Anat Cell Biol.
2019 Jun;52(2):128-133. 10.5115/acb.2019.52.2.128.
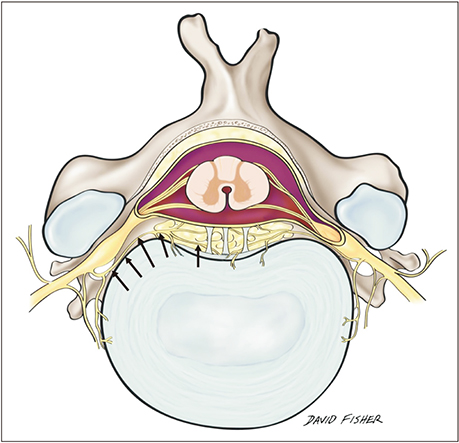
A comprehensive review of the sinuvertebral nerve with clinical applications
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomical Sciences, St. George's University, St. George's, Grenada, West Indies.
- 2Seattle Science Foundation, Seattle, WA, USA. joei@seattlesciencefoundation.org
- 3Swedish Neuroscience Institute, Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA, USA.
- KMID: 2451215
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2019.52.2.128
Abstract
- The anatomy and clinical significance of the sinuvertebral nerve is a topic of considerable interest among anatomists and clinicians, particularly its role in discogenic pain. It has required decades of research to appreciate its role, but not until recently could these studies be compiled to establish a more complete description of its clinical significance. The sinuvertebral nerve is a recurrent nerve that originates from the ventral ramus, re-entering the spinal canal via the intervertebral foramina to innervate multiple meningeal and non-meningeal structures. Its complex anatomy and relationship to discogenic pain have warranted great interest among clinical anatomists owing to its sympathetic contribution to the lumbar spine. Knowledge of the nerve has been used to design a variety of diagnostic and treatment procedures for chronic discogenic pain. This paper reviews the anatomy and clinical aspects of the sinuvertebral nerve.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Narrative Review of Pathophysiology and Endoscopic Management of Basivertebral and Sinuvertebral Neuropathy for Chronic Back Pain
Hyeun Sung Kim, Pang Hung Wu, Il-Tae Jang
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2023;66(4):344-355. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2022.0140.
Reference
-
1. Bogduk N. The innervation of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983; 8:286–293.
Article2. Edgar MA. The nerve supply of the lumbar intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89:1135–1139.
Article3. Bogduk N, Tynan W, Wilson AS. The nerve supply to the human lumbar intervertebral discs. J Anat. 1981; 132:39–56.4. Bogduk N, Windsor M, Inglis A. The innervation of the cervical intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988; 13:2–8.
Article5. Kojima Y, Maeda T, Arai R, Shichikawa K. Nerve supply to the posterior longitudinal ligament and the intervertebral disc of the rat vertebral column as studied by acetylcholinesterase histochemistry. II. Regional differences in the distribution of the nerve fibres and their origins. J Anat. 1990; 169:247–255.6. Kojima Y, Maeda T, Arai R, Shichikawa K. Nerve supply to the posterior longitudinal ligament and the intervertebral disc of the rat vertebral column as studied by acetylcholinesterase histochemistry. I. Distribution in the lumbar region. J Anat. 1990; 169:237–246.7. Groen GJ, Baljet B, Drukker J. The innervation of the spinal dura mater: anatomy and clinical implications. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1988; 92:39–46.
Article8. Van Buskirk C. Nerves in the vertebral canal: their relation to the sympathetic innervation of the upper extremities. Arch Surg. 1941; 43:427–432.9. Lazorthes G, Poulhes J, Espagno J. Etude sur les nerfs sinuvertebraux lombaires. Le nerf de roofe existe-t-il? C R Assoc Anat. 1947; 34:317–320.10. Cavanaugh JM, Ozaktay AC, Yamashita T, Avramov A, Getchell TV, King AI. Mechanisms of low back pain: a neurophysiologic and neuroanatomic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (335):166–180.
Article11. Lindblom K. Technique and results of diagnostic disc puncture and injection (discography) in the lumbar region. Acta Orthop Scand. 1951; 20:315–326.
Article12. Perey O. Contrast medium examination of the intervertebral discs of the lower lumbar spine. Acta Orthop Scand. 1951; 20:327–334.
Article13. Li YR, Hu X, Yang BZ. Studies on structural changes of collagen in silicosis. Biomed Environ Sci. 1994; 7:302–306.14. Shinohara H. Lumbar disc lesion, with special reference to the histological significance of nerve endings of the lumbar discs. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1970; 44:553–570.15. Olmarker K, Blomquist J, Strömberg J, Nannmark U, Thomsen P, Rydevik B. Inflammatogenic properties of nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:665–669.
Article16. Byrod G, Otani K, Brisby H, Rydevik B, Olmarker K. Methylprednisolone reduces the early vascular permeability increase in spinal nerve roots induced by epidural nucleus pulposus application. J Orthop Res. 2000; 18:983–987.17. Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 41st ed. New York: Elsevier;2016. p. 734–767.18. Moore KL, Agur AM, Dalley AF. Essestial clinical anatomy. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer;2015. p. 285.19. Groen GJ, Baljet B, Drukker J. Nerves and nerve plexuses of the human vertebral column. Am J Anat. 1990; 188:282–296.
Article20. Edgar MA, Ghadially JA. Innervation of the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (115):35–41.
Article21. Wiberg G. Back pain in relation to the nerve supply of the intervertebral disc. Acta Orthop Scand. 1949; 19:211–221.
Article22. Nakamura S, Takahashi K, Takahashi Y, Morinaga T, Shimada Y, Moriya H. Origin of nerves supplying the posterior portion of lumbar intervertebral discs in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:917–924.
Article23. Imai S, Hukuda S, Maeda T. Dually innervating nociceptive networks in the rat lumbar posterior longitudinal ligaments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:2086–2092.
Article24. Coppes MH, Marani E, Thomeer RT, Groen GJ. Innervation of “painful” lumbar discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:2342–2349.
Article25. Ahmed M, Bjurholm A, Kreicbergs A, Schultzberg M. Neuropeptide Y, tyrosine hydroxylase and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the vertebral bodies, discs, dura mater, and spinal ligaments of the rat lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18:268–273.
Article26. Konttinen YT, Grönblad M, Antti-Poika I, Seitsalo S, Santavirta S, Hukkanen M, Polak JM. Neuroimmunohistochemical analysis of peridiscal nociceptive neural elements. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990; 15:383–386.
Article27. Morinaga T, Takahashi K, Yamagata M, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Takahashi Y, Nakamura S, Suseki K, Moriya H. Sensory innervation to the anterior portion of lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:1848–1851.
Article28. Sekiguchi Y, Konnai Y, Kikuchi S, Sugiura Y. An anatomic study of neuropeptide immunoreactivities in thelumbar dura mater after lumbar sympathectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:925–930.29. Suseki K, Takahashi Y, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Yamagata M, Moriya H. Sensory nerve fibres from lumbar intervertebral discs pass through rami communicantes: a possible pathway for discogenic low back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80:737–742.30. Mooney V, Robertson J. The facet syndrome. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (115):149–156.
Article31. Bogduk N. The anatomy and pathophysiology of neck pain. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2003; 14:455–472.
Article32. Harata S, Tohno S, Kawagishi T. Osteoarthritis of the alantoaxial joint. Int Orthop. 1981; 5:277–282.33. Zapletal J, Hekster RE, Straver JS, Wilmink JT. Atlanto-odontoid osteoarthritis: appearance and prevalence at computed tomography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:49–53.34. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Pampati V, Damron KS, Barnhill RC, Beyer C, Cash KA. Evaluation of the relative contributions of various structures in chronic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2001; 4:308–316.35. Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, Fortin J, Kine G, Bogduk N. The prevalence and clinical features of internal disc disruption in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:1878–1883.
Article36. Ashton IK, Walsh DA, Polak JM, Eisenstein SM. Substance P in intervertebral discs: binding sites on vascular endothelium of the human annulus fibrosus. Acta Orthop Scand. 1994; 65:635–639.
