Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Apr;51(2):777-787. 10.4143/crt.2018.387.
A Phase II Trial of Osimertinib in the Second-Line Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with the EGFR T790M Mutation, Detected from Circulating Tumor DNA: LiquidLung-O-Cohort 2
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. kyc0923@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2464423
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.387
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Administering the best treatment after failure of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy requires knowledge of resistance status. In this trial, treatment efficacy of osimertinib was assessed in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) harboring the T790M resistance mutation, detected from circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) with unknown tumor mutation status.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
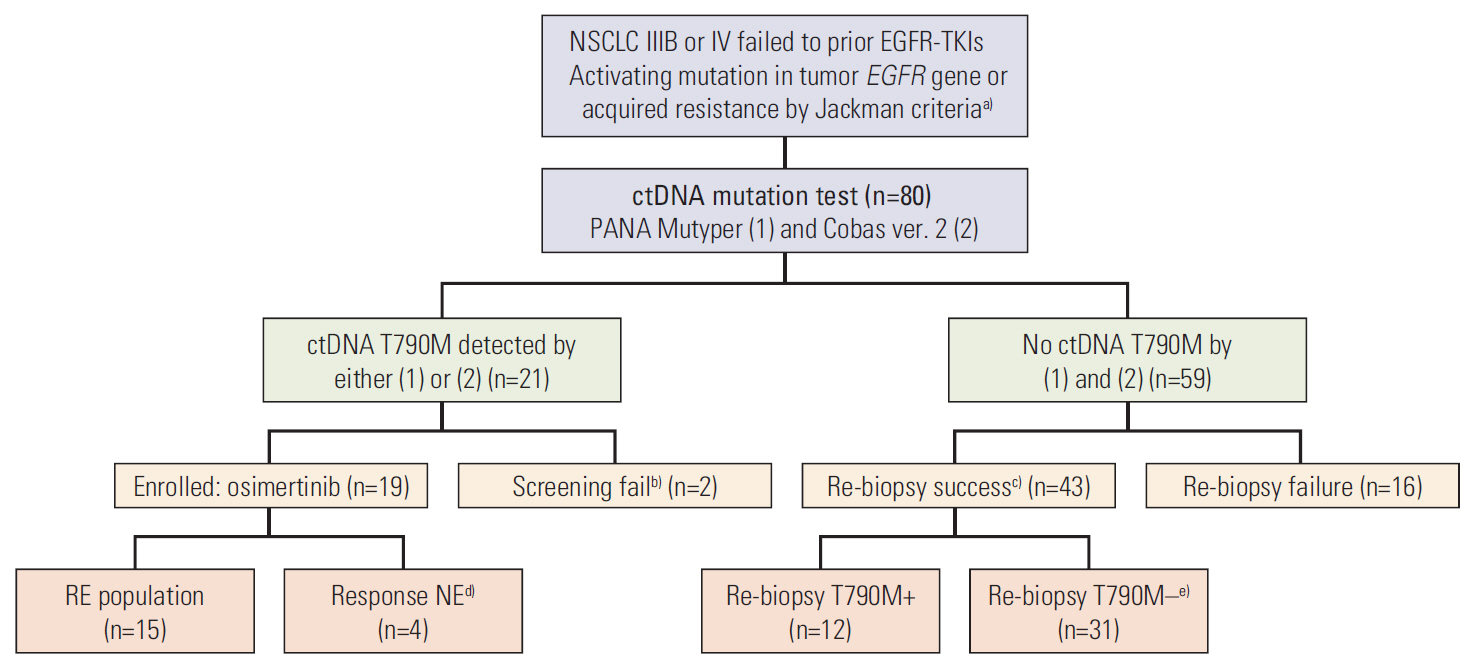
To extract ctDNA from plasma, 15 mL of peripheral blood was withdrawn and centrifuged immediately before storage. Cobas ver. 2 and PANA Mutyper were used for ctDNA genotyping. Patients with T790M, detected from ctDNA, were enrolled and they received a once-daily administration of osimertinib 80 mg. The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR), and secondary endpoints were ctDNA test sensitivity, progression-free survival (PFS), duration of response (DoR), and safety.
