J Breast Cancer.
2010 Jun;13(2):160-166. 10.4048/jbc.2010.13.2.160.
Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Triple-negative Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medical Research Center for Cancer Molecular Therapy, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kimhj@dau.ac.kr
- 3Department of Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2286541
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2010.13.2.160
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) are known to carry an increased risk of distant metastasis and poor survival. The principal objective of this study was to investigate survival after brain metastases in patients with TNBC.
METHODS
The authors retrospectively evaluated clinical data obtained from 66 patients who had been diagnosed with breast cancer and brain metastasis from 2003 to 2009. Estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth receptor-2 (HER2) statuses were determined via immunohistochemical staining. TNBCs were defined as those that were ER-negative, PR-negative, and HER2-negative. The time interval from initial diagnosis to brain metastasis and overall survival after brain metastasis was evaluated via the Kaplan-Meier method.
RESULTS
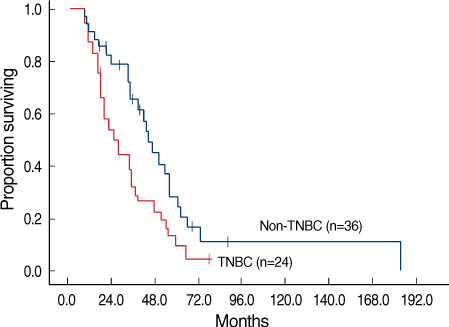
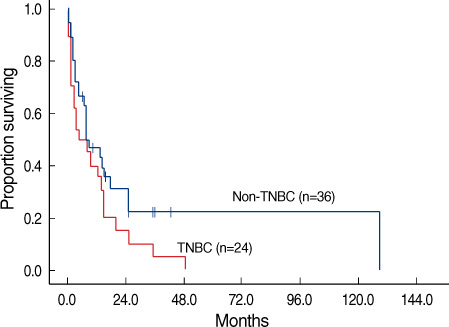
Twenty four (40.0%) of 60 patients were diagnosed with TNBC. The clinicopathologic characteristics did not differ between the TNBC and non-TNBC patients. The disease-free survival durations of the TNBC and non-TNBC subjects were 17.9 and 25.6 months, respectively (p=0.135). The time intervals from initial diagnosis to brain metastasis were 25.5 and 43.7 months, respectively (p=0.027). The time intervals from distant metastasis to brain metastasis were 8.4 and 19.5 months, respectively (p=0.006). Overall survival durations from brain metastasis to death were 4.3 and 7.6 months, respectively (p=0.046).
CONCLUSION
Patients with TNBC were more likely to develop brain metastasis earlier, and exhibit poor overall survival. Triple receptor status may be utilized as a prognostic marker for breast cancer patients with brain metastasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Simpson PT, Reis-Filho JS, Gale T, Lakhani SR. Molecular evolution of breast cancer. J Pathol. 2005. 205:248–254.
Article2. Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000. 406:747–752.
Article3. Fan C, Oh DS, Wessels L, Weigelt B, Nuyten DS, Nobel AB, et al. Concordance among gene-expression-based predictors for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006. 355:560–569.
Article4. Rakha EA, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO. Basal-like breast cancer: a critical review. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:2568–2581.
Article5. Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, et al. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:5367–5374.
Article6. Reis-Filho JS, Tutt AN. Triple negative tumours: a critical review. Histopathology. 2008. 52:108–118.
Article7. Lin NU, Claus E, Sohl J, Razzak AR, Arnaout A, Winer EP. Sites of distant recurrence and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: high incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer. 2008. 113:2638–2645.
Article8. Hines SL, Vallow LA, Tan WW, McNeil RB, Perez EA, Jain A. Clinical outcomes after a diagnosis of brain metastases in patients with estrogen- and/or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive versus triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2008. 19:1561–1565.
Article9. Dawood S, Broglio K, Esteva FJ, Yang W, Kau SW, Islam R, et al. Survival among women with triple receptor-negative breast cancer and brain metastases. Ann Oncol. 2009. 20:621–627.
Article10. Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP. CNS metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:3608–3617.
Article11. Shaffrey ME, Mut M, Asher AL, Burri SH, Chahlavi A, Chang SM, et al. Brain metastases. Curr Probl Surg. 2004. 41:665–741.
Article12. Ahr A, Karn T, Solbach C, Seiter T, Strebhardt K, Holtrich U, et al. Identification of high risk breast-cancer patients by gene expression profiling. Lancet. 2002. 359:131–132.
Article13. Fromm S, Bartsch R, Rudas M, de Vries A, Wenzel C, Steger GG, et al. Factors influencing the time to development of brain metastases in breast cancer. Breast. 2008. 17:512–516.
Article14. Heitz F, Harter P, Lueck HJ, Fissler-Eckhoff A, Lorenz-Salehi F, Scheil-Bertram S, et al. Triple-negative and HER2-overexpressing breast cancers exhibit an elevated risk and an earlier occurrence of cerebral metastases. Eur J Cancer. 2009. 45:2792–2798.
Article15. Taniguchi T, Tischkowitz M, Ameziane N, Hodgson SV, Mathew CG, Joenje H, et al. Disruption of the Fanconi anemia-BRCA pathway in cisplatin-sensitive ovarian tumors. Nat Med. 2003. 9:568–574.
Article16. Hoadley KA, Weigman VJ, Fan C, Sawyer LR, He X, Troester MA, et al. EGFR associated expression profiles vary with breast tumor subtype. BMC Genomics. 2007. 8:258.
Article17. Carey LA, Rugo HS, Marcom PK, Irvin W, Ferraro M, Burrows E, et al. TBCRC001: EGFR inhibition with cetuximab added to carboplatin in metastatic triple-negative (basal-like) breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:abstract #1009.18. O'Shaughnessy J, Weckstein DJ, Vukelja SJ, Mclntyre K, Krekow L, Holmes FA, et al. Preliminary results of a randomized phase II study of weekly irinotecan/carboplatin with or without cetuximab in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007. 106:abstract #308.19. Ashworth A. A synthetic lethal therapeutic approach: poly (ADP) ribose polymerase inhibitors for the treatment of cancers deficient in DNA double-strand break repair. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:3785–3790.
Article20. Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, Tutt A, Wu P, Mergui-Roelvink M, et al. Inhibition of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:123–134.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Predictive Factors and Survival Rate for Brain Metastasis from Breast Cancer
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Early Stage Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Comparison with Non-triple Negative Group
- Comment to “Patients with Concordant Triple-Negative Phenotype between Primary Breast Cancers and Corresponding Metastases Have Poor Prognosisâ€
- Treatment Outcomes of Weakly Positive Hormone Receptor Breast Cancer and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Overexpression of Cell Cycle Progression Inhibitor Geminin is Associated with Tumor Stem-Like Phenotype of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer