J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2023 Jul;66(4):344-355. 10.3340/jkns.2022.0140.
Narrative Review of Pathophysiology and Endoscopic Management of Basivertebral and Sinuvertebral Neuropathy for Chronic Back Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, Nanoori Gangnam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Juronghealth Campus, National University Health Systems, Singapore, Singapore
- KMID: 2543527
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2022.0140
Abstract
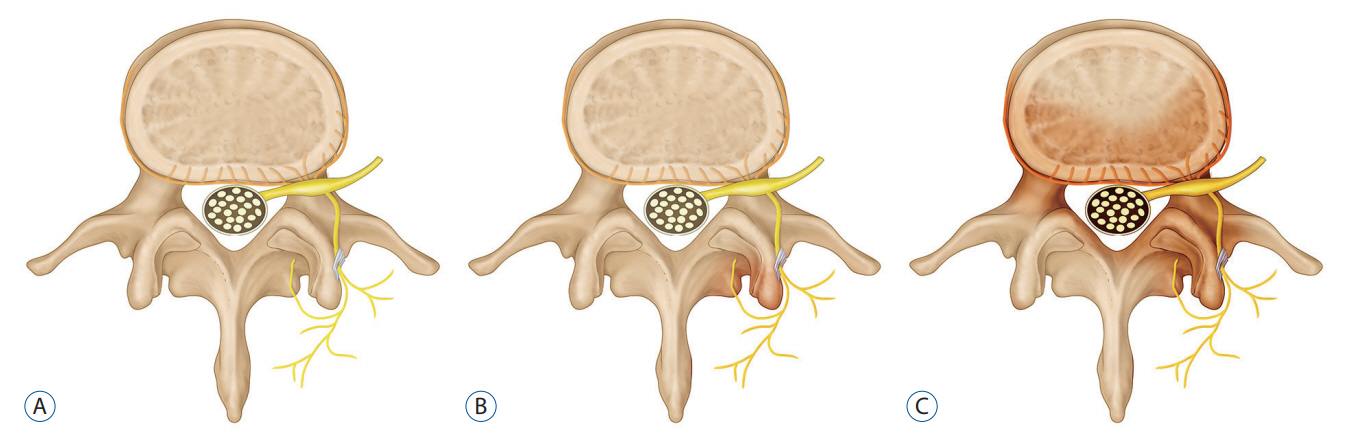
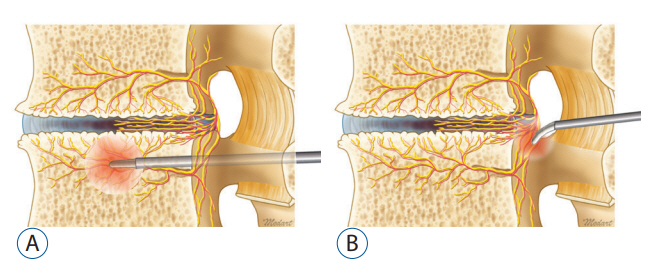
- Chronic lower back pain is a leading cause of disability in musculoskeletal system. Degenerative disc disease is one of the main contributing factor of chronic back pain in the aging population in the world. It is postulated that sinuvertebral nerve and basivertebral nerve main mediator of the nociceptive response in degenerative disc disease as a result of neurotization of sinuvertebral and basivertebral nerve. A review in literature is done on the pathoanatomy, pathophysiology and pain generation pathway in degenerative disc disease and chronic back pain and management strategy is discussed in this review to aid understanding of sinuvertebral and basivertebral neuropathy treatment strategies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ahmed M, Bjurholm A, Kreicbergs A, Schultzberg M. Neuropeptide Y, tyrosine hydroxylase and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the vertebral bodies, discs, dura mater, and spinal ligaments of the rat lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 18:268–273. 1993.
Article2. Akkiraju H, Nohe A. Role of chondrocytes in cartilage formation, progression of osteoarthritis and cartilage regeneration. J Dev Biol. 3:177–192. 2015.
Article3. Albert HB, Hauge E, Manniche C. Centralization in patients with sciatica: are pain responses to repeated movement and positioning associated with outcome or types of disc lesions? Eur Spine J. 21:630–636. 2012.
Article4. Alcaraz-Clariana S, García-Luque L, Garrido-Castro JL, Aranda-Valera IC, Ladehesa-Pineda L, Puche-Larrubia MÁ, et al. Paravertebral muscle mechanical properties in patients with axial spondyloarthritis or low back pain: a case-control study. Diagnostics (Basel). 11:1898. 2021.
Article5. Altinkaya N, Yildirim T, Demir S, Alkan O, Sarica FB. Factors associated with the thickness of the ligamentum flavum: is ligamentum flavum thickening due to hypertrophy or buckling? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 36:E1093–E1097. 2011.6. Anderson JT, Haas AR, Percy R, Woods ST, Ahn UM, Ahn NU. Chronic opioid therapy after lumbar fusion surgery for degenerative disc disease in a workers’ compensation setting. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 40:1775–1784. 2015.
Article7. Appleby D, Andersson G, Totta M. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of intradiscal electrothermal therapy (IDET). Pain Med. 7:308–316. 2006.
Article8. Ashton IK, Walsh DA, Polak JM, Eisenstein SM. Substance P in intervertebral discs. binding sites on vascular endothelium of the human annulus fibrosus. Acta Orthop Scand. 65:635–639. 1994.
Article9. Bailey JF, Liebenberg E, Degmetich S, Lotz JC. Innervation patterns of PGP 9.5-positive nerve fibers within the human lumbar vertebra. J Anat. 218:263–270. 2011.
Article10. Balkovec C, Adams MA, Dolan P, McGill SM. Annulus fibrosus can strip hyaline cartilage end plate from subchondral bone: a study of the intervertebral disk in tension. Global Spine J. 5:360–365. 2015.
Article11. Bjorland S, Moen A, Schistad E, Gjerstad J, Røe C. Genes associated with persistent lumbar radicular pain; a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 17:500. 2016.
Article12. Bogduk N, Tynan W, Wilson AS. The nerve supply to the human lumbar intervertebral discs. J Anat. 132:39–56. 1981.13. Borenstein DG, Wiesel SW, Boden SD. Low Back and Neck Pain. Comprehensive Diagnosis and Management, ed 3. Philadelphia: Saunders;2004. p. 87–88.14. Breemer MC, Malessy MJA, Notenboom RGE. Origin, branching pattern, foraminal and intraspinal distribution of the human lumbar sinuvertebral nerves. Spine J. 22:472–482. 2022.
Article15. Brown MF, Hukkanen MV, McCarthy ID, Redfern DR, Batten JJ, Crock HV, et al. Sensory and sympathetic innervation of the vertebral endplate in patients with degenerative disc disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 79:147–153. 1997.
Article16. Byröd G, Otani K, Brisby H, Rydevik B, Olmarker K. Methylprednisolone reduces the early vascular permeability increase in spinal nerve roots induced by epidural nucleus pulposus application. J Orthop Res. 18:983–987. 2000.
Article17. Canbulat N, Oktenoglu T, Ataker Y, Sasani M, Ercelen O, Cerezci O, et al. A rehabilitation protocol for patients with lumbar degenerative disc disease treated with posterior transpedicular dynamic stabilization. Turk Neurosurg. 27:426–435. 2017.18. Choi SH, Adsul N, Kim HS, Jang JS, Jang IT, Oh SH. Magnetic resonance imaging undetectable epiduroscopic hotspot in chronic diskogenic back pain-does sinuvertebral neuropathy actually exist? World Neurosurg. 110:354–358. 2018.
Article19. Coppes MH, Marani E, Thomeer RT, Groen GJ. Innervation of “painful” lumbar discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:2342–2349. discussion 2349-2350. 1997.
Article20. Dombrowski ME, Olsen AS, Vaudreuil N, Couch BK, Dong Q, Tucci M, et al. Rabbit annulus fibrosus cells express neuropeptide Y, which is influenced by mechanical and inflammatory stress. Neurospine. 17:69–76. 2020.
Article21. Dorman TA, Ravin TH. Diagnosis and injection techniques in orthopedic medicine. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;1991.22. Dowdell J, Erwin M, Choma T, Vaccaro A, Iatridis J, Cho SK. Intervertebral disk degeneration and repair. Neurosurgery. 80:S46–S54. 2017.
Article23. Dudli S, Fields AJ, Samartzis D, Karppinen J, Lotz JC. Pathobiology of Modic changes. Eur Spine J. 25:3723–3734. 2016.
Article24. Dudli S, Sing DC, Hu SS, Berven SH, Burch S, Deviren V, et al. ISSLS prize in basic science 2017: intervertebral disc/bone marrow cross-talk with Modic changes. Eur Spine J. 26:1362–1373. 2017.
Article25. Edgar MA. The nerve supply of the lumbar intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 89:1135–1139. 2007.
