Ann Lab Med.
2019 Jan;39(1):67-75. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.67.
Performance of Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen Versus Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Hepatitis B Virus DNA in Predicting HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative Chronic Hepatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Medicine, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center of Fudan University, Shanghai, China. doctorzzqsphc@163.com
- 2Research Unit, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center of Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
- KMID: 2420273
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.67
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
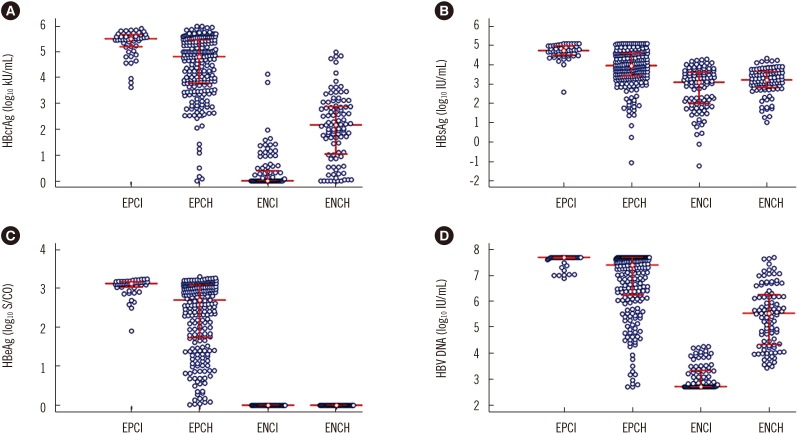
We examined changes in hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) during the four sequential phases of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection: hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive chronic infection (EPCI) and hepatitis (EPCH), followed by HBeAg-negative chronic infection (ENCI) and hepatitis (ENCH). We compared the performance of serum HBcrAg, hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), and HBV DNA in predicting EPCH and ENCH.
METHODS
We enrolled 492 consecutive patients: 49 with EPCI, 243 with EPCH, 101 with ENCI, and 99 with ENCH. HBcrAg was detected by chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassays. HBsAg and HBeAg were detected by chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassays. HBV DNA was detected by real-time PCR. Predictive performance of HBcrAg, HBsAg, and HBV DNA was evaluated using ROC curves.
RESULTS
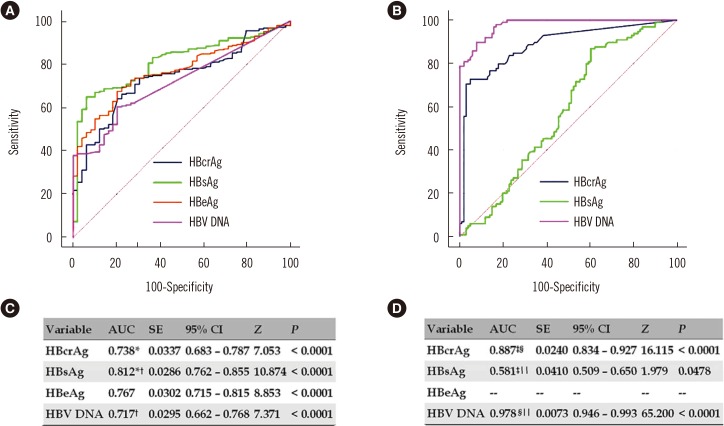
Areas under ROC curves (AUCs) of HBcrAg, HBsAg, and HBV DNA for predicting EPCH were 0.738, 0.812, and 0.717, respectively; optimal cutoffs were ≤1.43×105 kU/mL, ≤1.89×104 IU/mL, and ≤3.97×107 IU/mL, with sensitivities and specificities of 66.3% and 77.6%, 65.0% and 93.9%, and 60.5% and 79.6%, respectively. AUCs of HBcrAg, HBsAg, and HBV DNA for predicting ENCH were 0.887, 0.581, and 0.978, respectively; optimal cutoffs were >26.8 kU/mL, >2.29×102 IU/mL, and >8.75×103 IU/mL, with sensitivities and specificities of 72.7% and 95.1%, 86.9% and 39.6%, and 89.9% and 92.1%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
HBsAg and HBV DNA were the best predictors of EPCH and ENCH, respectively. HBcrAg is an important surrogate marker for predicting EPCH and ENCH.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Area Under Curve
Biomarkers
DNA
Hepatitis B e Antigens
Hepatitis B Surface Antigens*
Hepatitis B virus*
Hepatitis B*
Hepatitis B, Chronic
Hepatitis*
Hepatitis, Chronic*
Humans
Immunoassay
Immunoenzyme Techniques
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
ROC Curve
Biomarkers
DNA
Hepatitis B Surface Antigens
Hepatitis B e Antigens
Figure
Reference
-
1. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017; 67:370–398. PMID: 28427875.2. Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Murad MH, et al. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016; 63:261–283. PMID: 26566064.3. Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan HLY, Chen CJ, et al. Asian-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B: a 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 2016; 10:1–98.4. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2012; 57:167–185. PMID: 22436845.5. Wang L, Zou ZQ, Wang K, Yu JG, Liu XZ. Role of serum hepatitis B virus marker quantitation to differentiate natural history phases of HBV infection. Hepatol Int. 2016; 10:133–138. PMID: 26427997.6. Cornberg M, Wong VW, Locarnini S, Brunetto M, Janssen HLA, Chan HL. The role of quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen revisited. J Hepatol. 2017; 66:398–411. PMID: 27575311.7. Jia W, Song LW, Fang YQ, Wu XF, Liu DY, Xu C, et al. Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen levels in the natural history of chronic hepatitis B: a prospective observational study. Medicine. 