J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Nov;52(11):1362-1365.
A Case of Achromobacter Xylosoxidans Keratitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonbuk National University School of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea. you2ic@paran.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonbuk National University School of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
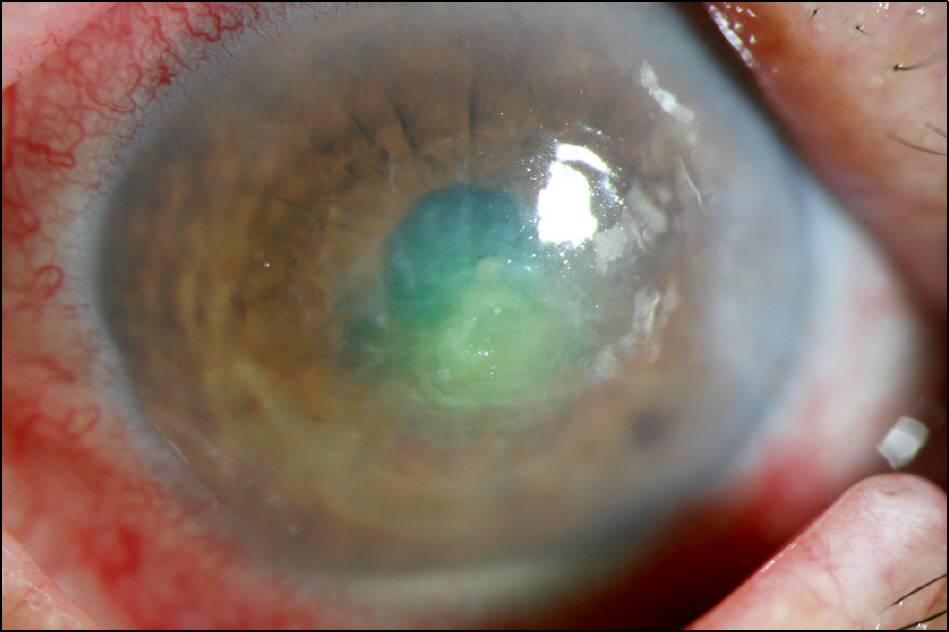
To report a case of corneal ulcer caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans in a farmer.
CASE SUMMARY
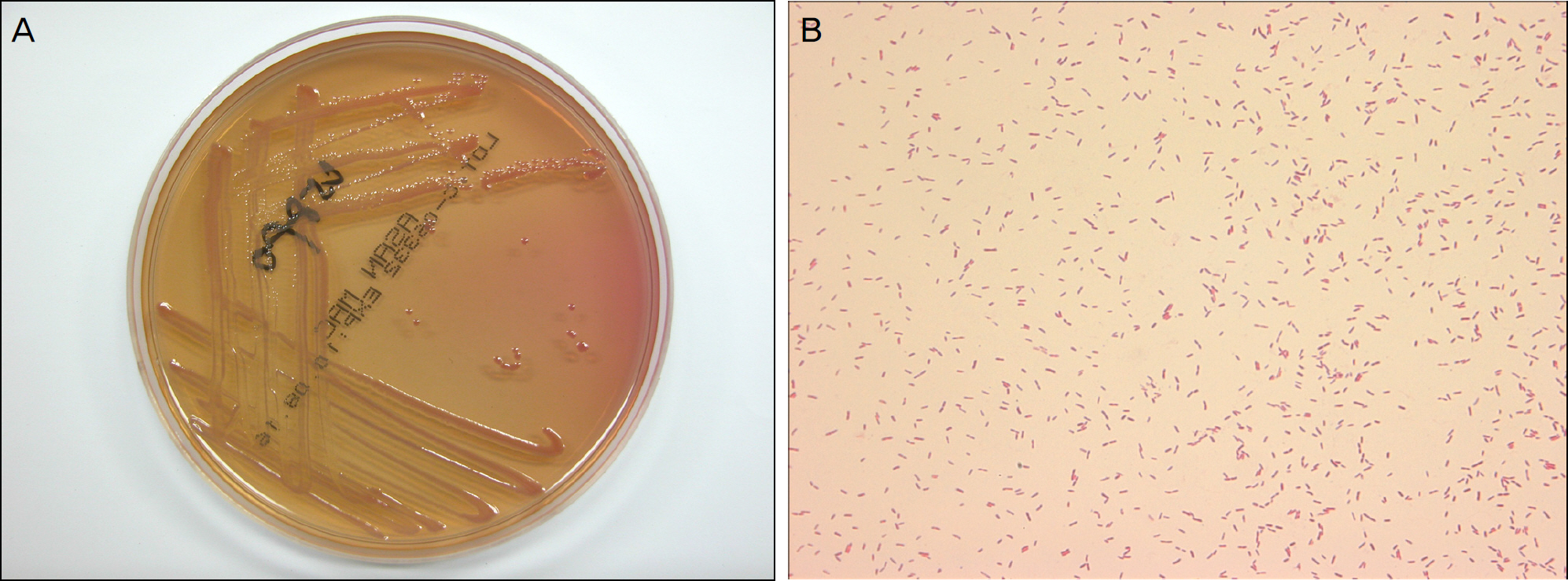
A previously healthy 68-year-old man presented with unilateral redness and irritation after his eye was grazed by a cow's tail. The patient had previously been treated in a local clinic for four days without improvement. Bacterial staining, culture, and an antibiotic sensitivity test were performed from a corneal scrape. The cultures revealed growth of A. xylosoxidans. The patient was treated with moxifloxacin and ceftazidime eyedrops. After three months of treatment, the infection was resolved with mild scarring.
