Ann Surg Treat Res.
2018 Nov;95(5):278-285. 10.4174/astr.2018.95.5.278.
Kidney transplantation using expanded criteria deceased donors with terminal acute kidney injury: a single center experience in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Vascular and Transplant Surgery, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jjungyong@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Organ Transplant Center, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2422937
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2018.95.5.278
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated the clinical outcomes of deceased donor kidney transplantation (KT) using kidneys with terminal acute kidney injury (AKI).
METHODS
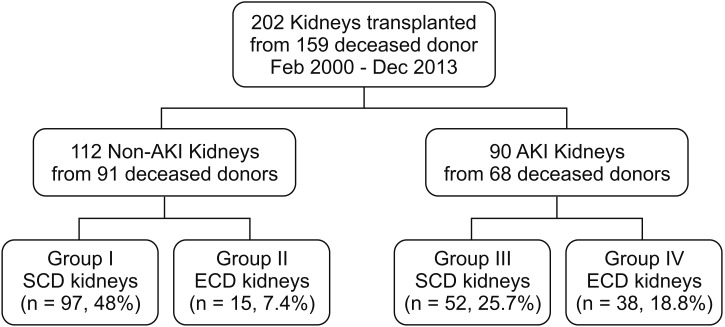
Between February 2000 and December 2013, we performed 202 deceased donor renal transplants from 159 brain dead donors. According to the expanded criteria donor (ECD) and AKI network criteria, we divided 202 recipients into 4 groups: Group I: Non-AKI & standard criteria donor (SCD) (n = 97); group II: Non-AKI & ECD (n = 15); group III: AKI & SCD (n = 52); and group IV: AKI & ECD (n = 38).
RESULTS
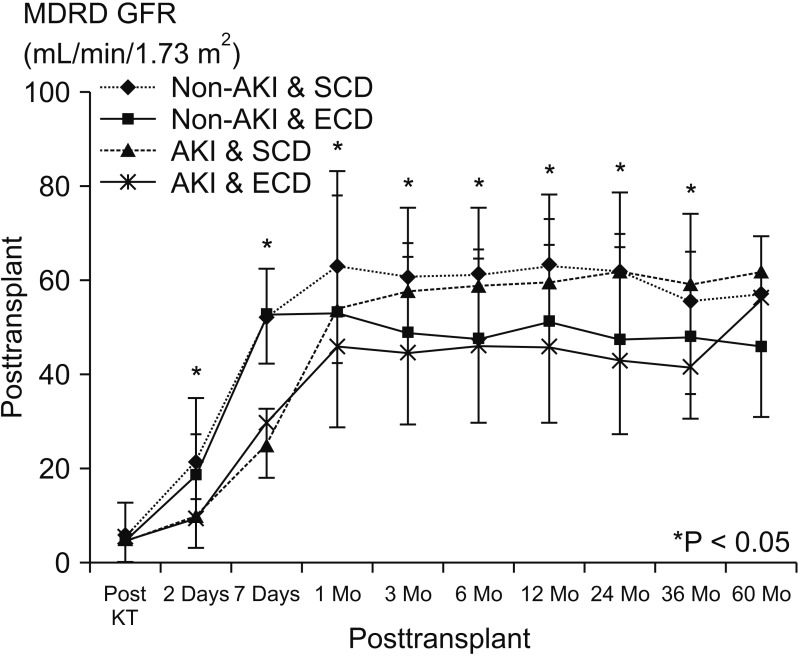
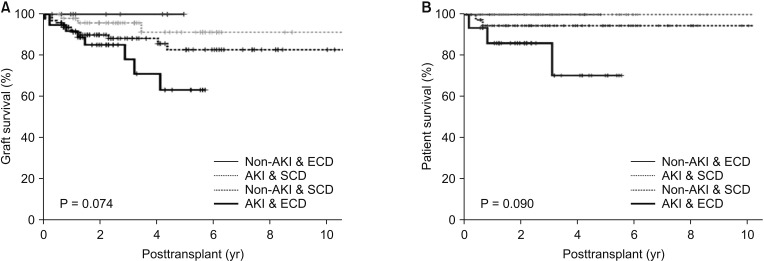
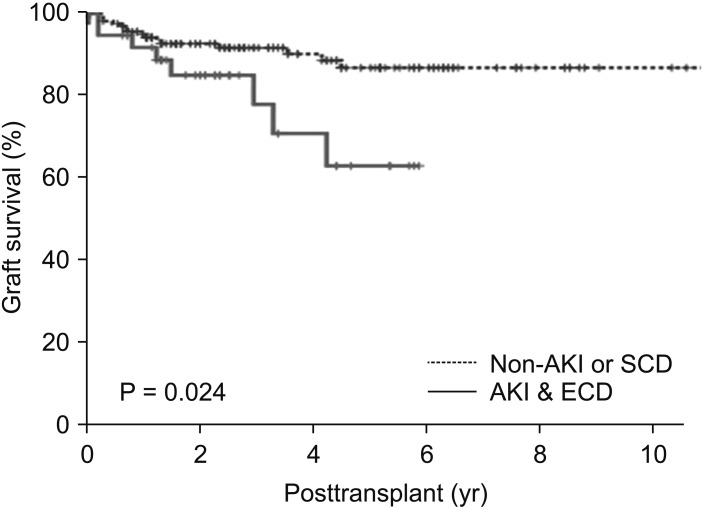
The incidence of delayed graft function (DFG) was significantly higher in patients with AKI than it was in the non-AKI group (P = 0.008). There were no significant differences among the 4 groups in graft survival (P = 0.074) or patient survival (P = 0.090). However, the long-term allograft survival rate was significantly lower in group IV than it was in other groups (P = 0.024).
CONCLUSION
Allografts from deceased donors with terminal AKI had a higher incidence of DGF than did those from donors without AKI. However, there is no significant difference in graft and patient survival rates among the groups. So, the utilization of renal grafts from ECDs with terminal AKI is a feasible approach to address the critical organ shortage.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lo CM. Deceased donation in Asia: challenges and opportunities. Liver Transpl. 2012; 18(Suppl 2):S5–S7. PMID: 22961949.
Article2. Jung CW, Park KT, Kim SY, Kim SJ, Kim MG, Jo SK, et al. Clinical outcomes in kidney transplantation patients from deceased donors with acute kidney injury. Transplant Proc. 2013; 45:2941–2945. PMID: 24157008.
Article3. Korean Network for Ogran Sharing. 2016 Annual data report [Internet]. Seoul: Korean Network for Ogran Sharing;cited 2017 Sep 8. Available from: http://konos.go.kr.4. Merion RM, Ashby VB, Wolfe RA, Distant DA, Hulbert-Shearon TE, Metzger RA, et al. Deceased-donor characteristics and the survival benefit of kidney transplantation. JAMA. 2005; 294:2726–2733. PMID: 16333008.
Article5. Summers DM, Johnson RJ, Allen J, Fuggle SV, Collett D, Watson CJ, et al. Analysis of factors that affect outcome after transplantation of kidneys donated after cardiac death in the UK: a cohort study. Lancet. 2010; 376:1303–1311. PMID: 20727576.
Article6. de Mendonca A, Vincent JL, Suter PM, Moreno R, Dearden NM, Antonelli M, et al. Acute renal failure in the ICU: risk factors and outcome evaluated by the SOFA score. Intensive Care Med. 2000; 26:915–921. PMID: 10990106.7. Bonventre JV, Yang L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest. 2011; 121:4210–4221. PMID: 22045571.
Article8. Anil Kumar MS, Khan SM, Jaglan S, Heifets M, Moritz MJ, Saeed MI, et al. Successful transplantation of kidneys from deceased donors with acute renal failure: Three-year results. Transplantation. 2006; 82:1640–1645. PMID: 17198251.