Article26. El-Badawy MA, El Mikkawy DM. Sympathetic dysfunction in patients with chronic low back pain and failed back surgery syndrome. Clin J Pain. 32:226–231. 2016.
Article27. Fagan A, Moore R, Vernon Roberts B, Blumbergs P, Fraser R. ISSLS prize winner: the innervation of the intervertebral disc: a quantitative analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 28:2570–2576. 2003.
Article28. Fassina A, Rubinacci A, Tessari L. Muscular contracture as a component of low back pain: evaluation criteria and significance of relaxant therapy. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 6:501–507. 1986.29. Fischgrund JS, Rhyne A, Franke J, Sasso R, Kitchel S, Bae H, et al. Intraosseous basivertebral nerve ablation for the treatment of chronic low back pain: 2-year results from a prospective randomized double-blind sham-controlled multicenter study. Int J Spine Surg. 13:110–119. 2019.
Article30. Fras C, Kravetz P, Mody DR, Heggeness MH. Substance P-containing nerves within the human vertebral body. An immunohistochemical study of the basivertebral nerve. Spine J. 3:63–67. 2003.31. Fujii K, Yamazaki M, Kang JD, Risbud MV, Cho SK, Qureshi SA, et al. Discogenic back pain: literature review of definition, diagnosis, and treatment. JBMR Plus. 3:e10180. 2019.
Article32. Groen GJ, Baljet B, Drukker J. Nerves and nerve plexuses of the human vertebral column. Am J Anat. 188:282–296. 1990.
Article33. Haimoto S, Nishimura Y, Hara M, Nakajima Y, Yamamoto Y, Ginsberg HJ, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of microscopic lumbar foraminal decompression: a pilot analysis of possible risk factors for restenosis. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 58:49–58. 2018.
Article34. Harms J. Dorsale repositionsspondylodese bei lumbalen spondylolisthesis. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 11:79. 1999.
Article35. Holm S, Holm AK, Ekström L, Karladani A, Hansson T. Experimental disc degeneration due to endplate injury. J Spinal Disord Tech. 17:64–71. 2004.
Article36. Imai S, Hukuda S, Maeda T. Dually innervating nociceptive networks in the rat lumbar posterior longitudinal ligaments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:2086–2092. 1995.
Article37. Isu T, Kim K, Morimoto D, Iwamoto N. Superior and middle cluneal nerve entrapment as a cause of low back pain. Neurospine. 15:25–32. 2018.
Article38. Järvinen J, Karppinen J, Niinimäki J, Haapea M, Grönblad M, Luoma K, et al. Association between changes in lumbar Modic changes and low back symptoms over a two-year period. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 16:98. 2015.
Article39. Jensen TS, Bendix T, Sorensen JS, Manniche C, Korsholm L, Kjaer P. Characteristics and natural course of vertebral endplate signal (Modic) changes in the Danish general population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 10:81. 2009.
Article40. Kapetanakis S, Gkantsinikoudis N, Charitoudis G. The role of full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy in surgical treatment of recurrent lumbar disc herniation: a health-related quality of life approach. Neurospine. 16:96–104. 2019.
Article41. Khanduja S, Loomba V, Salama-Hannah J, Upadhyay A, Khanduja N, Chauhan G. Retrospective review of magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbosacral spine: are we overinvestigating? Neurospine. 15:383–387. 2018.
Article42. Kim HS, Adsul N, Kapoor A, Choi SH, Kim JH, Kim KJ, et al. A mobile outside-in technique of transforaminal lumbar endoscopy for lumbar disc herniations. J Vis Exp. 138:57999. 2018.
Article43. Kim HS, Adsul N, Yudoyono F, Paudel B, Kim KJ, Choi SH, et al. Transforaminal epiduroscopic basivertebral nerve laser ablation for chronic low back pain associated with Modic changes: a preliminary open-label study. Pain Res Manag. 2018:6857983. 2018.
Article44. Kim HS, Kashlan ON, Singh R, Adsul NM, Yong Z, Oh SW, et al. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of the sinuvertebral nerve in an Olympian with a left L5 pedicle/pars interarticularis fracture-associated left L5-S1 disk desiccation. World Neurosurg X. 3:100032. 2019.
Article45. Kim HS, Paudel B, Chung SK, Jang JS, Oh SH, Jang IT. Transforaminal epiduroscopic laser ablation of sinuvertebral nerve in patients with chronic diskogenic back pain: technical note and preliminary result. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 78:529–534. 2017.
