Yonsei Med J.
2018 Sep;59(7):807-815. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.807.
Generation, Characteristics and Clinical Trials of Ex Vivo Generated Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. cklee@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2428906
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.807
Abstract
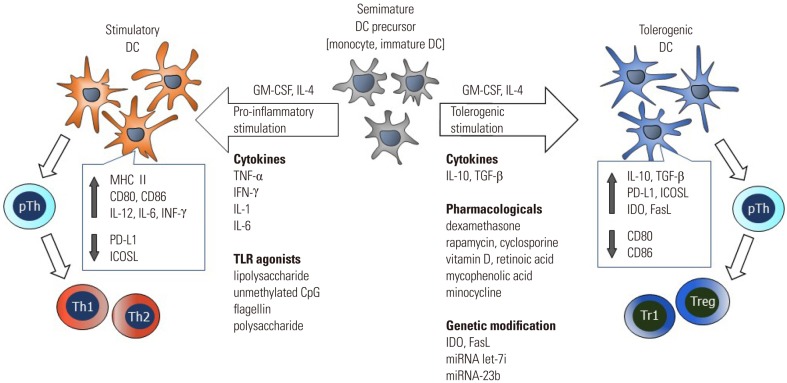
- Dendritic cells (DCs) play a key role not only in the initiation of primary immune responses, but also in the development and maintenance of immune tolerance. Numerous protocols have been developed to generate tolerogenic DCs (tolDCs) ex vivo, and the therapeutic efficacy of ex vivo-generated tolDCs has been demonstrated in autoimmune disease animal models. Based on successes in small animal models, several clinical trials have been completed or are on-going in patients with autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and Crohn's disease. Here we describe the methods used to generate tolDCs ex vivo, and the common features shared by tolDCs. In addition, we overview five completed clinical trials with reported outcomes and summarize the tolDC-based clinical trials that are currently registered with the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Although the number of tolDC-based clinical trials is much smaller than the hundreds of clinical trials using immunogenic DCs, tolDC-based treatment of autoimmune diseases is becoming a reality, and could serve as an innovative cellular therapy in the future.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Haniffa M, Collin M, Ginhoux F. Ontogeny and functional specialization of dendritic cells in human and mouse. Adv Immunol. 2013; 120:1–49. PMID: 24070379.
Article2. Appleman LJ, Boussiotis VA. T cell anergy and costimulation. Immunol Rev. 2003; 192:161–180. PMID: 12670403.
Article3. Maldonado RA, von Andrian UH. How tolerogenic dendritic cells induce regulatory T cells. Adv Immunol. 2010; 108:111–165. PMID: 21056730.
Article4. Raker VK, Domogalla MP, Steinbrink K. Tolerogenic dendritic cells for regulatory T cell induction in man. Front Immunol. 2015; 6:569. PMID: 26617604.
Article5. Lutz MB. Induction of CD4(+) regulatory and polarized effector/helper T cells by dendritic cells. Immune Netw. 2016; 16:13–25. PMID: 26937228.6. Horton C, Shanmugarajah K, Fairchild PJ. Harnessing the properties of dendritic cells in the pursuit of immunological tolerance. Biomed J. 2017; 40:80–93. PMID: 28521905.
Article7. Steinman RM, Hawiger D, Nussenzweig MC. Tolerogenic dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003; 21:685–711. PMID: 12615891.
Article8. Dhodapkar MV, Steinman RM, Krasovsky J, Munz C, Bhardwaj N. Antigen-specific inhibition of effector T cell function in humans after injection of immature dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 2001; 193:233–238. PMID: 11208863.
Article9. Dhodapkar MV, Steinman RM. Antigen-bearing immature dendritic cells induce peptide-specific CD8(+) regulatory T cells in vivo in humans. Blood. 2002; 100:174–177. PMID: 12070024.
Article10. Svajger U, Obermajer N, Jeras M. Novel findings in drug-induced dendritic cell tolerogenicity. Int Rev Immunol. 2010; 29:574–607. PMID: 21073328.11. Gordon JR, Ma Y, Churchman L, Gordon SA, Dawicki W. Regulatory dendritic cells for immunotherapy in immunologic diseases. Front Immunol. 2014; 5:7. PMID: 24550907.
Article12. Tuettenberg A, Huter E, Hubo M, Horn J, Knop J, Grimbacher B, et al. The role of ICOS in directing T cell responses: ICOS-dependent induction of T cell anergy by tolerogenic dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2009; 182:3349–3356. PMID: 19265111.
Article13. Unger WW, Laban S, Kleijwegt FS, van der, Roep BO. Induction of Treg by monocyte-derived DC modulated by vitamin D3 or dexamethasone: differential role for PD-L1. Eur J Immunol. 2009; 39:3147–3159. PMID: 19688742.14. Domogalla MP, Rostan PV, Raker VK, Steinbrink K. Tolerance through education: how tolerogenic dendritic cells shape immunity. Front Immunol. 2017; 8:1764. PMID: 29375543.
Article15. Yoo S, Ha SJ. Generation of tolerogenic dendritic cells and their therapeutic applications. Immune Netw. 2016; 16:52–60. PMID: 26937232.
Article16. Piemonti L, Monti P, Allavena P, Sironi M, Soldini L, Leone BE, et al. Glucocorticoids affect human dendritic cell differentiation and maturation. J Immunol. 1999; 162:6473–6481. PMID: 10352262.17. Lagaraine C, Hoarau C, Chabot V, Velge-Roussel F, Lebranchu Y. Mycophenolic acid-treated human dendritic cells have a mature migratory phenotype and inhibit allogeneic responses via direct and indirect pathways. Int Immunol. 2005; 17:351–363. PMID: 15710908.
Article18. Woltman AM, de Fijter JW, Kamerling SW, Paul LC, Daha MR, van Kooten C. The effect of calcineurin inhibitors and corticosteroids on the differentiation of human dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2000; 30:1807–1812. PMID: 10940869.
Article19. Li XL, Liu Y, Cao LL, Li H, Yue LT, Wang S, et al. Atorvastatin-modified dendritic cells in vitro ameliorate experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis by up-regulated Treg cells and shifted Th1/Th17 to Th2 cytokines. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013; 56:85–95. PMID: 23541702.
Article20. Bhatt S, Qin J, Bennett C, Qian S, Fung JJ, Hamilton TA, et al. All-trans retinoic acid induces arginase-1 and inducible nitric oxide synthase-producing dendritic cells with T cell inhibitory function. J Immunol. 2014; 192:5098–5108. PMID: 24790153.21. Kim N, Park CS, Im SA, Kim JW, Lee JH, Park YJ, et al. Minocycline promotes the generation of dendritic cells with regulatory properties. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:52818–52831. PMID: 27463004.
Article22. Piemonti L, Monti P, Sironi M, Fraticelli P, Leone BE, Dal Cin E, et al. Vitamin D3 affects differentiation, maturation, and function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2000; 164:4443–4451. PMID: 10779743.23. Griffin MD, Lutz W, Phan VA, Bachman LA, McKean DJ, Kumar R. Dendritic cell modulation by 1alpha,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its analogs: a vitamin D receptor-dependent pathway that promotes a persistent state of immaturity in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001; 98:6800–6805. PMID: 11371626.24. Penna G, Roncari A, Amuchastegui S, Daniel KC, Berti E, Colonna M, et al. Expression of the inhibitory receptor ILT3 on dendritic cells is dispensable for induction of CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Blood. 2005; 106:3490–3497. PMID: 16030186.25. Ferreira GB, Gysemans CA, Demengeot J, da Cunha JP, Vanherwegen AS, Overbergh L, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes tolerogenic dendritic cells with functional migratory properties in NOD mice. J Immunol. 2014; 192:4210–4220. PMID: 24663679.
