Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Oct;35(5):742-746. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.5.742.
Combined Therapy of Orthopedic Surgery after Deep Brain Stimulation in Cerebral Palsy Mixed Type: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department & Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea. srcho918@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea.
- KMID: 2267240
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.5.742
Abstract
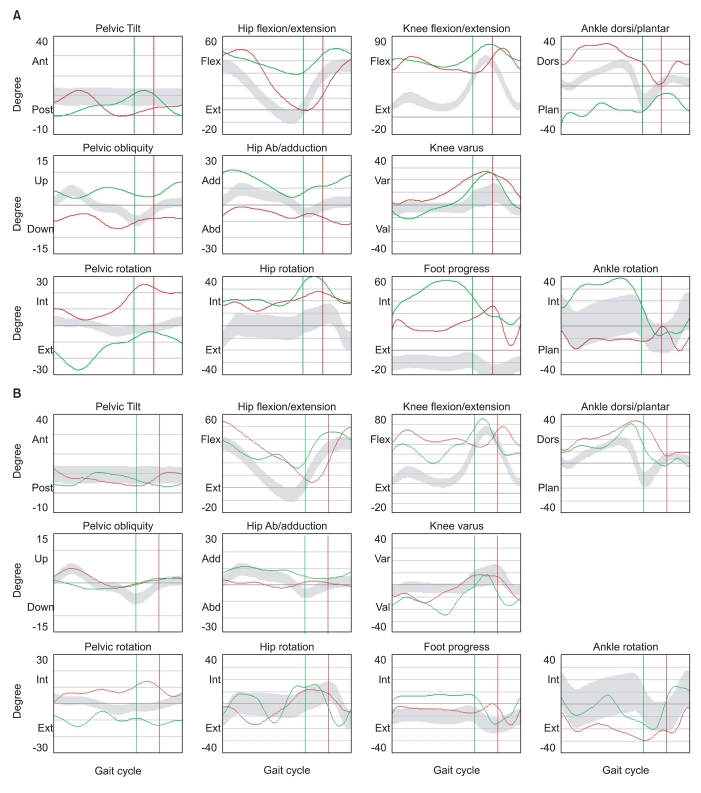
- Dystonia is a symptom defined by involuntary and irregular contractions of the muscles, which cause movement disorders and postural problems. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) in globus pallidus interna (GPi) is a good option for controlling dystonia. DBS has already been shown to have significant effects on primary dystonia as well as Parkinson's disease. Dystonia is very difficult to manage, as seen in cerebral palsy (CP) mixed with spasticity. As CP patients grow, their musculoskeletal problems may require orthopedic surgery. However, the outcome of orthopedic surgery is not usually suitable due to dystonia. Therefore, we attempted to control dystonia through DBS initially and perform orthopedic surgery to correct musculoskeletal deformities after treatment of dystonia. Herein, we report a case that showed remarkable improvement in terms of the dystonia rating scale and gait pattern after combined therapy of DBS and orthopedic surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Koman LA, Smith BP, Shilt JS. Cerebral palsy. Lancet. 2004; 363:1619–1631. PMID: 15145637.
Article2. Monbaliu E, Ortibus E, Roelens F, Desloovere K, Deklerck J, Prinzie P, de Cock P, Feys H. Rating scales for dystonia in cerebral palsy: reliability and validity. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010; 52:570–575. PMID: 20132143.
Article3. Cif L, El Fertit H, Vayssiere N, Hemm S, Hardouin E, Gannau A, Tuffery S, Coubes P. Treatment of dystonic syndromes by chronic electrical stimulation of the internal globus pallidus. J Neurosurg Sci. 2003; 47:52–55. PMID: 12900733.4. Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Benabid AL, Cornu P, Lagrange C, Tezenas du Montcel S, Dormont D, Grand S, et al. Bilateral deepbrain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:459–467. PMID: 15689584.
Article5. Kupsch A, Benecke R, Muller J, Trottenberg T, Schneider GH, Poewe W, Eisner W, Wolters A, Muller JU, Deuschl G, et al. Pallidal deep-brain stimulation in primary generalized or segmental dystonia. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:1978–1990. PMID: 17093249.
Article6. Vercueil L, Krack P, Pollak P. Results of deep brain stimulation for dystonia: a critical reappraisal. Mov Disord. 2002; 17(Suppl 3):S89–S93. PMID: 11948761.
Article7. Vidailhet M, Yelnik J, Lagrange C, Fraix V, Grabli D, Thobois S, Burbaud P, Welter ML, Xie-Brustolin J, Braga MC, et al. Bilateral pallidal deep brain stimulation for the treatment of patients with dystonia choreoathetosis cerebral palsy: a prospective pilot study. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8:709–717. PMID: 19576854.8. Zorzi G, Marras C, Nardocci N, Franzini A, Chiapparini L, Maccagnano E, Angelini L, Caldiroli D, Broggi G. Stimulation of the globus pallidus internus for childhood-onset dystonia. Mov Disord. 2005; 20:1194–1200. PMID: 15895426.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Outcomes of Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy Compared With Deep Brain Stimulation in a Patient With Dystonic Cerebral Palsy: A Case Report
- Malignant Neuroleptic Syndrome following Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery of Globus Pallidus Pars Internus in Cerebral Palsy
- Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Movement Disorders
- Deep Brain Stimulation of the Subthalamic Area for Dystonic Tremor
- Two-Year Outcomes of Deep Brain Stimulation in Adults With Cerebral Palsy