Article46. Kim HS, Paudel B, Jang JS, Lee K, Oh SH, Jang IT. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for all types of lumbar disc herniations (LDH) including severely difficult and extremely difficult LDH cases. Pain Physician. 21:E401–E408. 2018.47. Kim HS, Paudel B, Jang JS, Oh SH, Lee S, Park JE, et al. Percutaneous full endoscopic bilateral lumbar decompression of spinal stenosis through uniportal-contralateral approach: techniques and preliminary results. World Neurosurg. 103:201–209. 2017.
Article48. Kim HS, Wu PH, Jang IT. Lumbar degenerative disease part 1: anatomy and pathophysiology of intervertebral discogenic pain and radiofrequency ablation of basivertebral and sinuvertebral nerve treatment for chronic discogenic back pain: a prospective case series and review of literature. Int J Mol Sci. 21:1483. 2020.
Article49. Kim HS, Wu PH, Jang IT. Lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression outside-in approach: a proctorship guideline with 12 steps of effectiveness and safety. Neurospine. 17(Suppl 1):S99–S109. 2020.
Article50. Kim JY, Kim HS, Wu PH, Jang IT. Alleviating paravertebral muscle spasm after radiofrequency ablation treatment of hypersensitive basivertebral and sinuvertebral nerves for chronic discogenic back pain. Pain Physician. 24:E883–E892. 2021.
Article51. Kirnaz S, Capadona C, Wong T, Goldberg JL, Medary B, Sommer F, et al. Fundamentals of intervertebral disc degeneration. World Neurosurg. 157:264–273. 2022.
Article52. Kojima Y, Maeda T, Arai R, Shichikawa K. Nerve supply to the posterior longitudinal ligament and the intervertebral disc of the rat vertebral column as studied by acetylcholinesterase histochemistry. II. Regional differences in the distribution of the nerve fibres and their origins. J Anat. 169:247–255. 1990.53. Krock E, Rosenzweig DH, Chabot-Doré AJ, Jarzem P, Weber MH, Ouellet JA, et al. Painful, degenerating intervertebral discs up-regulate neurite sprouting and CGRP through nociceptive factors. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1213–1225. 2014.
Article54. Krzok G. Transforaminal endoscopic surgery: outside-in technique. Neurospine. 17(Suppl 1):S44–S57. 2020.
Article55. Kumar N, Kumar A, Siddharth MS, Sambhav PS, Tan J. Annulo-nucleoplasty using Disc-FX in the management of lumbar disc pathology: early results. Int J Spine Surg. 8:18. 2014.
Article56. Lee U, Kim CH, Kuo CC, Choi Y, Park SB, Yang SH, et al. Does preservation of ligamentum flavum in percutaneous endoscopic lumbar interlaminar discectomy improve clinical outcomes? Neurospine. 16:113–119. 2019.
Article57. Li YR, Hu X, Yang BZ. Studies on structural changes of collagen in silicosis. Biomed Environ Sci. 7:302–306. 1994.58. Lim KT, Meceda EJA, Park CK. Inside-out approach of lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression: a detailed technical description, rationale and outcomes. Neurospine. 17(Suppl 1):S88–S98. 2020.
Article59. Lotz JC, Fields AJ, Liebenberg EC. The role of the vertebral end plate in low back pain. Global Spine J. 3:153–164. 2013.
Article60. Ma J, Stefanoska D, Grad S, Alini M, Peroglio M. Direct and intervertebral disc-mediated sensitization of dorsal root ganglion neurons by hypoxia and low pH. Neurospine. 17:42–59. 2020.
Article61. Mackenzie J. Some points bearing on the association of sensory disorders and visceral disease. Brain. 16:321–354. 1893.
Article62. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Pampati V, Damron KS, Barnhill RC, Beyer C, et al. Evaluation of the relative contributions of various structures in chronic low back pain. Pain Physician. 4:308–316. 2001.63. McCarthy PW, Carruthers B, Martin D, Petts P. Immunohistochemical demonstration of sensory nerve fibers and endings in lumbar intervertebral discs of the rat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 16:653–655. 1991.
Article64. Mirkovic SR, Schwartz DG, Glazier KD. Anatomic considerations in lumbar posterolateral percutaneous procedures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:1965–1971. 1995.
Article65. Modic MT, Herfkens RJ. Intervertebral disk: normal age-related changes in MR signal intensity. Radiology. 177:332–333. discussion 333-334. 1990.
Article66. Modic MT, Steinberg PM, Ross JS, Masaryk TJ, Carter JR. Degenerative disk disease: assessment of changes in vertebral body marrow with MR imaging. Radiology. 166:193–199. 1988.
