Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Apr;63(4):209-215. 10.4166/kjg.2014.63.4.209.
Prognostic Factors for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer after First-line Chemotherapy with FOLFOX-4 or FOLFIRI Regimen
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea. parksj6406@daum.net
- KMID: 1791877
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.63.4.209
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Information on prognostic factors for metastatic colorectal cancer is an important basis for planning the treatment and predicting the outcomes of the patients; however, it has not been well established. The aim of this study was to identify factors that predict results of chemotherapy and to establish a plan for treatment of patients whose tumors are inoperable due to metastatic colorectal cancer.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective review of records from 75 patients treated for colorectal cancer in Kosin University Gospel Hospital, from October 2004 to September 2008. Patients with inoperable tumors due to metastasis at the time of diagnosis who were treated with oxaliplatin or irinotecan as the first-line treatment were included in this study. We investigated the factors that might have an effect on overall survival.
RESULTS
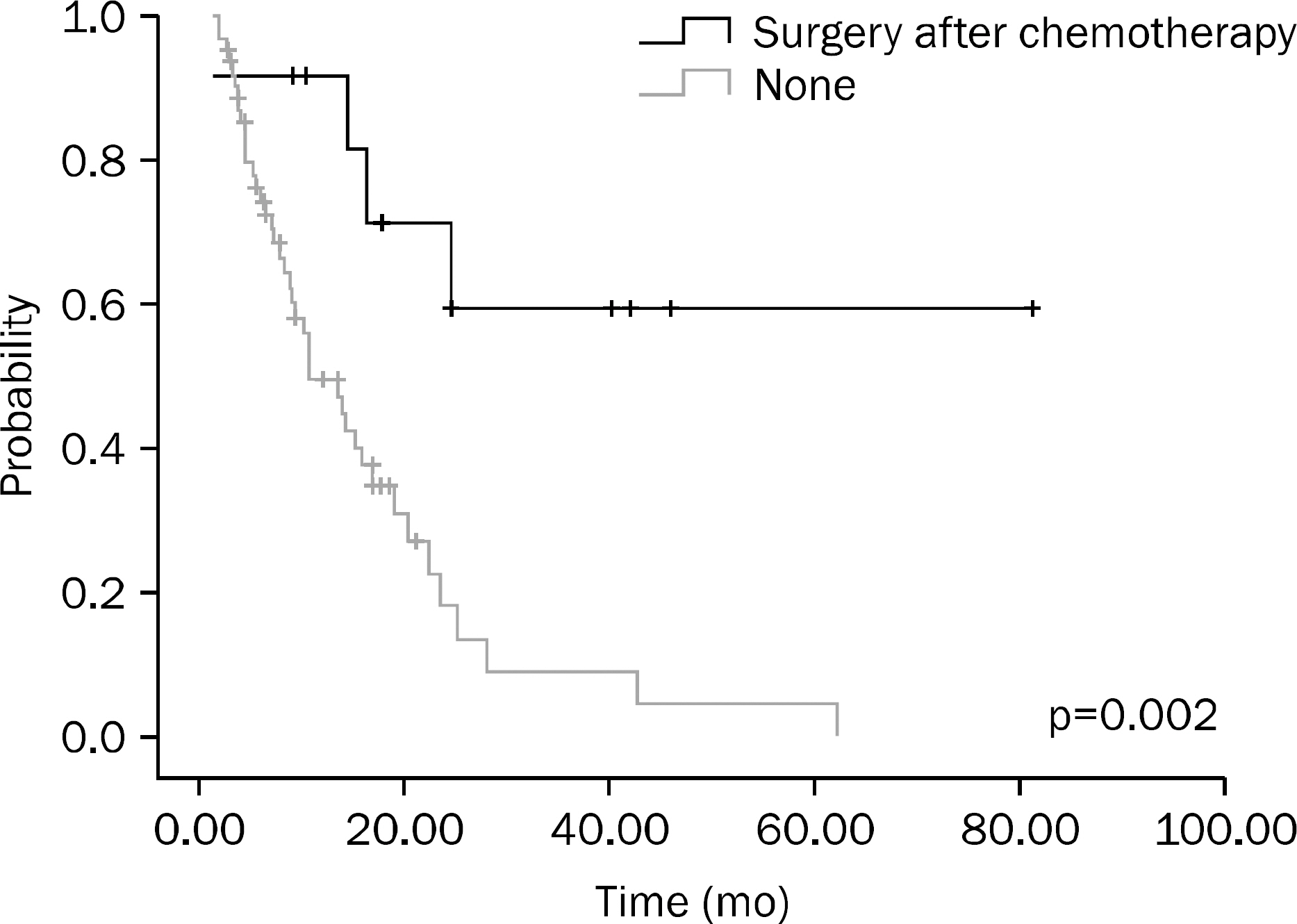
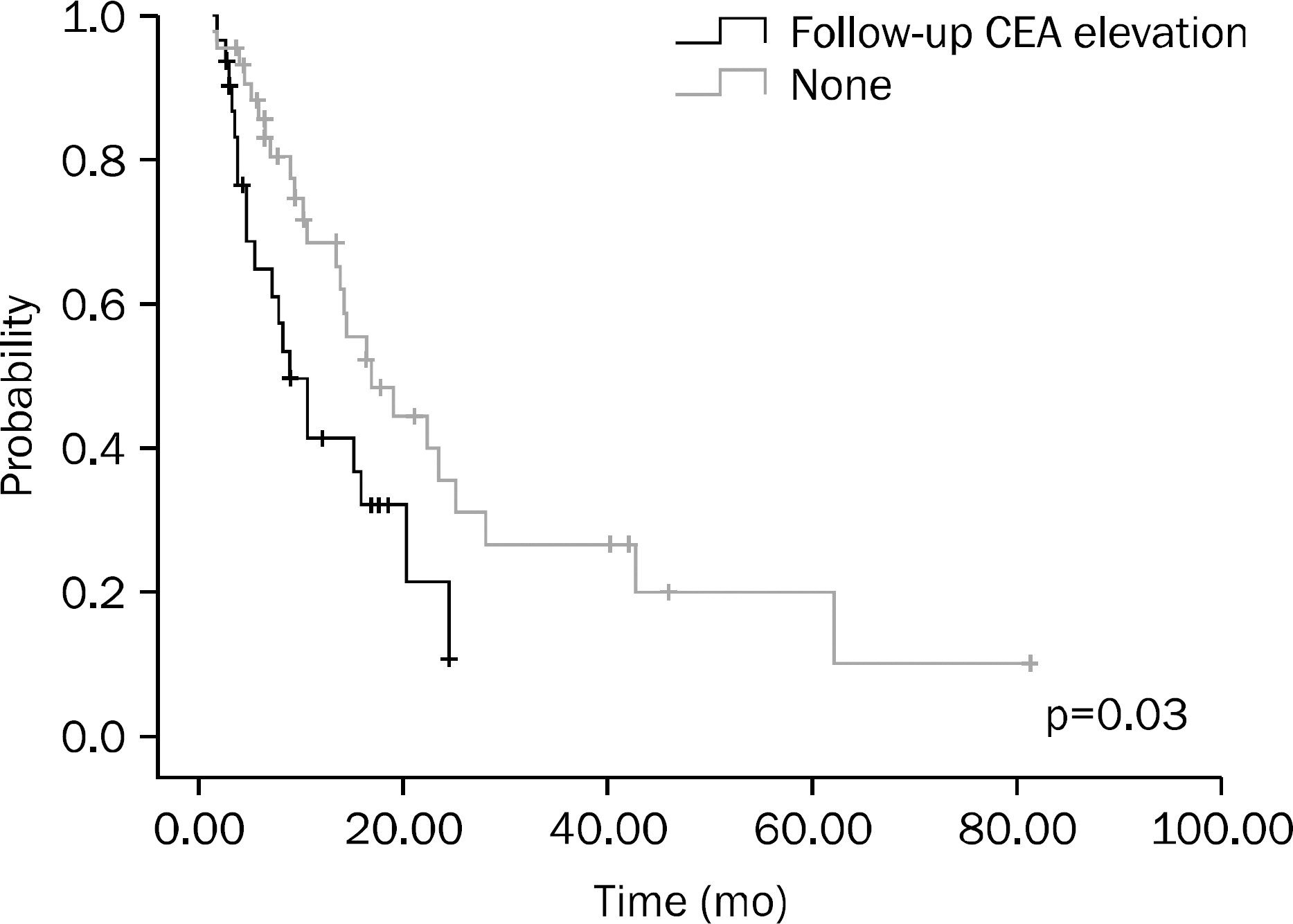
A total of 75 patients were included in this study. Results of univariate analysis showed that hemoglobin (Hb) > or =10 g/dL at the time of diagnosis, no increase in CEA on the follow-up examination after chemotherapy, chemotherapy plus surgery, and better response to chemotherapy were significant prognostic factors. Results of multivariate analysis showed that Hb > or =10 g/dL at the time of diagnosis (p<0.001), surgery after chemotherapy (p=0.001), and better response to chemotherapy (p=0.014) were significant prognostic factors.