Part 1: lumbar spine. Spine. 2005; 30:2208–2213. PMID: 16205348.34. Swezey RL. Outcome for lumbar stenosis. J Clin Rheumatol. 1996; 2:129–134. PMID: 19078047.35. Onel D, Sari H, Donmez C. Lumbar spinal stenosis: clinical/radiologic therapeutic evaluation in 145 patients. Conservative treatment or surgical intervention? Spine. 1993; 18:291–298. PMID: 8441947.36. Lahat A, Ben-Horin S, Lang A, Fudim E, Picard O, Chowers Y. Lidocaine down-regulates nuclear factor-kappaB signalling and inhibits cytokine production and T cell proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008; 152:320–327. PMID: 18355353.37. Gallos G, Jones DR, Nasr SH, Emala CW, Lee HT. Local anesthetics reduce mortality and protect against renal and hepatic dysfunction in murine septic peritonitis. Anesthesiology. 2004; 101:902–911. PMID: 15448523.
Article38. Cassuto J, Sinclair R, Bonderovic M. Anti-inflammatory properties of local anesthetics and their present and potential clinical implications. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006; 50:265–282. PMID: 16480459.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Management of Spinal Stenosis with Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis
- Surgical Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis with Multiple Spinal Stenosis
- Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 in Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis
- Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Multilevel Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Associated with Degenerative Scoliosis
- Cotrel - Dubousset Pedicle Screw Fixation After Posterior Decompression of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis