J Korean Soc Transplant.
2011 Dec;25(4):257-263. 10.4285/jkstn.2011.25.4.257.
Impact of Early Positive Culture Results on the Short-term Outcomes of Liver Transplants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. djjoo@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Research Institute for Transplantation, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1450974
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2011.25.4.257
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Infection is a major cause of morbidity and mortality following liver transplants. We evaluated the risk factors of mortality within 1 month of liver transplantation caused by post-transplant infections.
METHODS
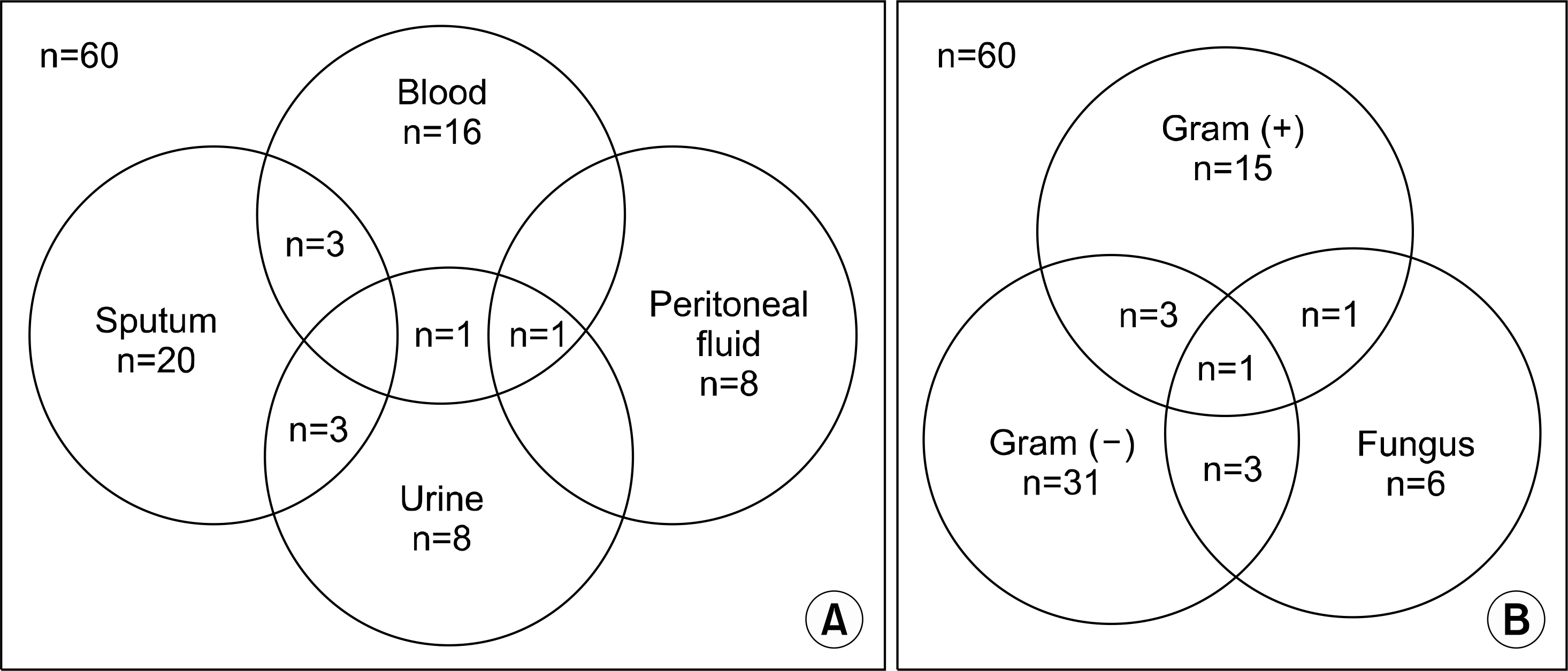
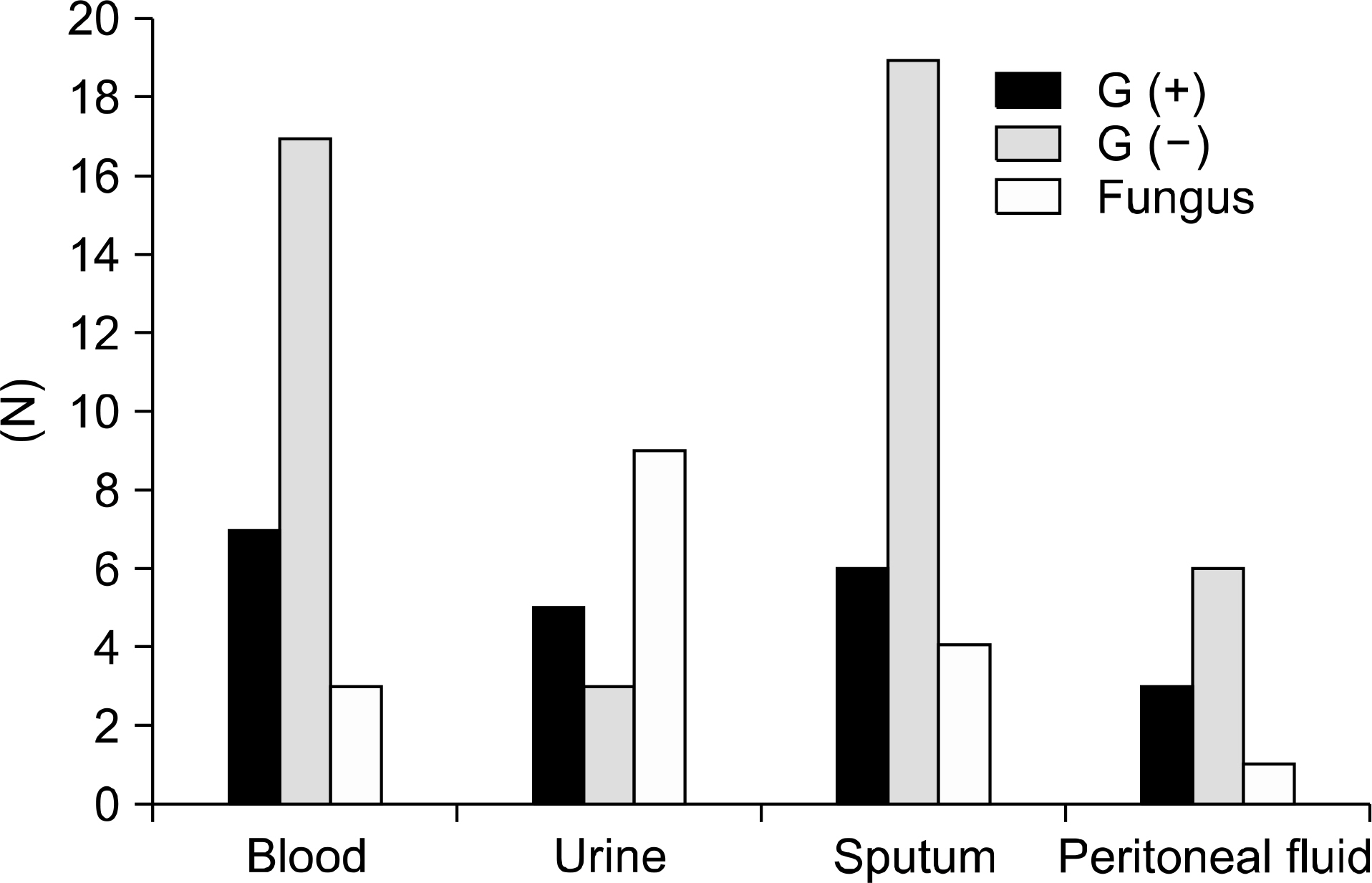
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 199 patients who underwent liver transplants from September 2005 to August 2010. We divided the enrolled patients into 3 groups. The first group, the Culture(-) group, was defined as those who had no significant culture results. The second group, the Culture(+)/survival group, was defined as those who tested positive for culture but survived longer than 1 month after transplantation. The third group, the Culture(+)/mortality group, was defined as those who died within 1 month of the transplant with positive culture test results.
