Korean Circ J.
2013 Jan;43(1):23-28. 10.4070/kcj.2013.43.1.23.
Hypercholesterolemia and In-Vivo Coronary Plaque Composition in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Virtual Histology - Intravascular Ultrasound Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Heart Center, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. janghobae@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 1722997
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2013.43.1.23
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Hypercholesterolemia is a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis. We sought to evaluate the relation between hypercholesterolemia and plaque composition in patients with coronary artery disease.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Study subjects consisted of 323 patients (mean 61.5 years, 226 males) who underwent coronary angiography and virtual histology-intravascular ultrasound examination. Patients were divided into two groups according to total cholesterol level: hypercholesterolemic group (> or =200 mg/dL, n=114) and normocholesterolemic group (<200 mg/dL, n=209).
RESULTS
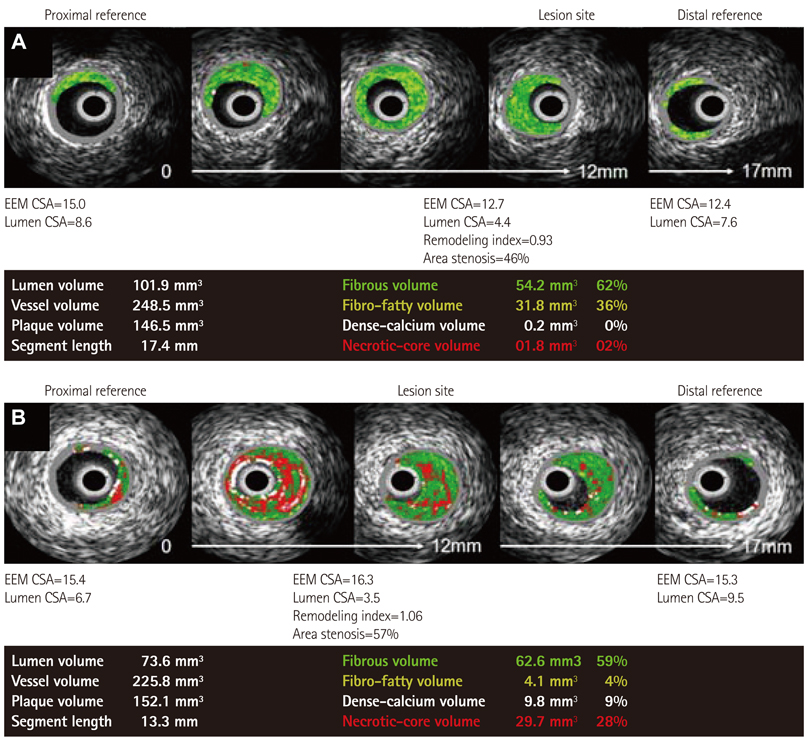
Hypercholesterolemic patients were younger (59.7+/-13.3 years vs. 62.6+/-11.5 years, p=0.036), than normocholesterolemic patients, whereas there were no significant differences in other demographics. Hypercholesterolemic patients had higher corrected necrotic core volume (1.23+/-0.85 mm3/mm vs. 1.02+/-0.80 mm3/mm, p=0.029) as well as percent necrotic core volume (20.5+/-8.5% vs. 18.0+/-9.2%, p=0.016) than normocholesterolemic patients. At the minimal lumen area site, percent necrotic core area (21.4+/-10.5% vs. 18.4+/-11.3%, p=0.019) and necrotic core area (1.63+/-1.09 mm2 vs. 1.40+/-1.20 mm2, p=0.088) were also higher than normocholesterolemic patients. Multivariate linear regression analysis showed that total cholesterol level was an independent factor of percent necrotic core volume in the culprit lesion after being adjusted with age, high density lipoprotein-cholesterol , hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking and acute coronary syndrome (beta 0.027, 95% confidence interval 0.02-0.053, p=0.037).
CONCLUSION
Hypercholesterolemia was associated with increased necrotic core volume in coronary artery plaque. This study suggests that hypercholesterolemia plays a role in making plaque more complex, which is characterized by a large necrotic core, in coronary artery disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Practical Application of Coronary Imaging Devices in Cardiovascular Intervention
- Early Differential Changes in Coronary Plaque Composition According to Plaque Stability Following Statin Initiation in Acute Coronary Syndrome: Classification and Analysis by Intravascular Ultrasound-Virtual Histology
- Tissue Characterization of Coronary Plaques Using Intravascular Ultrasound/Virtual Histology
- A Case of Coronary Pseudostenosis, Diagnosed by Intravascular Ultrasound
- In-Vivo Coronary Plaque Composition in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Virtual Histology Intravascular Ultrasound Study