Nutr Res Pract.
2007 Sep;1(3):200-205.
Effects of taurine on plasma and liver lipids, erythrocyte ouabain sensitive Na efflux and platelet aggregation in Sprague Dawley rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Foods & Nutrition, Cheju National University, Cheju 690-756, Korea. jungkang@cheju.ac.kr
- 2Division of life Sciences and Institute of Environment and Life Science, Hallym University, Chuncheon 200-702, Korea.
Abstract
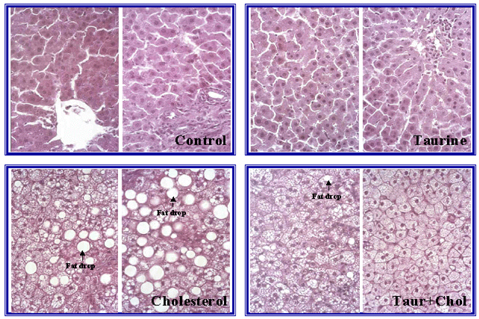
- The effects of taurine on plasma and liver cholesterol, erythrocyte ouabain sensitive Na efflux and platelet aggregation were examined in Sprague Dawley rats fed control or 0.5% cholesterol with 0.2% cholate diet. Plasma and liver levels of total cholesterol were increased significantly (p<0.05) in rats fed cholesterol diet compared to the control, and taurine significantly decreased the elevated plasma level of cholesterol in rats fed cholesterol diet (p<0.05). HDL-cholesterol was decreased in groups fed the cholesterol diet regardless of taurine supplementation and the difference between groups with and without cholesterol was significant (p<0.01). Plasma triglyceride was decreased and liver triglyceride was increased both significantly (p<0.05) in rats fed cholesterol compared to the control. Plasma and liver triglyceride in rats fed taurine was decreased significantly compared to the control (p<0.05). Intracellular Na tended to be lower in rats fed cholesterol or taurine and higher in rats fed cholesterol plus taurine compared to the control. Na efflux through Na-K ATPase and the passive leak of Na was somewhat reduced in rats fed cholesterol or taurine and was augmented in rats fed cholesterol plus taurine compared to the control, which showed a similar trend to the intracellular Na. Taurine supplementation caused a suppression of Na efflux in groups fed control diet and restored the suppressed Na efflux in groups fed cholesterol. Platelet aggregation was significantly decreased in the group fed taurine compared to the control (p<0.05) and the group fed cholesterol plus taurine was also a little lower in aggregation than the group fed cholesterol. Microscopic examination showed that taurine prevented fatty liver in rats fed cholesterol diet. Taurine known for stimulating Na-K ATPase in some cell types rather decreased erythrocyte ouabain sensitive Na-K ATPase in the present study. Taurine had hypolipidemic and hypocholesterolemic effects and inhibited platelet aggregation which may be favorable for prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burdakov D, Liss B, Ashcroft FM. Orexin excites GABAergic neuron of the arcuate nucleus by activating the sodium-calcium exchanger. J Neurosci. 2003. 25:4951–4957.2. Chen W, Matuda K, Nishimura N, Yokogoshi H. The effect of taurine on cholesterol degradation in mice fed a high-cholesterol diet. Life Sci. 2004. 27(74):1889–1898.
Article3. Elisaf M, Karabina SA, Bairaktari E, Goudevenos JA, Siamopoulos KC, Tselepis AD. Increased platelet reactivity to the aggregatory effect of platelet activating factor, in vitro, in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Platelets. 1999. 10:124–131.
Article4. Folch J, Lees M, Sloane stanley GH. A simple method for the isolation and rification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol chem. 1957. 226:497–509.
Article5. Friedrich B, Matskevich I, Lang F. Cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Contrib Nephrol. 2006. 152:1–8.
Article6. Hakam AC, Hussain T. Angiotensin type 2 receptor agonist directly inhibits proximal tubule sodium pump activity in obese but not in lean Zuker rats. Hypertension. 2006. 47:1117–1124.
Article7. Hall JA, Kirk J, Potts JR, Rae C, Kirk K. Anion channel blockers inhibit swelling-activated anion, cation and nonelectrolyte transport in HeLa cells. Am J Physiol. 1996. 271:C579–C588.
Article8. Handa RK, Stranhoy JW. Platelet activating factor (PAF) and solute transport process in the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. 284:274–281.9. Huxtable RJ. Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev. 1992. 72:101–163.
Article10. Igisu H, Izumi K, Goto I, Kina K. Effects of taurine on the ATPase activity in the human erythrocyte membrane. Pharmacology. 1976. 14:362–366.
Article11. Kang JS, Cregor MD, Smith JB. Effect of calcium on blood pressure, platelet aggregation and erythrocyte sodium transport in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J Hypertens. 1990. 8:245–250.12. Kontro P, Oja SS. Taurine and GABA release from mouse cerebral cotex slice: effects of structural analogues and drugs. Neurochem Res. 1987. 12:475–482.
Article13. Kurup RK, Kurup PA. Hypothalamic digoxin, hemispheric chemical dominance, and Alzheimer's disease. Int J Neurosci. 2003. 113:361–381.
Article14. Lijnen P, Petrov V. Cholesterol modulation of transmembrane cation transport systems in human erythrocytes. Biochem Mol Med. 1995. 56:52–62.