Article26. Xia CQ, Peng R, Beato F, Clare-Salzler MJ. Dexamethasone induces IL-10-producing monocyte-derived dendritic cells with durable immaturity. Scand J Immunol. 2005; 62:45–54. PMID: 16091124.
Article27. Turnquist HR, Raimondi G, Zahorchak AF, Fischer RT, Wang Z, Thomson AW. Rapamycin-conditioned dendritic cells are poor stimulators of allogeneic CD4+ T cells, but enrich for antigen-specific Foxp3+ T regulatory cells and promote organ transplant tolerance. J Immunol. 2007; 178:7018–7031. PMID: 17513751.28. Hackstein H, Taner T, Zahorchak AF, Morelli AE, Logar AJ, Gessner A, et al. Rapamycin inhibits IL-4--induced dendritic cell maturation in vitro and dendritic cell mobilization and function in vivo. Blood. 2003; 101:4457–4463. PMID: 12531798.
Article29. Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Roncarolo MG. Rapamycin selectively expands CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Blood. 2005; 105:4743–4748. PMID: 15746082.30. Taner T, Hackstein H, Wang Z, Morelli AE, Thomson AW. Rapamycin-treated, alloantigen-pulsed host dendritic cells induce ag-specific T cell regulation and prolong graft survival. Am J Transplant. 2005; 5:228–236. PMID: 15643982.
Article31. Lee JH, Park CS, Jang S, Kim JW, Kim SH, Song S, et al. Tolerogenic dendritic cells are efficiently generated using minocycline and dexamethasone. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:15087. PMID: 29118423.
Article32. Harry RA, Anderson AE, Isaacs JD, Hilkens CM. Generation and characterisation of therapeutic tolerogenic dendritic cells for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69:2042–2050. PMID: 20551157.
Article33. Torres-Aguilar H, Aguilar-Ruiz SR, González-Pérez G, Munguía R, Bajaña S, Meraz-Ríos MA, et al. Tolerogenic dendritic cells generated with different immunosuppressive cytokines induce antigen-specific anergy and regulatory properties in memory CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 2010; 184:1765–1775. PMID: 20083662.34. Gregori S, Tomasoni D, Pacciani V, Scirpoli M, Battaglia M, Magnani CF, et al. Differentiation of type 1 T regulatory cells (Tr1) by tolerogenic DC-10 requires the IL-10-dependent ILT4/HLA-G pathway. Blood. 2010; 116:935–944. PMID: 20448110.
Article35. Nayyar A, Dawicki W, Huang H, Lu M, Zhang X, Gordon JR. Induction of prolonged asthma tolerance by IL-10-differentiated dendritic cells: differential impact on airway hyperresponsiveness and the Th2 immunoinflammatory response. J Immunol. 2012; 189:72–79. PMID: 22634620.
Article36. Menges M, Rössner S, Voigtländer C, Schindler H, Kukutsch NA, Bogdan C, et al. Repetitive injections of dendritic cells matured with tumor necrosis factor alpha induce antigen-specific protection of mice from autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 2002; 195:15–21. PMID: 11781361.37. Eljaafari A, Li YP, Miossec P. IFN-gamma, as secreted during an alloresponse, induces differentiation of monocytes into tolerogenic dendritic cells, resulting in FoxP3+ regulatory T cell promotion. J Immunol. 2009; 183:2932–2945. PMID: 19696431.38. Rutella S, Bonanno G, Procoli A, Mariotti A, de Ritis DG, Curti A, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor favors monocyte differentiation into regulatory interleukin (IL)-10++IL-12low/neg accessory cells with dendritic-cell features. Blood. 2006; 108:218–227. PMID: 16527888.39. Brandt K, Bulfone-Paus S, Foster DC, Rückert R. Interleukin-21 inhibits dendritic cell activation and maturation. Blood. 2003; 102:4090–4098. PMID: 12893770.
Article40. Boks MA, Kager-Groenland JR, Haasjes MS, Zwaginga JJ, van Ham SM, ten Brinke A. IL-10-generated tolerogenic dendritic cells are optimal for functional regulatory T cell induction--a comparative study of human clinical-applicable DC. Clin Immunol. 2012; 142:332–342. PMID: 22225835.41. Kryczanowsky F, Raker V, Graulich E, Domogalla MP, Steinbrink K. IL-10-modulated human dendritic cells for clinical use: identification of a stable and migratory subset with improved tolerogenic activity. J Immunol. 2016; 197:3607–3617. PMID: 27683749.
Article42. Svajger U, Obermajer N, Jeras M. IFN-γ-rich environment programs dendritic cells toward silencing of cytotoxic immune responses. J Leukoc Biol. 2014; 95:33–46. PMID: 23924658.
Article43. Kerkar SP, Chinnasamy D, Hadi N, Melenhorst J, Muranski P, Spyridonidis A, et al. Timing and intensity of exposure to interferon-γ critically determines the function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Immunology. 2014; 143:96–108. PMID: 24678989.44. Takayama T, Nishioka Y, Lu L, Lotze MT, Tahara H, Thomson AW. Retroviral delivery of viral interleukin-10 into myeloid dendritic cells markedly inhibits their allostimulatory activity and promotes the induction of T-cell hyporesponsiveness. Transplantation. 1998; 66:1567–1574. PMID: 9884241.45. Lee WC, Zhong C, Qian S, Wan Y, Gauldie J, Mi Z, et al. Phenotype, function, and in vivo migration and survival of allogeneic dendritic cell progenitors genetically engineered to express TGF-beta. Transplantation. 1998; 66:1810–1817. PMID: 9884280.46. Lu L, Gambotto A, Lee WC, Qian S, Bonham CA, Robbins PD, et al. Adenoviral delivery of CTLA4Ig into myeloid dendritic cells promotes their in vitro tolerogenicity and survival in allogeneic recipients. Gene Ther. 1999; 6:554–563. PMID: 10476215.
Article47. Bianco NR, Kim SH, Ruffner MA, Robbins PD. Therapeutic effect of exosomes from indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-positive dendritic cells in collagen-induced arthritis and delayed-type hypersensitivity disease models. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60:380–389. PMID: 19180475.
Article48. Kim SH, Kim S, Oligino TJ, Robbins PD. Effective treatment of established mouse collagen-induced arthritis by systemic administration of dendritic cells genetically modified to express FasL. Mol Ther. 2002; 6:584–590. PMID: 12409256.
Article49. Zhang M, Liu F, Jia H, Zhang Q, Yin L, Liu W, et al. Inhibition of microRNA let-7i depresses maturation and functional state of dendritic cells in response to lipopolysaccharide stimulation via targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 1. J Immunol. 2011; 187:1674–1683. PMID: 21742974.
Article50. Zheng J, Jiang HY, Li J, Tang HC, Zhang XM, Wang XR, et al. MicroRNA-23b promotes tolerogenic properties of dendritic cells in vitro through inhibiting Notch1/NF-κB signalling pathways. Allergy. 2012; 67:362–370. PMID: 22229716.
Article51. Latchman YE, Liang SC, Wu Y, Chernova T, Sobel RA, Klemm M, et al. PD-L1-deficient mice show that PD-L1 on T cells, antigen-presenting cells, and host tissues negatively regulates T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:10691–10696. PMID: 15249675.
Article52. Vlad G, Chang CC, Colovai AI, Vasilescu ER, Cortesini R, Suciu-Foca N. Membrane and soluble ILT3 are critical to the generation of T suppressor cells and induction of immunological tolerance. Int Rev Immunol. 2010; 29:119–132. PMID: 20132030.
