Ewha Med J.
2013 Dec;36(Suppl):S17-S21. 10.12771/emj.2013.36.S.S17.
Radiation Recall Dermatitis Induced by Gefitinib
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hyosong77@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1726729
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2013.36.S.S17
Abstract
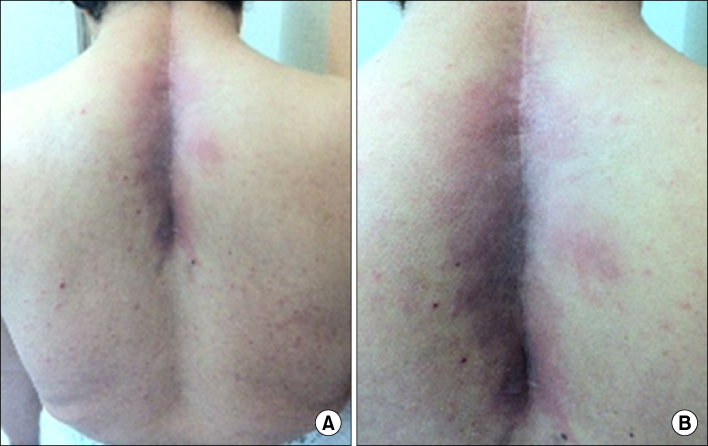
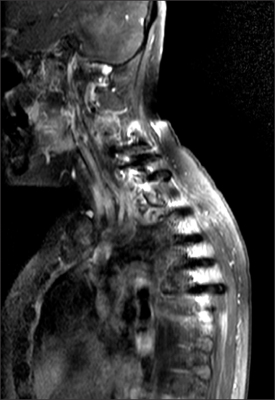
- Radiation recall dermatitis refers to an acute inflammatory reaction in a previously irradiated field triggered by the administration of certain drugs days to years after the exposure to radiation. Gefitinib is an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and is an effective treatment for patients with advanced stage of non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Here, we report a rare case of gefitinib induced radiation recall dermatitis. A 52-year-old woman with a metastatic NSCLC had received a palliative radiation therapy of 20 cGy on spine metastasis area (C6-T6). After 24 days of receiving radiation therapy, she had started to take gefitinib. Eight months after taking drug, pain, swelling and erythema of skin were occurred on previously irradiated field. These symptoms were resolved after the cessation of gefitinib for 6 days and the topical use of steroid.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. D'angio GJ. Clinical and biologic studies of actinomycin D and roentgen irradiation. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1962; 87:106–109.2. Donaldson SS, Glick JM, Wilbur JR. Letter: adriamycin activating a recall phenomenon after radiation therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1974; 81:407–408.3. Etcubanas E, Wilbur JR. Letter: uncommon side effects of adriamycin (NSC-123127). Cancer Chemother Rep. 1974; 58:757–758.4. Schweitzer VG, Juillard GJ, Bajada CL, Parker RG. Radiation recall dermatitis and pneumonitis in a patient treated with paclitaxel. Cancer. 1995; 76:1069–1072.5. Raghavan VT, Bloomer WD, Merkel DE. Taxol and radiation recall dermatitis. Lancet. 1993; 341:1354.6. Camidge DR, Kunkler IH. Docetaxel-induced radiation recall dermatitis and successful rechallenge without recurrence. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2000; 12:272–273.7. Nemechek PM, Corder MC. Radiation recall associated with vinblastine in a patient treated for Kaposi sarcoma related to acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Cancer. 1992; 70:1605–1606.8. Stelzer KJ, Griffin TW, Koh WJ. Radiation recall skin toxicity with bleomycin in a patient with Kaposi sarcoma related to acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Cancer. 1993; 71:1322–1325.9. Castellano D, Hitt R, Cortes-Funes H, Romero A, Rodriguez-Peralto JL. Side effects of chemotherapy. Case 2. Radiation recall reaction induced by gemcitabine. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:695–696.10. Abadir R, Liebmann J. Radiation reaction recall following simvastatin therapy: a new observation. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 1995; 7:325–326.11. Bostrom A, Sjolin-Forsberg G, Wilking N, Bergh J. Radiation recall--another call with tamoxifen. Acta Oncol. 1999; 38:955–959.12. Extermann M, Vogt N, Forni M, Dayer P. Radiation recall in a patient with breast cancer treated for tuberculosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1995; 48:77–78.13. Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, et al. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2003; 290:2149–2158.14. Park JH, Oh JJ, Choi YL, Kim WS, Lee JH, Lee ES. Cutaneous adverse effects associated with Iressa(R)(Gefitinib) medication. Korean J Dermatol. 