Article15. Liu CH, Huang MT, Huang PC. Source of triglyceride accumulation in liver of rats fed a cholesterol supplemented diet. Lipids. 1995. 30:527–531.
Article16. Mayol V, Duran MJ, Gerbi A, Levy S, Sampol J, Maixent JM. Cholesterol and omega 3 fatty acids inhibit Na-K ATPase activity in human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 1999. 142:327–333.
Article17. McCarty MF. Sub-optimal taurine status may promote platelet hyperaggregability in vegetarians. Med Hypotheses. 2004. 63:426–433.
Article18. Mochizuki H, Takido J, Oda H, Yokogoshi H. Improving effect of dietary taurine on marked hypercholesterolemia induced by a high cholesterol diet in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1999. 63:1984–1987.
Article19. Mrsny RJ, Meizel S. Inhibition of hamster sperm Na+, K+-ATPase activity by taurine and hypotaurine. Life Sci. 1985. 36:271–275.
Article20. Murakami S, Kondo Y, Toda Y, Kitajima H, Kameo K, Sakono M, Fukuda N. Effect of taurine on cholesterol metabolism in hamsters: up-regulation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor by taurine. Life Sci. 2002. 70:2355–2366.
Article21. Oh IS, Kang JA, Kang JS. Gender difference in the effects of gonadectomy and hypercholesterol diet on plasma and liver cholesterol and TG levels, platelet aggregation and liver tissue in Sprague Dawley rats. Nutritional Sciences. 2002. 35:15–23.22. Qi B, Yamagami T, Naruse Y, Sokejima S, Kagamimori S. Effect of taurine on depletion of erythrocyte membrane Na-K ATPase activity due to ozone exposure or cholesterol enrichment. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. 1995. 41:627–634.
Article23. Rabini RA, Staffolani R, Martarelli D, Fumelli P, Ravaglia F, Dousset N, Curatola G, Mazzanti L. Influence of low density lipoprotein from insulin-dependent diabetic patients on platelet functions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. 84:3770–3774.
Article24. Shefer S, Nguyen LB, Salen G, Ness GC, Chowdhary IR, Lerner S, Batta AK, Tint GS. Differing effects of cholesterol and taurocholate on steady state hepatic HMG-CoA reductase and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activities and mRNA levels in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1992. 33:1193–2000.
Article25. Smith JB, Ash KO, Sprowell WL, Hentchel WM, Williams RR. An improved non-radioisotopic method for increasing ouabain sensitive Na efflux from erythrocytes. Clin Chim Acta. 1984. 143:295–299.
Article26. Sobolová L, Skottová N, Vecera R, Urbánek K. Effect of silymarin and its polyphenolic fraction on cholesterol absorption in rats. Pharmacol Res. 2006. 53:104–112.
Article27. Sorci-Thomas M, Prack MM, Dashti N, Johnson F, Rudel LL, Williams DL. Differential effects of dietary fat on the tissue specific expression of apo A-1 gene; relationship to plasma concentration of high density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1989. 30:1397–1403.
Article28. Thut PD, Hruska RE, Huxtable RJ, Bressler R. Huxtable RJ, Barbeau A, editors. Effect of taurine on eating and drinking behavior. Taurine. 1976. USA: New York Raven;357–364.29. Tranquilli AL, Cester N, Nanetti L, Mazzanti L. Plasma lipids and physicochemical properties of the erythrocyte plasma membrane throughout pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2004. 83:443–448.
Article30. Tufft LS, Jensen LS. Influence of dietary taurine on performance and fat retention in broilers and turkey poults fed varying levels of fat. Poult Sci. 1992. 71:880–885.
Article31. Winocour PD, Vickers JD, Kinlough-Rathbone RL, Packham MA, Mustard JF. Thrombin-induced inositol phosphate production by platelets from rats with diet induced or genetically determined hypercholesterolemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1990. 115:241–248.32. Yamamoto K, Yoshitama A, Sakono M, Nasu T, Murakami S, Fukuda N. Dietary taurine decreases hepatic secretion of cholesterol ester in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Pharmacology. 2000. 60:27–33.
Article33. Yoshimura H, Nariai Y, Terashima M, Mitani T, Tanigawq Y. Taurine suppresses platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) BB-induced PDGF-beta receptor phosphorylation by protein tyrosine phosphatase-mediated dephosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. 1745:350–360.
Article34. Zicha J, Negrin CD, Dobesová Z, Kunes J, Dominiczak AF. Altered Na+-K+ pump activity and plasma lipids in salt-hypertensive Dahl rats: relationship to Atp1a1 gene. Physiol Genomics. 2001. 6:99–104.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Cholesterol Diet and Exercise on Plasma and Liver Lipids, Platelet Aggregation and Erythrocyte Na Efflux in Rats
- Effect of onion and beet on plasma and liver lipids, platelet aggregation, and erythrocyte Na efflux in simvastatin treated hypercholesterolmic rats
- Effects of green tea or Sasa quelpaertensis bamboo leaves on plasma and liver lipids, erythrocyte Na efflux, and platelet aggregation in ovariectomized rats
- Effects of dietary taurine supplementation on plasma and liver lipids in OVX rats fed calcium-deficient diet
- Effect of Coenzyme Q10 and green tea on plasma and liver lipids, platelet aggregation, TBARS production and erythrocyte Na leak in simvastatin treated hypercholesterolmic rats