RESULTS
The culture(+)/mortality group consisted of more deceased donor liver transplants than other groups. Also, the Culture(+)/mortality group showed more evidence of pre-transplant infections, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, continuous post-transplant renal replacement therapy (CRRT), and a higher MELD score than other groups. The risk factors of early mortality combined with infection 1 month after liver transplantation are hospitalization in ICU before transplantation (HR=16.3, CI=2.6~102.3, P=0.003) and the positive results of culture within 7 days of the operation (HR=38.7, CI=4.1~368.8, P=0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Hospitalization in ICU before transplantation and an early positive culture result can be an early clinical indicator of a good prognosis after liver transplantation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Varo Perez E, Castroagudin JF. The future of liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42:613–6.2). Razonable RR, Findlay JY, O'Riordan A, Burroughs SG, Ghobrial RM, Agarwal B, et al. Critical care issues in patients after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2011; 17:511–27.
Article3). Kim SI, Kim YJ, Jun YH, Wie SH, Kim YR, Choi JY, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors for bacteremia in 144 consecutive living-donor liver transplant recipients. Yonsei Med J. 2009; 50:112–21.
Article4). Markin RS, Stratta RJ, Woods GL. Infection after liver transplantation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990; 14(Suppl 1):64–78.5). Fishman JA, Rubin RH. Infection in organ-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:1741–51.
Article6). Paya CV, Hermans PE. Bacterial infections after liver transplantation. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989; 8:499–504.
Article7). Kusne S, Dummer JS, Singh N, Iwatsuki S, Makowka L, Esquivel C, et al. Infections after liver transplantation. An analysis of 101 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1988; 67:132–43.8). Reid GE, Grim SA, Sankary H, Benedetti E, Oberholzer J, Clark NM. Early intra-abdominal infections associated with orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2009; 87:1706–11.
Article9). Dehghani SM, Derakhshan A, Taghavi SA, Gholami S, Jalaeian H, Malek-Hosseini SA. Prevalence and risk factors of renal dysfunction after liver transplant: a singlecenter experience. Exp Clin Transplant. 2008; 6:25–9.10). Nah YW, Lee SG, Lee YJ, Park KM, Hwang S, Choi DL, et al. Infection after adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2001; 15:93–105. (나양원, 이승규, 이영주, 박광민, 황신, 최동락 등. 성인대 성인간 생체 부분 간이식 후 감염. 대한이식학회지 2001;15: 93–105.).11). Bekeris LG, Jones BA, Walsh MK, Wagar EA. Urine culture contamination: a College of American Pathologists Q-Probes study of 127 laboratories. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008; 132:913–7.
Article12). Murray CK, Hospenthal DR. Acinetobacter infection in the ICU. Crit Care Clin. 2008; 24:237–48.
Article13). Corona A, Raimondi F. Prevention of nosocomial infection in the ICU setting. Minerva Anestesiol. 2004; 70:329–37.14). Hanaoka N, Araki M. Problem of infection in the ICU. Masui. 2010; 59:46–55.15). Valles J, Ferrer R. Bloodstream infection in the ICU. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2009; 23:557–69.16). Sun HY, Cacciarelli TV, Singh N. Identifying a targeted population at high risk for infections after liver transplantation in the MELD era. Clin Transplant. 2011; 25.
Article17). Benckert C, Quante M, Thelen A, Bartels M, Laudi S, Berg T, et al. Impact of the MELD allocation after its implementation in liver transplantation. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:941–8.
Article18). Selzner M, Kashfi A, Cattral MS, Selzner N, McGilvray ID, Greig PD, et al. Live donor liver transplantation in high MELD score recipients. Ann Surg. 2010; 251:153–7.
Article19). Brandao A, Fuchs SC, Gleisner AL, Marroni C, Zanotelli ML, Cantisani G. Liver Transplantation Group. MELD and other predictors of survival after liver transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2009; 23:220–7.20). Schaub N, Frei R, Muller C. Addressing unmet clinical needs in the early diagnosis of sepsis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2011; 141:w13244.
Article21). Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:138–50.
Article22). Cohen J. Recent developments in the identification of novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of patients with sepsis and septic shock. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003; 35:690–6.
Article23). Sharma VK, Dellinger RP. Recent developments in the treatment of sepsis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2003; 12:139–52.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long Term Outcomes after Pediatric Liver Transplantation
- The impact of post-warming culture duration on clinical outcomes of vitrified-warmed single blastocyst transfer cycles
- Clinical Application of Short Term Chemotherapy in the Genitourinary Tuberculosis
- Pediatric liver transplantation in Korea: long-term outcomes and allocations
- Simple Auxiliary Liver Transplantation without Bile Duct Reconstruction in the Rat