2005; 43:92–95.15. Jang YH, Choi JH, Lim HY, Lee ES. Study of clinical features of cutaneous side effects associated with ZD 1839. Korean J Dermatol. 2005; 43:22–28.16. Hellman S, Botnick LE. Stem cell depletion: an explanation of the late effects of cytotoxins. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1977; 2:181–184.17. Seymour CB, Mothersill C, Alper T. High yields of lethal mutations in somatic mammalian cells that survive ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1986; 50:167–179.18. Phillips TL, Fu KK. Quantification of combined radiation therapy and chemotherapy effects on critical normal tissues. Cancer. 1976; 37:2 Suppl. 1186–1200.19. Wintroub BU, Stern R. Cutaneous drug reactions: pathogenesis and clinical classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985; 13(2 Pt 1):167–179.20. Vozenin-Brotons MC, Gault N, Sivan V, Tricaud Y, Dubray B, Clough K, et al. Histopathological and cellular studies of a case of cutaneous radiation syndrome after accidental chronic exposure to a cesium source. Radiat Res. 1999; 152:332–337.21. Johnston CJ, Piedboeuf B, Rubin P, Williams JP, Baggs R, Finkelstein JN. Early and persistent alterations in the expression of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA levels in fibrosis-resistant and sensitive mice after thoracic irradiation. Radiat Res. 1996; 145:762–767.22. Camidge R, Price A. Characterizing the phenomenon of radiation recall dermatitis. Radiother Oncol. 2001; 59:237–245.23. Burdon J, Bell R, Sullivan J, Henderson M. Adriamycin-induced recall phenomenon 15 years after radiotherapy. JAMA. 1978; 239:931.24. Fontana JA. Radiation recall associated with VP-16-213 therapy. Cancer Treat Rep. 1979; 63:224–225.25. Dauendorffer JN, Dupuy A. Radiation recall dermatitis induced by erlotinib. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009; 61:1086.26. Kim HM, Lee SH, Kim CY. Erlotinib HCL (Tarceva(R)) induced radiation recall dermatitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2010; 48:872–875.27. Kim YY, Kim MY, Park YM, Kim HO. A case of radiation recall dermatitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2006; 44:479–482.28. Lynch TJ Jr, Kim ES, Eaby B, Garey J, West DP, Lacouture ME. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-associated cutaneous toxicities: an evolving paradigm in clinical management. Oncologist. 2007; 12:610–621.29. Togashi Y, Masago K, Mishima M, Fukudo M, Inui K. A case of radiation recall pneumonitis induced by erlotinib, which can be related to high plasma concentration. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:924–925.30. Arakawa H, Johkoh T, Sakai F, Kusumoto M, Hataji O, Taguchi O. Exacerbation of radiation fibrosis with erlotinib: another pattern of radiation recall phenomenon. Jpn J Radiol. 2011; 29:587–589.31. Onal C, Abali H, Koc Z, Kara S. Radiation recall pneumonitis caused by erlotinib after palliative definitive radiotherapy. Onkologie. 2012; 35:191–194.32. Miya T, Ono Y, Tanaka H, Koshiishi Y, Goya T. Radiation recall pneumonitis induced by Gefitinib (Iressa): a case report. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2003; 41:565–568.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of cetuximab-induced radiation recall skin dermatitis and review of the literature
- A Case of Radiation Recall Dermatitis which Developed in a Patient with Kaposi Sarcoma
- Erlotinib HCL (Tarceva(R)) Induced Radiation Recall Dermatitis
- Radiation recall dermatitis induced by tamoxifen during adjuvant breast cancer treatment
- Radiation Recall Dermatitis Induced by Methotrexate