J Vet Sci.
2012 Dec;13(4):429-432.
Development of monoclonal antibodies against the abnormal prion protein isoform (PrPres) associated with chronic wasting disease (CWD)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Infectious Diseases, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea. ischoi@konkuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Public Health, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea.
- 3Swine Science Division, National Institute of Animal Science, Rural Development Administration, Cheonan 331-801, Korea.
- 4Ilsong Institute of Life Science, Hallym University, Anyang 431-060, Korea.
Abstract
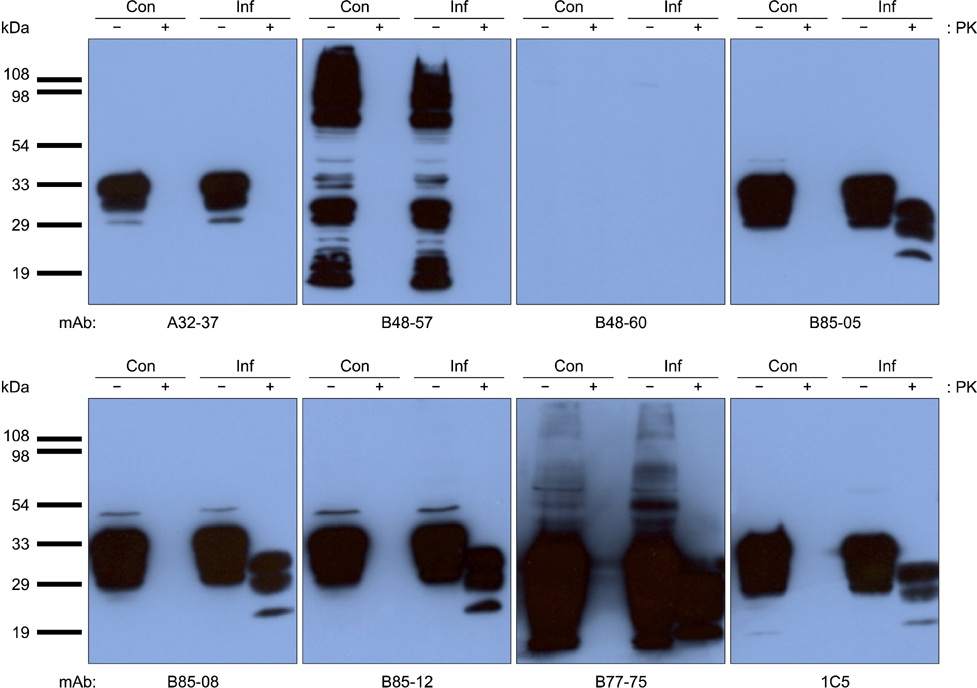
- Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) specific for the abnormal prion protein isoform (PrPres) are indispensable for diagnosing chronic wasting disease (CWD). In this study, eight mAbs were developed by immunizing PrP knockout mice with recombinant elk PrP and an immunogenic PrP peptide. The reactivity of the mAbs to recombinant PrP and the PrP peptide was measured, and their isotypes were subsequently determined. Among them, four mAbs (B85-05, B85-08, B85-12, and B77-75) were shown by Western blotting to recognize proteinase K-treated brain homogenate derived from an elk suffering from CWD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi JK, Park SJ, Jun YC, Oh JM, Jeong BH, Lee HP, Park SN, Carp RI, Kim YS. Generation of monoclonal antibody recognized by the GXXXG motif (glycine zipper) of prion protein. Hybridoma (Larchmt). 2006. 25:271–277.
Article2. Furuoka H, Yabuzoe A, Horiuchi M, Tagawa Y, Yokoyama T, Yamakawa Y, Shinagawa M, Sata T. Species-specificity of a panel of prion protein antibodies for the immunohistochemical study of animal and human prion diseases. J Comp Pathol. 2007. 136:9–17.
Article3. Gilch S, Chitoor N, Taguchi Y, Stuart M, Jewell JE, Schätzl HM. Chronic wasting disease. Top Curr Chem. 2011. 305:51–77.
Article4. Haley NJ, Mathiason CK, Carver S, Zabel M, Telling GC, Hoover EA. Detection of chronic wasting disease prions in salivary, urinary, and intestinal tissues of deer: potential mechanisms of prion shedding and transmission. J Virol. 2011. 85:6309–6318.
Article5. Korth C, Stierli B, Streit P, Moser M, Schaller O, Fischer R, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Kretzschmar H, Raeber A, Braun U, Ehrensperger F, Hornemann S, Glockshuber R, Riek R, Billeter M, Wüthrich K, Oesch B. Prion (PrPSc)-specific epitope defined by a monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1997. 390:74–77.
Article6. McKinley MP, Bolton DC, Prusiner SB. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983. 35:57–62.
Article7. Miller MW, Williams ES. Prion disease: horizontal prion transmission in mule deer. Nature. 2003. 425:35–36.8. O'Rourke KI, Baszler TV, Miller JM, Spraker TR, Sadler-Riggleman I, Knowles DP. Monoclonal antibody F89/160.1.5 defines a conserved epitope on the ruminant prion protein. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. 36:1750–1755.9. O'Rourke KI, Zhuang D, Lyda A, Gomez G, Williams ES, Tuo W, Miller MW. Abundant PrPCWD in tonsil from mule deer with preclinical chronic wasting disease. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2003. 15:320–323.10. Race RE, Raines A, Baron TGM, Miller MW, Jenny A, Williams ES. Comparison of abnormal prion protein glycoform patterns from transmissible spongiform encephalopathy agent-infected deer, elk, sheep, and cattle. J Virol. 2002. 76:12365–12368.
Article11. Sohn HJ, Kim JH, Choi KS, Nah JJ, Joo YS, Jean YH, Ahn SW, Kim OK, Kim DY, Balachandran A. A case of chronic wasting disease in an elk imported to Korea from Canada. J Vet Med Sci. 2002. 64:855–858.
Article12. Spraker TR, Miller MW, Williams ES, Getzy DM, Adrian WJ, Schoonveld GG, Spowart RA, O'Rourke KI, Miller JM, Merz PA. Spongiform encephalopathy in free-ranging mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus), white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) and Rocky Mountain elk (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) in northcentral Colorado. J Wildl Dis. 1997. 33:1–6.
Article13. Spraker TR, O'Rourke KI, Balachandran A, Zink RR, Cummings BA, Miller MW, Powers BE. Validation of monoclonal antibody F99/97.6.1 for immunohistochemical staining of brain and tonsil in mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) with chronic wasting disease. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2002. 14:3–7.
Article14. Williams ES, Young S. Chronic wasting disease of captive mule deer: a spongiform encephalopathy. J Wildl Dis. 1980. 16:89–98.
Article15. Williams ES, Young S. Spongiform encephalopathies in Cervidae. Rev Sci Tech. 1992. 11:551–567.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pathological characterization of TgElk mice injected with brain homogenate from elk with chronic wasting disease
- BMD42-2910, a Novel Benzoxazole Derivative, Shows a Potent Anti-prion Activity and Prolongs the Mean Survival in an Animal Model of Prion Disease
- Production of Monoclonal Antibody Against Human 14 - 3 - 3 Zeta Isoform Expressed in Escherichia coli
- Generation and Characterization of Anti - Human CTLA - 4 Monoclonal Antibodies
- Characterizing affinity epitopes between prion protein and beta-amyloid using an epitope mapping immunoassay