2014; 93:e322. PMID: 25546679.8. Song LW, Liu PG, Liu CJ, Zhang TY, Cheng XD, Wu HL, et al. Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015; 21:197–203. PMID: 25658546.9. Yuan Q, Song LW, Cavallone D, Moriconi F, Cherubini B, Colombatto P, et al. Total hepatitis B core antigen antibody, a quantitative non-invasive marker of hepatitis B virus induced liver disease. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e130209.10. Rokuhara A, Tanaka E, Matsumoto A, Kimura T, Yamaura T, Orii K, et al. Clinical evaluation of a new enzyme immunoassay for hepatitis B virus core-related antigen; a marker distinct from viral DNA for monitoring lamivudine treatment. J Viral Hepat. 2003; 10:324–330. PMID: 12823601.11. Suzuki F, Miyakoshi H, Kobayashi M, Kumada H. Correlation between serum hepatitis B virus core-related antigen and intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Med Virol. 2009; 81:27–33. PMID: 19031469.12. Kimura T, Ohno N, Terada N, Rokuhara A, Matsumoto A, Yagi S, et al. Hepatitis B virus DNA-negative Dane particles lack core protein but contain a 22-kDa precore protein without C-terminal arginine-rich domain. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280:21713–21719. PMID: 15814524.13. Seto WK, Wong DK, Fung J, Huang FY, Liu KS, Lai CL, et al. Linearized hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core-related antigen in the natural history of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014; 20:1173–1180. PMID: 24975365.14. Maasoumy B, Wiegand SB, Jaroszewicz J, Bremer B, Lehmann P, Deterding K, et al. Hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection in a large European cohort predominantly infected with genotypes A and D. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015; 21:606.e1–606.e10. PMID: 25700889.15. Brunt EM. Grading and staging the histopathological lesions of chronic hepatitis: the Knodell histology activity index and beyond. Hepatology. 2000; 31:241–246. PMID: 10613753.16. Martinot-Peignoux M, Carvalho-Filho R, Lapalus M, Netto-Cardoso AC, Lada O, Batrla R, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen serum level is associated with fibrosis severity in treatment-naïve, e antigen-positive patients. J Hepatol. 2013; 58:1089–1095. PMID: 23369792.17. Lebossé F, Testoni B, Fresquet J, Facchetti F, Galmozzi E, Fournier M, et al. Intrahepatic innate immune response pathways are downregulated in untreated chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2017; 66:897–909. PMID: 28043874.18. Kondo Y, Ninomiya M, Kakazu E, Kimura O, Shimosegawa T. Hepatitis B surface antigen could contribute to the immunopathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2013; 2013:935295. PMID: 23401786.19. Zhang ZQ, Lu W, Wang YB, Weng QC, Zhang ZY, Yang ZQ, et al. Measurement of the hepatitis B core-related antigen is valuable for predicting the pathological status of liver tissues in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Virol Methods. 2016; 235:92–98. PMID: 27230224.20. Horst AK, Neumann K, Diehl L, Tiegs G. Modulation of liver tolerance by conventional and nonconventional antigen-presenting cells and regulatory immune cells. Cell Mol Immunol. 2016; 13:277–292. PMID: 27041638.21. Gou Y, Zhao Y, Rao C, Feng S, Wang T, Li D, et al. Predictive value of hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) during the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Lab. 2017; 63:1063–1070. PMID: 28792701.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of the mutation in the carboxyl-terminal processing site of the hepatitis B virus core antigen on the HBeAg secretion
- A Study on Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Tear of Hepatitis Patients
- A Study on Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Tear of Hepatitis Patients
- A study on the relationship between HBeAg and hepatitis B virus DNAamong healthy HBsAg carries
- Relationship between Intrahepatic Expression of Hepatitis Be Antigen and Histology in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Infection