Ann Lab Med.
2018 Mar;38(2):119-124. 10.3343/alm.2018.38.2.119.
Comparative Evaluation of the Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Detecting Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea. psoas95@gmail.com
- 2Korean Institute of Tuberculosis, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2403356
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.2.119
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Early detection of tuberculosis (TB) is challenging in resource-poor settings because of limited accessibility to molecular diagnostics. The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification kit (TB-LAMP) for TB diagnosis compared with conventional and molecular tests.
METHODS
A total of 290 consecutive sputum samples were collected from May till September, 2015. All samples were processed using the N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NALC) NaOH method and tested by smear microscopy, solid and liquid culture, real-time PCR, and TB-LAMP.
RESULTS
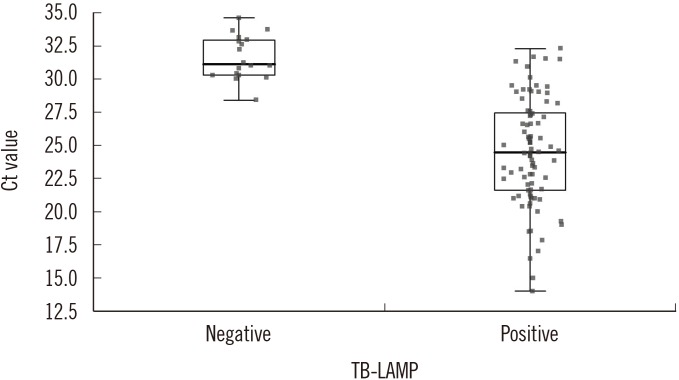
The sensitivity of TB-LAMP for smear-positive and smear-negative samples with culture positivity was 92.0% and 58.8%, respectively. TB-LAMP was positive in 14.9% of TB culture-negative samples; however, all those samples were also positive by real-time PCR. In addition, none of the samples positive for nontuberculous mycobacteria by culture were positive by TB-LAMP. The overall agreement between TB-LAMP and real-time PCR was good; however, the concordance rate was significantly lower for real-time PCR positive samples with Ct values of 30-35.
CONCLUSIONS
TB-LAMP could replace smear microscopy and increase TB diagnostic capacity when Xpert MTB/RIF is not feasible because of poor infrastructure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report. 2015.2. Pai M, Behr MA, Dowdy D, Dheda K, Divangahi M, Boehme CC, et al. Tuberculosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016; 2:16076. PMID: 27784885.3. Parsons LM, Somoskovi A, Gutierrez C, Lee E, Paramasivan CN, Abimiku A, et al. Laboratory diagnosis of tuberculosis in resource-poor countries: challenges and opportunities. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011; 24:314–350. PMID: 21482728.4. Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000; 28:E63. PMID: 10871386.5. Notomi T, Mori Y, Tomita N, Kanda H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): principle, features, and future prospects. J Microbiol. 2015; 53:1–5. PMID: 25557475.6. Bojang AL, Mendy FS, Tientcheu LD, Otu J, Antonio M, Kampmann B, et al. Comparison of TB-LAMP, GeneXpert MTB/RIF and culture for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in The Gambia. J Infect. 2016; 72:332–337. PMID: 26724771.7. Nagai K, Horita N, Yamamoto M, Tsukahara T, Nagakura H, Tashiro K, et al. Diagnostic test accuracy of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:39090. PMID: 27958360.8. Global Laboratory Initiative. Mycobacteriology Laboratory Manual. Geneva, Switzerland: Global Laboratory Initiative;2014.9. Ko Y, Lee HK, Lee YS, Kim MY, Shin JH, Shim EJ, et al. Accuracy of Xpert® MTB/RIF assay compared with AdvanSure™ TB/NTM real-time PCR using bronchoscopy specimens. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2016; 20:115–120. PMID: 26688537.10. Boehme CC, Nabeta P, Henostroza G, Raqib R, Rahim Z, Gerhardt M, et al. Operational feasibility of using loop-mediated isothermal amplification for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in microscopy centers of developing countries. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:1936–1940. PMID: 17392443.11. Kaku T, Minamoto F, D'Meza R, Morose W, Boncy J, Bijou J, et al. Assessment of Accuracy of LAMP-TB Method for Diagnosing Tuberculosis in Haiti. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2016; 69:488–492. PMID: 27000457.12. Ou X, Li Q, Xia H, Pang Y, Wang S, Zhao B, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the PURE-LAMP test for pulmonary tuberculosis at the county-level laboratory in China. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e94544. PMID: 24788724.13. Yoshida H, Onohara K, Tazawa T, Tsurinaga Y, Kurokawa M, Han Y, et al. Comparative study of the efficacy of the COBAS TaqMan and LAMP assay for the rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis. Kekkaku. 