Article67. Montenegro TS, Elia C, Hines K, Buser Z, Wilson J, Ghogawala Z, et al. Are lumbar fusion guidelines followed? A survey of North American spine surgeons. Neurospine. 18:389–396. 2021.
Article68. Murata K, Akeda K, Takegami N, Cheng K, Masuda K, Sudo A. Morphology of intervertebral disc ruptures evaluated by vacuum phenomenon using multi-detector computed tomography: association with lumbar disc degeneration and canal stenosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 19:164. 2018.
Article69. Nachemson A, Lewin T, Maroudas A, Freeman MA. In vitro diffusion of dye through the end-plates and the annulus fibrosus of human lumbar inter-vertebral discs. Acta Orthop Scand. 41:589–607. 1970.
Article70. Nakamura S, Takahashi K, Takahashi Y, Morinaga T, Shimada Y, Moriya H. Origin of nerves supplying the posterior portion of lumbar intervertebral discs in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 21:917–924. 1996.
Article71. Ohtori S, Miyagi M, Inoue G. Sensory nerve ingrowth, cytokines, and instability of discogenic low back pain: a review. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2:11–17. 2018.
Article72. Olmarker K, Blomquist J, Strömberg J, Nannmark U, Thomsen P, Rydevik B. Inflammatogenic properties of nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:665–669. 1995.
Article73. Otluoglu GD, Konya D, Toktas ZO. The influence of mechanic factors in disc degeneration disease as a determinant for surgical indication. Neurospine. 17:215–220. 2020.
Article74. Peng B, Hao J, Hou S, Wu W, Jiang D, Fu X, et al. Possible pathogenesis of painful intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31:560–566. 2006.
Article75. Peng B, Wu W, Hou S, Li P, Zhang C, Yang Y. The pathogenesis of discogenic low back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 87:62–67. 2005.
Article76. Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 26:1873–1878. 2001.
Article77. Pooni JS, Hukins DW, Harris PF, Hilton RC, Davies KE. Comparison of the structure of human intervertebral discs in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions of the spine. Surg Radiol Anat. 8:175–182. 1986.
Article78. Purmessur D, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA. Expression and regulation of neurotrophins in the nondegenerate and degenerate human intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:R99. 2008.
Article79. Quinn KP, Bauman JA, Crosby ND, Winkelstein BA. Anomalous fiber realignment during tensile loading of the rat facet capsular ligament identifies mechanically induced damage and physiological dysfunction. J Biomech. 43:1870–1875. 2010.
Article80. Quinones S, Konschake M, Aguilar LL, Simon C, Aragones P, Hernández LM, et al. Clinical anatomy of the lumbar sinuvertebral nerve with regard to discogenic low back pain and review of literature. Eur Spine J. 30:2999–3008. 2021.
Article81. Raj PP. Intervertebral disc: anatomy-physiology-pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract. 8:18–44. 2008.
Article82. Raoul S, Faure A, Robert R, Rogez JM, Hamel O, Cuillère P, et al. Role of the sinu-vertebral nerve in low back pain and anatomical basis of therapeutic implications. Surg Radiol Anat. 24:366–371. 2003.
Article83. Risbud MV, Shapiro IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:44–56. 2014.
Article84. Ruetten S, Komp M, Merk H, Godolias G. Surgical treatment for lumbar lateral recess stenosis with the full-endoscopic interlaminar approach versus conventional microsurgical technique: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. J Neurosurg Spine. 10:476–485. 2009.
Article85. Schliessbach J, Siegenthaler A, Heini P, Bogduk N, Curatolo M. Blockade of the sinuvertebral nerve for the diagnosis of lumbar diskogenic pain: an exploratory study. Anesth Analg. 111:204–206. 2010.
Article86. Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, Fortin J, Kine G, Bogduk N. The prevalence and clinical features of internal disc disruption in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:1878–1883. 1995.
Article87. Sekiguchi Y, Konnai Y, Kikuchi S, Sugiura Y. An anatomic study of neuropeptide immunoreactivities in the lumbar dura mater after lumbar sympathectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 21:925–930. 1996.
Article88. Shayota B, Wong TL, Fru D, David G, Iwanaga J, Loukas M, et al. A comprehensive review of the sinuvertebral nerve with clinical applications. Anat Cell Biol. 52:128–133. 2019.
Article89. Shen M, Razi A, Lurie JD, Hanscom B, Weinstein J. Retrolisthesis and lumbar disc herniation: a preoperative assessment of patient function. Spine J. 7:406–413. 2007.