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, Hb > or =10 g/dL at the time of diagnosis, surgery after chemotherapy, and better response to chemotherapy were significant prognostic factors for metastatic colorectal cancer.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Antineoplastic Combined Chemotherapy Protocols/*therapeutic use
Camptothecin/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Colorectal Neoplasms/*diagnosis/*drug therapy/mortality/surgery
Female
Fluorouracil/administration & dosage/therapeutic use
Hemoglobins/analysis
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Leucovorin/administration & dosage/therapeutic use
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Metastasis
Odds Ratio
Organoplatinum Compounds/therapeutic use
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Camptothecin
Fluorouracil
Hemoglobins
Leucovorin
Organoplatinum Compounds
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Parkin DM. Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol. 2001; 2:533–543.
Article2. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Seo HG, Lee JS. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival and prevalence in 2010. Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 45:1–14.
Article3. Okano M, Yamamoto H, Ohkuma H, et al. Significance of INHBA expression in human colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2013; 30:2903–2908.
Article4. Qian J, Jiang B, Li M, Chen J, Fang M. Prognostic significance of microRNA-16 expression in human colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 2013; 37:2944–2949.
Article5. Sunaga T, Suzuki S, Kogo M, et al. The association between neutropenia and prognosis in stage III colorectal cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2013. DOI: doi: 10.1111/ecc.12120. [Epub ahead of print].
Article6. Jung W, Hong KD, Jung WY, et al. SIRT1 expression is associated with good prognosis in colorectal cancer. Korean J Pathol. 2013; 47:332–339.
Article7. Cheung WY, Shi Q, O'Connell M, et al. ACCENT Collaborative Group. The predictive and prognostic value of sex in early-stage colon cancer: a pooled analysis of 33,345 patients from the ACCENT database. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2013; 12:179–187.8. Rao BN, Pratt CB, Fleming ID, Dilawari RA, Green AA, Austin BA. Colon carcinoma in children and adolescents. A review of 30 cases. Cancer. 1985; 55:1322–1326.
Article9. Odone V, Chang L, Caces J, George SL, Pratt CB. The natural history of colorectal carcinoma in adolescents. Cancer. 1982; 49:1716–1720.
Article10. Schellerer VS, Merkel S, Schumann SC, et al. Despite aggressive histopathology survival is not impaired in young patients with colorectal cancer: CRC in patients under 50 years of age. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012; 27:71–79.11. Ishihara S, Watanabe T, Akahane T, et al. Tumor location is a prognostic factor in poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma, mucinous adenocarcinoma, and signet-ring cell carcinoma of the colon. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012; 27:371–379.
Article12. Meyerhardt JA, Niedzwiecki D, Hollis D, et al. Cancer and Leukemia Group B 89803. Impact of body mass index and weight change after treatment on cancer recurrence and survival in patients with stage III colon cancer: findings from Cancer and Leukemia Group B 89803. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:4109–4115.