Article9. Ugarte R, Kraus E, Montgomery RA, Burdick JF, Ratner L, Haas M, et al. Excellent outcomes after transplantation of deceased donor kidneys with high terminal creatinine and mild pathologic lesions. Transplantation. 2005; 80:794–800. PMID: 16210967.
Article10. Kellum JA. Diagnostic criteria for acute kidney injury: present and future. Crit Care Clin. 2015; 31:621–632. PMID: 26410133.11. Lee MH, Jeong EG, Chang JY, Kim Y, Kim JI, Moon IS, et al. Clinical outcome of kidney transplantation from deceased donors with acute kidney injury by Acute Kidney Injury Network criteria. J Crit Care. 2014; 29:432–437. PMID: 24468572.
Article12. Metzger RA, Delmonico FL, Feng S, Port FK, Wynn JJ, Merion RM. Expanded criteria donors for kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2003; 3(Suppl 4):114–125. PMID: 12694055.
Article13. Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, et al. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2007; 11:R31. PMID: 17331245.
Article14. Hoste EA, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury: epidemiology and diagnostic criteria. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2006; 12:531–537. PMID: 17077682.
Article15. Uchino S, Bellomo R, Bagshaw SM, Goldsmith D. Transient azotaemia is associated with a high risk of death in hospitalized patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010; 25:1833–1839. PMID: 20054022.
Article16. Kolonko A, Chudek J, Pawlik A, Wilk J, Jałowiecki P, Wiecek A. Acute kidney injury before organ procurement is associated with worse long-term kidney graft outcome. Transplant Proc. 2011; 43:2871–2874. PMID: 21996176.
Article17. Siedlecki A, Irish W, Brennan DC. Delayed graft function in the kidney transplant. Am J Transplant. 2011; 11:2279–2296. PMID: 21929642.
Article18. Heilman RL, Devarapalli Y, Chakkera HA, Mekeel KL, Moss AA, Mulligan DC, et al. Impact of subclinical inflammation on the development of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2010; 10:563–570. PMID: 20121731.
Article19. Perico N, Cattaneo D, Sayegh MH, Remuzzi G. Delayed graft function in kidney transplantation. Lancet. 2004; 364:1814–1827. PMID: 15541456.
Article20. Chawla LS, Kimmel PL. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: an integrated clinical syndrome. Kidney Int. 2012; 82:516–524. PMID: 22673882.
Article21. Macedo E, Bouchard J, Mehta RL. Renal recovery following acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2008; 14:660–665. PMID: 19005306.
Article22. Boffa C, van de Leemkolk F, Curnow E, Homan van der Heide J, Gilbert J, Sharples E, et al. Transplantation of kidneys from donors with acute kidney injury: friend or foe? Am J Transplant. 2017; 17:411–419. PMID: 27428556.
Article23. Hall IE, Schroppel B, Doshi MD, Ficek J, Weng FL, Hasz RD, et al. Associations of deceased donor kidney injury with kidney discard and function after transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15:1623–1631. PMID: 25762442.
Article24. Heilman RL, Smith ML, Kurian SM, Huskey J, Batra RK, Chakkera HA, et al. Transplanting kidneys from deceased donors with severe acute kidney injury. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15:2143–2151. PMID: 25808278.
Article25. Farney AC, Rogers J, Orlando G, al-Geizawi S, Buckley M, Farooq U, et al. Evolving experience using kidneys from deceased donors with terminal acute kidney injury. J Am Coll Surg. 2013; 216:645–655. PMID: 23395159.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation and Utilization of Expanded Criteria Dornor
- Primary non-function in a deceased donor kidney transplant even with a Kidney Donor Risk Index less than 1.0: a case report
- Kidney Transplantation from Expanded Criteria Donor in Korea: It's Time to Have Our Own Criteria Based on Our Experiences
- A Preliminary Study to Revise the Marginal Donor Criteria of KONOS in Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation
- Thrombotic microangiopathy, rare cause of deceased donor acute kidney injury: is a donor biopsy necessary before donation?