Nutr Res Pract.
2021 Aug;15(4):456-467. 10.4162/nrp.2021.15.4.456.
Effects of intragastric balloon on obesity in obese Korean women for 6 months post removal
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Changwon National University, Changwon 51140, Korea
- 2Clinic B, Seoul 06035, Korea
- 3Interdisciplinary Program in Senior Human Ecology (BK21 Four Program), Changwon National University, Changwon 51140, Korea
- KMID: 2518755
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2021.15.4.456
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
The prevalence of morbid obesity in Korean women has consistently been increasing, while the overall prevalence rate of obesity in Korean women seems to be stable. In addition to bariatric surgery, intragastric balloons (IGBs), as a nonsurgical therapy, have been reported to be effective in weight loss. However, the beneficial effects of IGB in Korean women with obesity have not been fully investigated. The aim of this study was to evaluate the changes in fat mass in Korean women with obesity who had undergone IGB treatment for 6 mon.
SUBJECTS/METHODS
Seventy-four women with obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥ 25.0 kg/m 2 ) were recruited. Clinical data, including general information, comorbidities with obesity, anthropometric data, and changes in the body fat composition before and after IGB treatment, were obtained from the subjects.
RESULTS
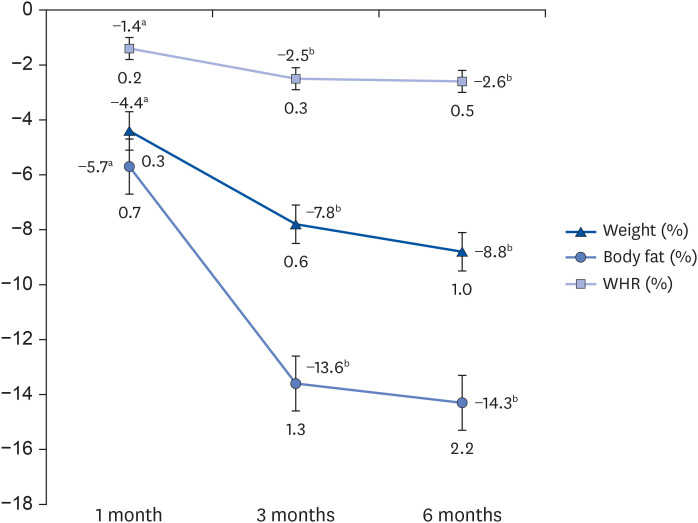
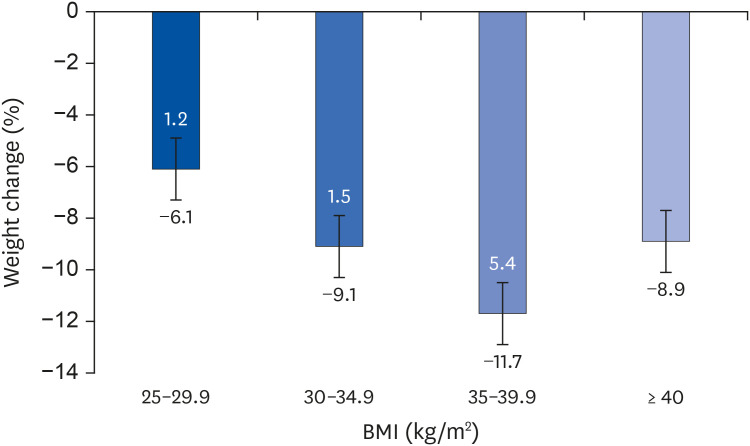
Most subjects had one or more comorbidities, such as osteoarthropathy and woman's disease, and had poor eating behaviors, including irregular mealtimes, eating quickly, and frequent overeating. Body composition measurements showed that weight, fat mass, and waist-hip circumference ratio decreased significantly at 6 mon after IGB treatment. In particular, women with morbid obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m 2 ) showed 33% excess weight loss. There was no significant difference in skeletal muscle mass and mineral contents after IGB treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggested that 6 mon of IGB treatment can be a beneficial treatment for obesity without muscle mass and bone mineral loss.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Fact sheets: obesity and overweight [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2020. cited 2020 April 1. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.2. Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2020; 360:1–8.3. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2018: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Sejong: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2020.4. Shin HY, Kang HT. Recent trends in the prevalence of underweight, overweight, and obesity in Korean adults: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 1998 to 2014. J Epidemiol. 2017; 27:413–419. PMID: 28420559.
Article5. Seo MH, Lee WY, Kim SS, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim KK, Kim BY, Kim YH, Kim WJ, Kim EM, et al. 2018 Korean society for the study of obesity guideline for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019; 28:40–45. PMID: 31089578.
Article6. Preiss K, Brennan L, Clarke D. A systematic review of variables associated with the relationship between obesity and depression. Obes Rev. 2013; 14:906–918. PMID: 23809142.
Article7. Baranowski T, Cullen KW, Nicklas T, Thompson D, Baranowski J. Are current health behavioral change models helpful in guiding prevention of weight gain efforts? Obes Res. 2003; 11(Suppl):23S–43S. PMID: 14569036.
Article8. Felson DT, Zhang Y, Anthony JM, Naimark A, Anderson JJ. Weight loss reduces the risk for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in women. The Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med. 1992; 116:535–539. PMID: 1543306.9. Molyneaux E, Poston L, Ashurst-Williams S, Howard LM. Obesity and mental disorders during pregnancy and postpartum: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014; 123:857–867. PMID: 24785615.10. Neuhouser ML, Aragaki AK, Prentice RL, Manson JE, Chlebowski R, Carty CL, Ochs-Balcom HM, Thomson CA, Caan BJ, Tinker LF, et al. Overweight, obesity, and postmenopausal invasive breast cancer risk: a secondary analysis of the women's health initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA Oncol. 2015; 1:611–621. PMID: 26182172.11. Alhusen JL, Ayres L, DePriest K. Effects of maternal mental health on engagement in favorable health practices during pregnancy. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2016; 61:210–216. PMID: 26849176.
Article12. Ruban A, Stoenchev K, Ashrafian H, Teare J. Current treatments for obesity. Clin Med (Lond). 2019; 19:205–212. PMID: 31092512.
Article13. Caudwell P, Hopkins M, King NA, Stubbs RJ, Blundell JE. Exercise alone is not enough: weight loss also needs a healthy (Mediterranean) diet? Public Health Nutr. 2009; 12:1663–1666. PMID: 19689837.
Article14. Look AHEAD Research Group. Eight-year weight losses with an intensive lifestyle intervention: the look AHEAD study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014; 22:5–13. PMID: 24307184.15. Sacks FM, Bray GA, Carey VJ, Smith SR, Ryan DH, Anton SD, McManus K, Champagne CM, Bishop LM, Laranjo N, et al. Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:859–873. PMID: 19246357.
Article16. Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Leccesi L, Nanni G, Pomp A, Castagneto M, Ghirlanda G, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:1577–1585. PMID: 22449317.
Article17. Daniel S, Soleymani T, Garvey WT. A complications-based clinical staging of obesity to guide treatment modality and intensity. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013; 20:377–388. PMID: 23974764.
Article18. Nguyen NT, Vu S, Kim E, Bodunova N, Phelan MJ. Trends in utilization of bariatric surgery, 2009–2012. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:2723–2727. PMID: 26659240.
Article19. Sullivan S, Edmundowicz SA, Thompson CC. Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies: new and emerging technologies. Gastroenterology. 2017; 152:1791–1801. PMID: 28192103.
Article20. Gleysteen JJ. A history of intragastric balloons. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016; 12:430–435. PMID: 26775045.
Article21. Tate CM, Geliebter A. Intragastric balloon treatment for obesity: review of recent studies. Adv Ther. 2017; 34:1859–1875. PMID: 28707286.
Article22. Choi SJ, Choi HS. Various intragastric balloons under clinical investigation. Clin Endosc. 2018; 51:407–415. PMID: 30257544.
Article23. Cecil RL, Goldman L, Schafer AI. Goldman's Cecil Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Saunders;2012.24. O'Rourke RW. Inflammation in obesity-related diseases. Surgery. 2009; 145:255–259. PMID: 19231576.25. Gómez R, Conde J, Scotece M, Gómez-Reino JJ, Lago F, Gualillo O. What's new in our understanding of the role of adipokines in rheumatic diseases? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011; 7:528–536. PMID: 21808287.
Article26. Garnero P, Rousseau JC, Delmas PD. Molecular basis and clinical use of biochemical markers of bone, cartilage, and synovium in joint diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:953–968. PMID: 10817547.
Article27. Reyes C, Leyland KM, Peat G, Cooper C, Arden NK, Prieto-Alhambra D. Association between overweight and obesity and risk of clinically diagnosed knee, hip, and hand osteoarthritis: a population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68:1869–1875. PMID: 27059260.
Article28. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Obesity fact sheet for Koreans [Internet]. Seoul: Korean Society for the Study of Obesity;2017. cited 2020 August 25. Available from: http://www.kosso.or.kr/popup/obesity_fact_sheet.html.29. Crea N, Pata G, Della Casa D, Minelli L, Maifredi G, Di Betta E, Mittempergher F. Improvement of metabolic syndrome following intragastric balloon: 1 year follow-up analysis. Obes Surg. 2009; 19:1084–1088. PMID: 19506981.