Article53. Chang CC, Ciubotariu R, Manavalan JS, Yuan J, Colovai AI, Piazza F, et al. Tolerization of dendritic cells by T(S) cells: the crucial role of inhibitory receptors ILT3 and ILT4. Nat Immunol. 2002; 3:237–243. PMID: 11875462.
Article54. Sanjabi S, Zenewicz LA, Kamanaka M, Flavell RA. Anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory roles of TGF-beta, IL-10, and IL-22 in immunity and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009; 9:447–453. PMID: 19481975.55. Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Draghici E, Gregori S, Mocchetti C, Bonifacio E, et al. Rapamycin and interleukin-10 treatment induces T regulatory type 1 cells that mediate antigen-specific transplantation tolerance. Diabetes. 2006; 55:40–49. PMID: 16380475.
Article56. Levings MK, Gregori S, Tresoldi E, Cazzaniga S, Bonini C, Roncarolo MG. Differentiation of Tr1 cells by immature dendritic cells requires IL-10 but not CD25+CD4+ Tr cells. Blood. 2005; 105:1162–1169. PMID: 15479730.57. Frumento G, Rotondo R, Tonetti M, Damonte G, Benatti U, Ferrara GB. Tryptophan-derived catabolites are responsible for inhibition of T and natural killer cell proliferation induced by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J Exp Med. 2002; 196:459–468. PMID: 12186838.
Article58. Munn DH, Sharma MD, Lee JR, Jhaver KG, Johnson TS, Keskin DB, et al. Potential regulatory function of human dendritic cells expressing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Science. 2002; 297:1867–1870. PMID: 12228717.
Article59. Mellor AL, Baban B, Chandler P, Marshall B, Jhaver K, Hansen A, et al. Cutting edge: induced indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase expression in dendritic cell subsets suppresses T cell clonal expansion. J Immunol. 2003; 171:1652–1655. PMID: 12902462.
Article60. Huang H, Dawicki W, Zhang X, Town J, Gordon JR. Tolerogenic dendritic cells induce CD4+CD25hiFoxp3+ regulatory T cell differentiation from CD4+CD25−/loFoxp3− effector T cells. J Immunol. 2010; 185:5003–5010. PMID: 20870943.61. Qian L, Qian C, Chen Y, Bai Y, Bao Y, Lu L, et al. Regulatory dendritic cells program B cells to differentiate into CD19hiFcγIIbhi regulatory B cells through IFN-β and CD40L. Blood. 2012; 120:581–591. PMID: 22692512.62. Hsu SM, Mathew R, Taylor AW, Stein-Streilein J. Ex-vivo tolerogenic F4/80+ antigen-presenting cells (APC) induce efferent CD8+regulatory T cell-dependent suppression of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014; 176:37–48. PMID: 24266626.63. Barbi J, Pardoll D, Pan F. Treg functional stability and its responsiveness to the microenvironment. Immunol Rev. 2014; 259:115–139. PMID: 24712463.
Article64. Hori S. Lineage stability and phenotypic plasticity of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Immunol Rev. 2014; 259:159–172. PMID: 24712465.65. Jung MK, Kwak JE, Shin EC. IL-17A-producing Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and human diseases. Immune Netw. 2017; 17:276–286. PMID: 29093649.66. Akbari O, DeKruyff RH, Umetsu DT. Pulmonary dendritic cells producing IL-10 mediate tolerance induced by respiratory exposure to antigen. Nat Immunol. 2001; 2:725–731. PMID: 11477409.
Article67. Chen W, Jin W, Hardegen N, Lei KJ, Li L, Marinos N, et al. Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25− naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med. 2003; 198:1875–1886. PMID: 14676299.68. Mahnke K, Johnson TS, Ring S, Enk AH. Tolerogenic dendritic cells and regulatory T cells: a two-way relationship. J Dermatol Sci. 2007; 46:159–167. PMID: 17428639.
Article69. Kornete M, Piccirillo CA. Functional crosstalk between dendritic cells and Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells in the maintenance of immune tolerance. Front Immunol. 2012; 3:165. PMID: 22737152.
Article70. Popov I, Li M, Zheng X, San H, Zhang X, Ichim TE, et al. Preventing autoimmune arthritis using antigen-specific immature dendritic cells: a novel tolerogenic vaccine. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006; 8:R141. PMID: 16911769.71. van Duivenvoorde LM, Han WG, Bakker AM, Louis-Plence P, Charbonnier LM, Apparailly F, et al. Immunomodulatory dendritic cells inhibit Th1 responses and arthritis via different mechanisms. J Immunol. 2007; 179:1506–1515. PMID: 17641016.
Article72. Ahmed MS, Bae YS. Dendritic cell-based immunotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis: from bench to bedside. Immune Netw. 2016; 16:44–51. PMID: 26937231.
Article73. Phillips BE, Giannoukakis N, Trucco M. Dendritic cell mediated therapy for immunoregulation of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008; 5:873–879. PMID: 18552749.74. Tai N, Yasuda H, Xiang Y, Zhang L, Rodriguez-Pinto D, Yokono K, et al. IL-10-conditioned dendritic cells prevent autoimmune diabetes in NOD and humanized HLA-DQ8/RIP-B7.1 mice. Clin Immunol. 2011; 139:336–349. PMID: 21458378.
Article75. Chorny A, Gonzalez-Rey E, Fernandez-Martin A, Pozo D, Ganea D, Delgado M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide induces regulatory dendritic cells with therapeutic effects on autoimmune disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:13562–13567. PMID: 16150720.
Article76. Horibe EK, Sacks J, Unadkat J, Raimondi G, Wang Z, Ikeguchi R, et al. Rapamycin-conditioned, alloantigen-pulsed dendritic cells promote indefinite survival of vascularized skin allografts in association with T regulatory cell expansion. Transpl Immunol. 2008; 18:307–318. PMID: 18158116.
Article77. Raimondi G, Sumpter TL, Matta BM, Pillai M, Corbitt N, Vodovotz Y, et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition and alloantigen-specific regulatory T cells synergize to promote long-term graft survival in immunocompetent recipients. J Immunol. 2010; 184:624–636. PMID: 20007530.
Article78. Benham H, Nel HJ, Law SC, Mehdi AM, Street S, Ramnoruth N, et al. Citrullinated peptide dendritic cell immunotherapy in HLA risk genotype-positive rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci Transl Med. 2015; 7:290ra87.
Article79. Bell GM, Anderson AE, Diboll J, Reece R, Eltherington O, Harry RA, et al. Autologous tolerogenic dendritic cells for rheumatoid and inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76:227–234. PMID: 27117700.
Article80. Giannoukakis N, Phillips B, Finegold D, Harnaha J, Trucco M. Phase I (safety) study of autologous tolerogenic dendritic cells in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:2026–2032. PMID: 21680720.
Article81. Jauregui-Amezaga A, Cabezón R, Ramírez-Morros A, España C, Rimola J, Bru C, et al. Intraperitoneal administration of autologous tolerogenic dendritic cells for refractory Crohn's disease: a phase I study. J Crohns Colitis. 2015; 9:1071–1078. PMID: 26303633.
Article82. Nafarrate IZ, Florez G, Vila G, Cabezón R, España C, Benitez D, et al. Phase 1b clinical trial with antigen-specific tolerogenic dendritic in Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis optica: safety and immunological effects (P2.330). Neurology. 2017; 88(16 Supplement):P2.330.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Generation of Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells and Their Therapeutic Applications
- Dendritic Cell-based Immunotherapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis: from Bench to Bedside
- Vaccine strategies utilizing C-type lectin receptors on dendritic cells in vivo
- Lactoferrin Induces Tolerogenic Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells
- Strategies to Improve Dendritic Cell-based Immunotherapy against Cancer