CONCLUSIONS
Although it is a rare pathogen, A. xylosoxidans should be considered as a potential pathogen in patients presenting with corneal ulceration due to trauma from an object contaminated by soil or animal feces and having a slowly progressive disease and localized infiltrate but showing Gram-negative bacilli on smear examination.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Krzewinski JW, Nguyen CD, Foster JM, Burns JL. Use of random amplified polymorphic DNA PCR to examine epidemiology of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Achromobacter (Alcaligenes) xylosoxidans from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2001; 39:3597–602.2. Reddy AK, Garg P, Shah V, Gopinathan U. Clinical, microbiological profile and treatment outcome of ocular infections caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Cornea. 2009; 28:1100–3.
Article3. Igra-Siegman Y, Chmel H, Cobbs C. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of Achromobacter xylosoxidans infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980; 11:141–5.
Article4. Yabuuchi E, Oyama A. Achromobacter xylosoxidans n. sp. from human ear discharge. Jpn J Microbiol. 1971; 15:477–81.5. McGuckin MB, Thorpe RJ, Koch KM, et al. An outbreak of Achromobacter xylosoxidans related to diagnostic tracer procedures. Am J Epidemiol. 1982; 115:785–93.
Article6. Holmes B, Snell JJ, Lapage SP. Strains of Achromobacter xylosoxidans from clinical material. J Clin Pathol. 1977; 30:595–601.7. Oh J-Y, Shin YJ, Wee WR. A case of epidemic keratoconjunctivitis complicated by Alcaligenes xylosoxidans infection. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:233–4.8. Cho YK, Gi DH, Kim HK, La TY. A case of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans keratitis in a soft contact lens wearer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010; 51:1525–7.9. Mandell WF, Garvey GJ, Neu HC. Achromobacter xylosoxidans bacteremia. Rev Infect Dis. 1987; 5:1001–5.
Article10. Han YS, Chung IY, Park JM. A case of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans endophthalmitis after cataract extraction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:186–9.11. Newman PE, Hider P, Waring GO 3rd, et al. Corneal ulcer due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984; 68:472–4.
Article12. Pan TH, Heidemann DG, Dunn SP, et al. Delayed onset and recurrent Alcaligenes xylosoxidans keratitis. Cornea. 2000; 19:243–5.
Article13. Fiscella R, Noth J. Achromobacter xylosoxidans corneal ulcer in a therapeutic soft contact lens wearer. Cornea. 1989; 8:267–9.
Article14. Siganos DS, Tselentis IG, Papatzanaki ME, et al. Achromobacter xylosoxidans keratitis following penetrating keratoplasty. Refract Corneal Surg. 1993; 9:71–3.
Article15. Kiernan DF, Chin EK, Sclafani LA, Saidel MA. Multiple drug-re-sistant Alcaligenes xylosoxidans keratitis in a sanitation worker. Eye Contact Lens. 2009; 35:212–4.
Article16. Linke SJ, Skevas C, Richard G, Katz T. Bilateral Achromobacter xylosoxidans keratitis after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1045–7.
Article17. Rush R, Friedlander M. Alcaligenes xylosoxidans conjunctivitis. Cornea. 2007; 26:868–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Achromobacter xylosoxidans Keratitis after Contact Lens Usage
- A case of scalp abscess caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans after vacuum delivery
- A Case of Peritonitis Due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp. xylosoxidans in a Patient Undergoing Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
- Achromobacter xylosoxidans Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- A Case of Chronic Dacryocystitis Caused by Achromobacter Xylosoxidans