Article30. Suchartlikitwong S, Laoveeravat P, Mingbunjerdsuk T, Vutthikraivit W, Ismail A, Islam S, Islam E. Usefulness of the ReShape intragastric balloon for obesity. Proc Bayl Univ Med Cent. 2019; 32:192–195. PMID: 31191125.
Article31. Mui WL, Ng EKW, Tsung BYS, Lam CH, Yung MY. Impact on obesity-related illnesses and quality of life following intragastric balloon. Obes Surg. 2010; 20:1128–1132. PMID: 19015930.
Article32. Hassan NE, Wahba SA, El-Masry SA, Elhamid ER, Boseila SA, Ahmed NH, Ibrahim TS. Eating habits and lifestyles among a sample of obese working Egyptian women. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2015; 3:12–17. PMID: 27275190.
Article33. Lee HA, Lee WK, Kong KA, Chang N, Ha EH, Hong YS, Park H. The effect of eating behavior on being overweight or obese during preadolescence. J Prev Med Public Health. 2011; 44:226–233. PMID: 22020188.
Article34. Kang EY, Yim JE. Differences in dietary intakes, body compositions, and biochemical indices between metabolically healthy and metabolically abnormal obese Korean women. Nutr Res Pract. 2019; 13:488–497. PMID: 31814924.
Article35. Kim SH, Chun HJ, Choi HS, Kim ES, Keum B, Jeen YT. Current status of intragastric balloon for obesity treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:5495–5504. PMID: 27350727.
Article36. Buzga M, Kupka T, Siroky M, Narwan H, Machytka E, Holeczy P, Švagera Z. Short-term outcomes of the new intragastric balloon End-Ball® for treatment of obesity. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2016; 11:229–235. PMID: 28194241.37. Keren D, Rainis T. Intragastric balloons for overweight populations 1-year post removal. Obes Surg. 2018; 28:2368–2373. PMID: 29497962.38. Herve J, Wahlen CH, Schaeken A, Dallemagne B, Dewandre JM, Markiewicz S, Monami B, Weerts J, Jehaes C. What becomes of patients one year after the intragastric balloon has been removed? Obes Surg. 2005; 15:864–870. PMID: 15978160.
Article39. Angrisani L, Lorenzo M, Borrelli V, Giuffré M, Fonderico C, Capece G. Is bariatric surgery necessary after intragastric balloon treatment? Obes Surg. 2006; 16:1135–1137. PMID: 16989695.
Article40. Stein EM, Silverberg SJ. Bone loss after bariatric surgery: causes, consequences, and management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:165–174. PMID: 24622720.
Article41. Cava E, Yeat NC, Mittendorfer B. Preserving healthy muscle during weight loss. Adv Nutr. 2017; 8:511–519. PMID: 28507015.
Article42. Papageorgiou M, Kerschan-Schindl K, Sathyapalan T, Pietschmann P. Is weight loss harmful for skeletal health in obese older adults? Gerontology. 2020; 66:2–14. PMID: 31256166.
Article43. Fleischer J, Stein EM, Bessler M, Della Badia M, Restuccia N, Olivero-Rivera L, McMahon DJ, Silverberg SJ. The decline in hip bone density after gastric bypass surgery is associated with extent of weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:3735–3740. PMID: 18647809.
Article44. Carrasco F, Ruz M, Rojas P, Csendes A, Rebolledo A, Codoceo J, Inostroza J, Basfi-Fer K, Papapietro K, Rojas J, et al. Changes in bone mineral density, body composition and adiponectin levels in morbidly obese patients after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2009; 19:41–46. PMID: 18683014.
Article45. Sjöström L, Narbro K, Sjöström CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H, Lystig T, Sullivan M, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, et al. Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:741–752. PMID: 17715408.
Article46. Heber D, Greenway FL, Kaplan LM, Livingston E, Salvador J, Still C. Endocrine Society. Endocrine and nutritional management of the post-bariatric surgery patient: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:4823–4843. PMID: 21051578.
Article47. Maekawa S, Niizawa M, Harada M. A comparison of the weight loss effect between a low-carbohydrate diet and a calorie-restricted diet in combination with intragastric balloon therapy. Intern Med. 2020; 59:1133–1139. PMID: 32378654.
Article48. Papalazarou A, Yannakoulia M, Kavouras SA, Komesidou V, Dimitriadis G, Papakonstantinou A, Sidossis LS. Lifestyle intervention favorably affects weight loss and maintenance following obesity surgery. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010; 18:1348–1353. PMID: 19834466.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Various Intragastric Balloons Under Clinical Investigation
- Gastric Ulceration and Bleeding with Hemodynamic Instability Caused by an Intragastric Balloon for Weight Loss
- Short-term Outcomes of Intragastric Balloon Placement for Obesity Treatment
- Comparison of the Effects of an Exercise Program in Non-obese and Obese Women
- Gastric Perforation Caused by an Intragastric Balloon: Endoscopic Findings