Article13. Wolmark N, Wieand HS, Rockette HE, et al. The prognostic significance of tumor location and bowel obstruction in Dukes B and C colorectal cancer. Findings from the NSABP clinical trials. Ann Surg. 1983; 198:743–752.14. Steinberg SM, Barkin JS, Kaplan RS, Stablein DM. Prognostic indicators of colon tumors. The Gastrointestinal Tumor Study Group experience. Cancer. 1986; 57:1866–1870.
Article15. Beahrs OH, Sanfelippo PM. Factors in prognosis of colon and rectal cancer. Cancer. 1971; 28:213–218.
Article16. Pescatori M, Maria G, Beltrani B, Mattana C. Site, emergency, and duration of symptoms in the prognosis of colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 1982; 25:33–40.
Article17. Chapuis PH, Dent OF, Fisher R, et al. A multivariate analysis of clinical and pathological variables in prognosis after resection of large bowel cancer. Br J Surg. 1985; 72:698–702.
Article18. Tartter PI. The association of perioperative blood transfusion with colorectal cancer recurrence. Ann Surg. 1992; 216:633–638.
Article19. Griffin MR, Bergstralh EJ, Coffey RJ, Beart RW Jr, Melton LJ 3rd. Predictors of survival after curative resection of carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1987; 60:2318–2324.
Article20. Minsky BD, Mies C, Rich TA, Recht A. Lymphatic vessel invasion is an independent prognostic factor for survival in colorectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989; 17:311–318.
Article21. Bognel C, Rekacewicz C, Mankarios H, et al. Prognostic value of neural invasion in rectal carcinoma: a multivariate analysis on 339 patients with curative resection. Eur J Cancer. 1995; 31A:894–898.
Article22. Jass JR, Love SB, Northover JM. A new prognostic classification of rectal cancer. Lancet. 1987; 1:1303–1306.23. Visscher DW, Zarbo RJ, Ma CK, Sakr WA, Crissman JD. Flow cytometric DNA and clinicopathologic analysis of Dukes' A&B colonic adenocarcinomas: a retrospective study. Mod Pathol. 1990; 3:709–712.24. Jen J, Kim H, Piantadosi S, et al. Allelic loss of chromosome 18q and prognosis in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331:213–221.
Article25. Tomoda H, Kakeji Y, Furusawa M. Prognostic significance of flow cytometric analysis of DNA content in colorectal cancer: a prospective study. J Surg Oncol. 1993; 53:144–148.
Article26. Zeng ZS, Sarkis AS, Zhang ZF, et al. p53 nuclear overexpression: an independent predictor of survival in lymph node–positive colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12:2043–2050.
Article27. Webb A, Scott-Mackie P, Cunningham D, et al. The prognostic value of CEA, beta HCG, AFP, CA125, CA19–9 and C-erb B-2, beta HCG immunohistochemistry in advanced colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 1995; 6:581–587.28. Andersen SN, Rognum TO, Lund E, Meling GI, Hauge S. Strong HLA-DR expression in large bowel carcinomas is associated with good prognosis. Br J Cancer. 1993; 68:80–85.
Article29. Stelzner S, Hellmich G, Koch R, Ludwig K. Factors predicting survival in stage IV colorectal carcinoma patients after palliative treatment: a multivariate analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2005; 89:211–217.
Article30. Rougier P, Milan C, Lazorthes F, et al. Prospective study of prognostic factors in patients with unresected hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Fondation Française de Cancérologie Digestive. Br J Surg. 1995; 82:1397–1400.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of an Irinotencan, 5-Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin Combination Chemotherapy (FOLFIRI) in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
- Retrospective Analysis of Patients Treated with Cetuximab plus FOLFIRI for Previous Irinotecan-combined Chemotherapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
- FOLFIRI as Second-line Chemotherapy after Failure of FOLFOX4 in Advanced Colorectal Cancer: A Korean Single-center Experience
- Modified FOLFIRI as Second-Line Chemotherapy after Failure of Modified FOLFOX-4 in Advanced Gastric Cancer
- Drug-induced immune-mediated thrombocytopenia due to bevacizumab-FOLFOX therapy: a case report