Article90. Shinohara H. Lumbar disc lesion, with special reference to the histological significance of nerve endings of the lumbar discs. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 44:553–570. 1970.91. Shuang F, Hou SX, Zhu JL, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Zhang CL, et al. Clinical anatomy and measurement of the medial branch of the spinal dorsal ramus. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e2367. 2015.
Article92. Simon J, McAuliffe M, Shamim F, Vuong N, Tahaei A. Discogenic low back pain. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 25:305–317. 2014.
Article93. Steelman T, Lewandowski L, Helgeson M, Wilson K, Olsen C, Gwinn D. Population-based risk factors for the development of degenerative disk disease. Clin Spine Surg. 31:E409–E412. 2018.
Article94. Suseki K, Takahashi Y, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Yamagata M, Moriya H. Sensory nerve fibres from lumbar intervertebral discs pass through rami communicantes. a possible pathway for discogenic low back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 80:737–742. 1998.95. Tagliaferri SD, Miller CT, Owen PJ, Mitchell UH, Brisby H, Fitzgibbon B, et al. Domains of chronic low back pain and assessing treatment effectiveness: a clinical perspective. Pain Pract. 20:211–225. 2020.
Article96. Takahashi M, Iwamoto K, Kuzuyama M, Inami H, Matsumoto Y, Ueda S, et al. Incidence of spinal instability among patients with discogenic low back pain with different backgrounds. J Phys Ther Sci. 33:601–605. 2021.
Article97. Urrutia J, Besa P, Campos M, Cikutovic P, Cabezon M, Molina M, et al. The Pfirrmann classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration: an independent inter- and intra-observer agreement assessment. Eur Spine J. 25:2728–2733. 2016.98. Vo N, Couch B, Lee J, Sowa G, Kang J, Rebecca S. Actions of prostaglandins on human nucleus pulposus metabolism inferred by cyclooxygenase 2 inhibition of cytokine activated cells. Neurospine. 17:60–68. 2020.99. von Luschka H. Die Nerven des menschlichen Wirbelkanales. Tübingen: Laupp;1850.100. Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 380:2163–2196. 2012.101. Wang JC. Commentary on “Are lumbar fusion guidelines followed? A survey of North American spine surgeons”. Neurospine. 18:397–398. 2021.102. Wu PH, Kim HS, Jang IT. How I do it? Uniportal full endoscopic contralateral approach for lumbar foraminal stenosis with double crush syndrome. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 162:305–310. 2020.103. Wu PH, Kim HS, Jang IT. Intervertebral disc diseases PART 2: a review of the current diagnostic and treatment strategies for intervertebral disc disease. Int J Mol Sci. 21:2135. 2020.
Article104. Wu PH, Sebastian M, Kim HS, Heng GTY. How I do it? Uniportal full endoscopic pseudoarthrosis release of left L5/S1 Bertolotti’s syndrome under intraoperative computer tomographic guidance in an ambulatory setting. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 163:2789–2795. 2021.
Article105. Yeater TD, Clark DJ, Hoyos L, Valdes-Hernandez PA, Peraza JA, Allen KD, et al. Chronic pain is associated with reduced sympathetic nervous system reactivity during simple and complex walking tasks: potential cerebral mechanisms. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 5:24705470211030273. 2021.
Article106. Yeung A, Roberts A, Zhu L, Qi L, Zhang J, Lewandrowski KU. Treatment of soft tissue and bony spinal stenosis by a visualized endoscopic transforaminal technique under local anesthesia. Neurospine. 16:52–62. 2019.
Article107. Yeung AT, Yeung CA. Advances in endoscopic disc and spine surgery: foraminal approach. Surg Technol Int. 11:255–263. 2003.108. Yoo BR, Son S, Lee SG, Kim WK, Jung JM. Factors predicting the clinical outcome after trans-sacral epiduroscopic laser decompression for lumbar disc herniation. Neurospine. 18:336–343. 2021.
Article109. Zhang S, Bassett DS, Winkelstein BA. Stretch-induced network reconfiguration of collagen fibres in the human facet capsular ligament. J R Soc Interface. 13:20150883. 2016.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Low Back Pain: Review of Anatomy and Pathophysiology
- Analgesic therapy according to disease specific pathophysiology
- Current Concepts of Degenerative Disc Disease -A Significance of Endplate-
- Management of patients with neuropathic pain
- A comprehensive review of the sinuvertebral nerve with clinical applications