RESULTS
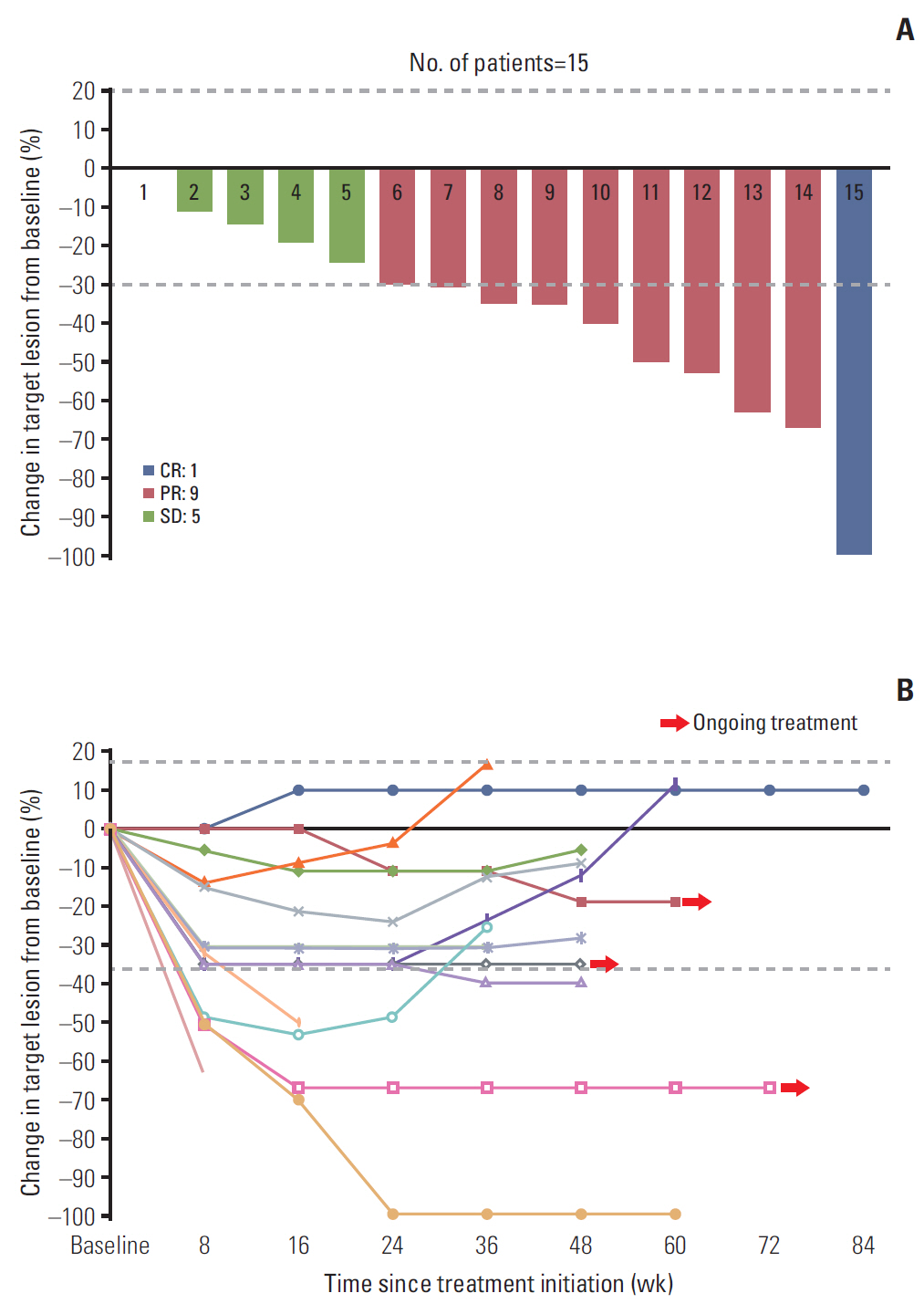
Eighty patients with acquired resistance to prior EGFR-TKI therapies were screened. ctDNA of 21 patients showed T790M positivity, and 19 patients were enrolled. In the response-evaluable population (n=15), ORR was 66.7% (10/15). Median PFS was 8.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 7.9 to 8.7) and median DoR was 6.8 months (95% CI, 5.3 to 8.3) in the intent-to-treat population (n=19). No subject experienced drug-related adverse event of grades ≥ 3 or required dose reduction. The sensitivity of the ctDNA tests was 56.8% using both methods and 45.9% with either method from the estimated T790M-positive cases.
CONCLUSION
Osimertinib has favorable efficacy in patients with NSCLC harboring T790M, detected from ctDNA with unknown tumor mutation status, in whom disease had progressed during prior EGFR-TKI therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Phase II Trial of Osimertinib as the First-Line Treatment of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Activating
EGFR Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA: LiquidLung-O-Cohort 1
Cheol-Kyu Park, Hyun-Ju Cho, Yoo-Duk Choi, In-Jae Oh, Young-Chul Kim
Cancer Res Treat. 2021;53(1):93-103. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.459.
Reference
-
References
1. Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS, Zakowski MF, Pao W, et al. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:2240–7.