Article37. Palmgren T, Gronblad M, Virri J, Kääpä E, Karaharju E. An immunohistochemical study of nerve structures in the anulus fibrosus of human normal lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24:2075–2079.
Article38. McCarthy PW, Carruthers B, Martin D, Petts P. Immunohistochemical demonstration of sensory nerve fibers and endings in lumbar intervertebral discs of the rat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991; 16:653–655.
Article39. Peng B, Wu W, Hou S, Li P, Zhang C, Yang Y. The pathogenesis of discogenic low back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:62–67.
Article40. Takebayashi T, Cavanaugh JM, Cuneyt Ozaktay A, Kallakuri S, Chen C. Effect of nucleus pulposus on the neural activity of dorsal root ganglion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:940–945.
Article41. Ohtori S, Miyagi M, Inoue G. Sensory nerve ingrowth, cytokines, and instability of discogenic low back pain: a review. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018; 2:11–17.
Article42. Fagan A, Moore R, Vernon Roberts B, Blumbergs P, Fraser R. ISSLS prize winner: the innervation of the intervertebral disc: a quantitative analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:2570–2576.
Article43. Purmessur D, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA. Expression and regulation of neurotrophins in thenondegenerate and degenerate human intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008; 10:R99.44. Kokubo Y, Uchida K, Kobayashi S, Yayama T, Sato R, Nakajima H, Takamura T, Mwaka E, Orwotho N, Bangirana A, Baba H. Herniated and spondylotic intervertebral discs of the human cervical spine: histological and immunohistological findings in 500 en bloc surgical samples. Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008; 9:285–295.45. Bennett GJ. Are the complex regional pain syndromes due to neurogenic inflammation? Neurology. 2001; 57:2161–2162.
Article46. Peng B, Wu W, Li Z, Guo J, Wang X. Chemical radiculitis. Pain. 2007; 127:11–16.
Article47. Sjaastad O, Saunte C, Hovdahl H, Breivik H, Grønbaek E. “Cervicogenic” headache: an hypothesis. Cephalalgia. 1983; 3:249–256.
Article48. Slipman CW, Lipetz JS, Jackson HB, Plastaras CT, Vresilovic EJ. Outcomes of therapeutic selective nerve root blocks for whiplash induced cervical radicular pain. Pain Physician. 2001; 4:167–174.49. Choi SH, Adsul N, Kim HS, Jang JS, Jang IT, Oh SH. Magnetic resonance imaging undetectable epiduroscopic hotspot in chronic diskogenic back pain: does sinuvertebral neuropathy actually exist? World Neurosurg. 2018; 110:354–358.50. Schliessbach J, Siegenthaler A, Heini P, Bogduk N, Curatolo M. Blockade of the sinuvertebral nerve for the diagnosis of lumbar diskogenic pain: an exploratory study. Anesth Analg. 2010; 111:204–206.51. Derby R, Eek B, Chen Y, O'Neill C, Ryan D. Intradiscal electrothermal annuloplasty (IDET): a novel approach for treating chronic discogenic back pain. Neuromodulation. 2000; 3:82–88.
Article52. Kim HS, Paudel B, Chung SK, Jang JS, Oh SH, Jang IT. Transforaminal epiduroscopic laser ablation of sinuvertebral nerve in patients with chronic diskogenic back pain: technical note and preliminary result. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2017; 78:529–534.
Article53. Chou LH, Lenrow DA. Cervicogenic headache. Pain Physician. 2002; 5:215–225.
Article54. Blume HG. Cervicogenic headaches: radiofrequency neurotomy and the cervical disc and fusion. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2000; 18:2 Suppl 19. S53–S58.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Narrative Review of Pathophysiology and Endoscopic Management of Basivertebral and Sinuvertebral Neuropathy for Chronic Back Pain
- The laryngopharyngeal nerve: a comprehensive review
- Ansa cervicalis: a comprehensive review of its anatomy, variations, pathology, and surgical applications
- Effectiveness of Mobile Health Application Use to Improve Health Behavior Changes: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Triangles of the neck: a review with clinical/surgical applications