2013; 88:727–733. PMID: 24432481.14. George G, Mony P, Kenneth J. Comparison of the efficacies of loop-mediated isothermal amplification, fluorescence smear microscopy and culture for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e21007. PMID: 21695047.15. Nliwasa M, MacPherson P, Chisala P, Kamdolozi M, Khundi M, Kaswaswa K, et al. The sensitivity and specificity of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for tuberculosis diagnosis in adults with chronic cough in Malawi. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0155101. PMID: 27171380.16. Jung YJ, Kim JY, Song DJ, Koh WJ, Huh HJ, Ki CS, et al. Evaluation of three real-time PCR assays for differential identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and nontuberculous mycobacteria species in liquid culture media. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016; 85:186–191. PMID: 27105774.17. Yang B, Wang X, Li H, Li G, Cao Z, Cheng X. Comparison of loop-mediated isothermal amplification and real-time PCR for the diagnosis of tuberculous pleurisy. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2011; 53:525–531. PMID: 21883320.18. Kim MJ, Nam YS, Cho SY, Park TS, Lee HJ. Comparison of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay and real-time PCR for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2015; 45:327–332. PMID: 26116598.19. Cho WH, Won EJ, Choi HJ, Kee SJ, Shin JH, Ryang DW, et al. Comparison of AdvanSure TB/NTM PCR and COBAS TaqMan MTB PCR for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in routine clinical practice. Ann Lab Med. 2015; 35:356–361. PMID: 25932446.20. Mitarai S, Okumura M, Toyota E, Yoshiyama T, Aono A, Sejimo A, et al. Evaluation of a simple loop-mediated isothermal amplification test kit for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011; 15:1211–1217. PMID: 21943848.21. Kwak N, Choi SM, Lee J, Park YS, Lee CH, Lee SM, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and turnaround time of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay in routine clinical practice. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e77456. PMID: 24204834.22. Huh HJ, Jeong BH, Jeon K, Koh WJ, Ki CS, Lee NY. Performance evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay according to its clinical application. BMC Infect Dis. 2014; 14:589. PMID: 25395048.23. Ley S, Carter R, Millan K, Phuanukoonnon S, Pandey S, Coulter C, et al. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria: baseline data from three sites in Papua New Guinea, 2010-2012. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2015; 6:24–29. PMID: 26798558.24. Aliyu G, El-Kamary SS, Abimiku A, Brown C, Tracy K, Hungerford L, et al. Prevalence of non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections among tuberculosis suspects in Nigeria. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e63170. PMID: 23671669.25. Gray CM, Katamba A, Narang P, Giraldo J, Zamudio C, Joloba M, et al. Feasibility and operational performance of tuberculosis detection by loop-mediated isothermal amplification platform in decentralized settings: Results from a multicenter study. J Clin Microbiol. 2016; 54:1984–1991. PMID: 27194691.26. World Health Organization. Automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: xpert MTB/RIF assay for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB in adults and children: Policy update. Geneva: World Health Organization;2013.27. World Health Organization. The use of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (TB-LAMP) for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis: Policy guidance. Geneva: World Health Organization;2016.28. Creswell J, Codlin AJ, Andre E, Micek MA, Bedru A, Carter EJ, et al. Results from early programmatic implementation of Xpert MTB/RIF testing in nine countries. BMC Infect Dis. 2014; 14:2. PMID: 24383553.29. Geojith G, Dhanasekaran S, Chandran SP, Kenneth J. Efficacy of loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for the laboratory identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in a resource limited setting. J Microbiol Methods. 2011; 84:71–73. PMID: 21047534.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the detection of Salmonella spp. in pig feces
- A reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay to rapidly diagnose foot-and-mouth disease virus C
- Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Giardia lamblia Infection in Pet Dogs using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification
- Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella species targeting the hilA gene using a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay
- Rapid detection of Mycobacterium leprae for the diagnosis of leprosy: comparison between loop-mediated isothermal amplification and PCR.