Article2. Janne PA, Yang JC, Kim DW, Planchard D, Ohe Y, Ramalingam SS, et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:1689–99.
Article3. Yang JC, Ahn MJ, Kim DW, Ramalingam SS, Sequist LV, Su WC, et al. Osimertinib in pretreated T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: AURA study phase II extension component. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:1288–96.
Article4. Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim HR, Ramalingam SS, et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:629–40.
Article5. Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113–25.6. Ricciuti B, Baglivo S, Paglialunga L, De Giglio A, Bellezza G, Chiari R, et al. Osimertinib in patients with advanced epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer: rationale, evidence and place in therapy. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2017; 9:387–404.
Article7. Crowley E, Di Nicolantonio F, Loupakis F, Bardelli A. Liquid biopsy: monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013; 10:472–84.
Article8. Douillard JY, Ostoros G, Cobo M, Ciuleanu T, Cole R, McWalter G, et al. Gefitinib treatment in EGFR mutated caucasian NSCLC: circulating-free tumor DNA as a surrogate for determination of EGFR status. J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9:1345–53.
Article9. Qiu M, Wang J, Xu Y, Ding X, Li M, Jiang F, et al. Circulating tumor DNA is effective for the detection of EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2015; 24:206–12.
Article10. Thress KS, Brant R, Carr TH, Dearden S, Jenkins S, Brown H, et al. EGFR mutation detection in ctDNA from NSCLC patient plasma: a cross-platform comparison of leading technologies to support the clinical development of AZD9291. Lung Cancer. 2015; 90:509–15.11. Oxnard GR, Thress KS, Alden RS, Lawrance R, Paweletz CP, Cantarini M, et al. Association between plasma genotyping and outcomes of treatment with osimertinib (AZD9291) in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:3375–82.
Article12. Jenkins S, Yang JC, Ramalingam SS, Yu K, Patel S, Weston S, et al. Plasma ctDNA Analysis for detection of the EGFR T790M mutation in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017; 12:1061–70.13. Jackman D, Pao W, Riely GJ, Engelman JA, Kris MG, Janne PA, et al. Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:357–60.
Article14. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009; 45:228–47.
Article15. Kawamura T, Kenmotsu H, Taira T, Omori S, Nakashima K, Wakuda K, et al. Rebiopsy for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer after epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure. Cancer Sci. 2016; 107:1001–5.
Article16. Sundaresan TK, Sequist LV, Heymach JV, Riely GJ, Janne PA, Koch WH, et al. Detection of T790M, the acquired resistance EGFR mutation, by tumor biopsy versus noninvasive blood-based analyses. Clin Cancer Res. 2016; 22:1103–10.
Article17. Kawamura T, Kenmotsu H, Omori S, Nakashima K, Wakuda K, Ono A, et al. Clinical factors predicting detection of T790M mutation in rebiopsy for EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018; 19:e247–52.
Article18. Ballard P, Yates JW, Yang Z, Kim DW, Yang JC, Cantarini M, et al. Preclinical comparison of osimertinib with other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC brain metastases models, and early evidence of clinical brain metastases activity. Clin Cancer Res. 2016; 22:5130–40.
Article19. Goss G, Tsai CM, Shepherd FA, Ahn MJ, Bazhenova L, Crino L, et al. CNS response to osimertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced NSCLC: pooled data from two phase II trials. Ann Oncol. 2018; 29:687–93.
Article20. Mok T, Ahn MJ, Han JY, Kang JH, Katakami N, Kim H, et al. CNS response to osimertinib in patients (pts) with T790M-positive advanced NSCLC: data from a randomized phase III trial (AURA3). J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35(15 Suppl):9005.
Article21. Yang JC, Kim DW, Kim SW, Cho BC, Lee JS, Ye X, et al. Osimertinib activity in patients (pts) with leptomeningeal (LM) disease from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): updated results from BLOOM, a phase I study. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34(15 Suppl):9002.
Article22. Sacher AG, Paweletz C, Dahlberg SE, Alden RS, O'Connell A, Feeney N, et al. Prospective validation of rapid plasma genotyping for the detection of EGFR and KRAS mutations in advanced lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016; 2:1014–22.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Phase II Trial of Osimertinib as the First-Line Treatment of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Activating EGFR Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA: LiquidLung-O-Cohort 1
- Assessment of Anti-tumor Efficacy of Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients by Liquid Biopsy Using Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid, Plasma, or Pleural Effusion
- Real-World Analysis of the Efficacy of Rebiopsy and EGFR Mutation Test of Tissue and Plasma Samples in Drug-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Lazertinib: on the Way to Its Throne
- Rare Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in Korean Patients with EGFR-mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer