Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Patients with Brain Injury and Dysphagia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 138-736, Korea. mhchun@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju 690-767, Korea.
- KMID: 2266801
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.765
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
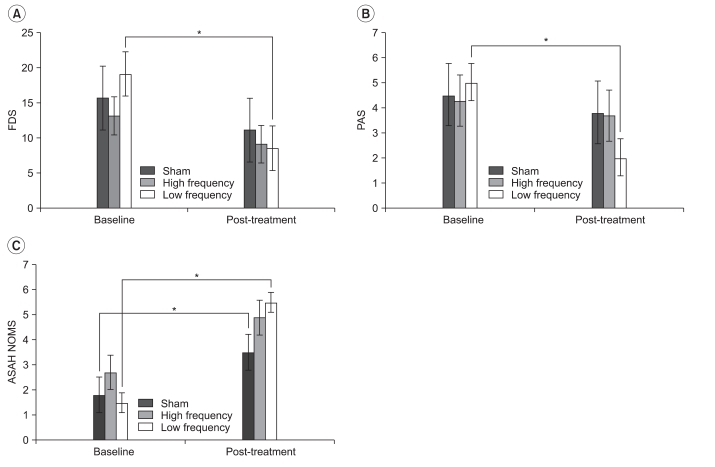
To investigate the effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) on recovery of the swallowing function in patients with a brain injury. METHOD: Patients with a brain injury and dysphagia were enrolled. Patients were randomly assigned to sham, and low and high frequency stimulation groups. We performed rTMS at 100% of motor evoked potential (MEP) threshold and a 5 Hz frequency for 10 seconds and then repeated this every minute in the high frequency group. In the low frequency group, magnetic stimulation was conducted at 100% of MEP threshold and a 1 Hz frequency. The sham group was treated using the same parameters as the high frequency group, but the coil was rotated 90degrees to create a stimulus noise. The treatment period was 2 weeks (5 days per week, 20 minutes per session). We evaluated the Functional Dysphagia Scale (FDS) and the Penetration Aspiration Scale (PAS) with a videofluoroscopic swallowing study before and after rTMS.
RESULTS
Thirty patients were enrolled, and mean patient age was 68.2 years. FDS and PAS scores improved significantly in the low frequency group after rTMS, and American Speech-Language Hearing Association National Outcomes Measurements System Swallowing Scale scores improved in the sham and low frequency groups. FDS and PAS scores improved significantly in the low frequency group compared to those in the other groups.
CONCLUSION
We demonstrated that low frequency rTMS facilitated the recovery of swallowing function in patients with a brain injury, suggesting that rTMS is a useful modality to recover swallowing function.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Effect of Low-Frequency rTMS and NMES on Subacute Unilateral Hemispheric Stroke With Dysphagia
Kil-Byung Lim, Hong-Jae Lee, Jeehyun Yoo, Yong-Geol Kwon
Ann Rehabil Med. 2014;38(5):592-602. doi: 10.5535/arm.2014.38.5.592.Effects of Hand Training During the Aftereffect Period of Low-Frequency rTMS in Subacute Stroke Patients
Joo Won Park, Sang Beom Kim, Kyeong Woo Lee, Jong Hwa Lee, Jin Gee Park, Sook Joung Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(4):521-527. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.521.Clinical Practice Guidelines for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
Seoyon Yang, Jin-Woo Park, Kyunghoon Min, Yoon Se Lee, Young-Jin Song, Seong Hee Choi, Doo Young Kim, Seung Hak Lee, Hee Seung Yang, Wonjae Cha, Ji Won Kim, Byung-Mo Oh, Han Gil Seo, Min-Wook Kim, Hee-Soon Woo, Sung-Jong Park, Sungju Jee, Ju Sun Oh, Ki Deok Park, Young Ju Jin, Sungjun Han, DooHan Yoo, Bo Hae Kim, Hyun Haeng Lee, Yeo Hyung Kim, Min-Gu Kang, Eun-Jae Chung, Bo Ryun Kim, Tae-Woo Kim, Eun Jae Ko, Young Min Park, Hanaro Park, Min-Su Kim, Jungirl Seok, Sun Im, Sung-Hwa Ko, Seong Hoon Lim, Kee Wook Jung, Tae Hee Lee, Bo Young Hong, Woojeong Kim, Weon-Sun Shin, Young Chan Lee, Sung Joon Park, Jeonghyun Lim, Youngkook Kim, Jung Hwan Lee, Kang-Min Ahn, Jun-Young Paeng, JeongYun Park, Young Ae Song, Kyung Cheon Seo, Chang Hwan Ryu, Jae-Keun Cho, Jee-Ho Lee, Kyoung Hyo Choi
Ann Rehabil Med. 2023;47(Suppl 1):S1-S26. doi: 10.5535/arm.23069.
Reference
-
1. Lindgren S, Janzon L. Prevalence of swallowing complaints and clinical findings among 50-79-year-old men and women in an urban population. Dysphagia. 1991; 6:187–192. PMID: 1778094.
Article2. Gordon C, Hewer RL, Wade DT. Dysphagia in acute stroke. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987; 295:411–414.
Article3. Khedr EM, Abo-Elfetoh N, Rothwell JC. Treatment of post-stroke dysphagia with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Acta Neurol Scand. 2009; 119:155–161. PMID: 18771521.
Article4. Dennis M. Dysphagia in acute stroke: A long-awaited trial. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:16–17. PMID: 16361015.
Article5. Barer DH. The natural history and functional consequences of dysphagia after hemispheric stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989; 52:236–241. PMID: 2564884.
Article6. Langmore SE, Miller RM. Behavioral treatment for adults with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1994; 75:1154–1160. PMID: 7944924.
Article7. Permsirivanich W, Tipchatyotin S, Wongchai M, Leelamanit V, Setthawatcharawanich S, Sathirapanya P, Phabphal K, Juntawises U, Boonmeeprakob A. Comparing the effects of rehabilitation swallowing therapy vs. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy among stroke patients with persistent pharyngeal dysphagia: A randomized controlled study. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009; 92:259–265. PMID: 19253803.8. Bulow M, Speyer R, Baijens L, Woisard V, Ekberg O. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (nmes) in stroke patients with oral and pharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia. 2008; 23:302–309. PMID: 18437464.
Article9. Clark H, Lazarus C, Arvedson J, Schooling T, Frymark T. Evidence-based systematic review: effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on swallowing and neural activation. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2009; 18:361–375. PMID: 19726568.
Article10. Alonso-Alonso M, Fregni F, Pascual-Leone A. Brain stimulation in poststroke rehabilitation. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007; 24(Suppl 1):157–166. PMID: 17971652.
Article11. Hummel F, Celnik P, Giraux P, Floel A, Wu WH, Gerloff C, Cohen LG. Effects of non-invasive cortical stimulation on skilled motor function in chronic stroke. Brain. 2005; 128:490–499. PMID: 15634731.
Article12. Hummel FC, Cohen LG. Non-invasive brain stimulation: A new strategy to improve neuro rehabilitation after stroke? Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:708–712. PMID: 16857577.13. Fregni F, Boggio PS, Mansur CG, Wagner T, Ferreira MJ, Lima MC, Rigonatti SP, Marcolin MA, Freedman SD, Nitsche MA, Pascual-Leone A. Transcranial direct current stimulation of the unaffected hemisphere in stroke patients. Neuroreport. 2005; 16:1551–1555. PMID: 16148743.
Article14. Jang SH, Ahn SH, Byun WM, Kim CS, Lee MY, Kwon YH. The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on the cortical activation by motor task in the human brain: An fmri study. Neurosci Lett. 2009; 460:117–120. PMID: 19450657.
Article15. Profice P, Pilato F, Dileone M, Ranieri F, Capone F, Musumeci G, P AT, Di Lazzaro V. Use of transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain in stroke rehabilitation. Expert Rev Neurother. 2007; 7:249–258. PMID: 17341173.
Article16. Fregni F, Boggio PS, Nitsche M, Bermpohl F, Antal A, Feredoes E, Marcolin MA, Rigonatti SP, Silva MT, Paulus W, Pascual-Leone A. Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation of prefrontal cortex enhances working memory. Exp Brain Res. 2005; 166:23–30. PMID: 15999258.
Article17. Jo JM, Kim YH, Ko MH, Ohn SH, Joen B, Lee KH. Enhancing the working memory of stroke patients using tdcs. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 88:404–409. PMID: 19620953.
Article18. Jefferson S, Mistry S, Michou E, Singh S, Rothwell JC, Hamdy S. Reversal of a virtual lesion in human pharyngeal motor cortex by high frequency contralesional brain stimulation. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137:841–849. 849 e841PMID: 19427312.
Article19. Verin E, Leroi AM. Poststroke dysphagia rehabilitation by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: A noncontrolled pilot study. Dysphagia. 2009; 24:204–210. PMID: 18956227.
Article20. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. Quantifying swallowing function after stroke: A functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic studies. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2001; 82:677–682. PMID: 11346847.
Article21. Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996; 11:93–98. PMID: 8721066.
Article22. Mullen R, Schooling T. The national outcomes measurement system for pediatric speech-language pathology. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 2010; 41:44–60. PMID: 19833827.
Article23. Mullen R. Evidence for whom?: Asha's national outcomes measurement system. J Commun Disord. 2004; 37:413–417. PMID: 15231421.
Article24. Khedr EM, Abo-Elfetoh N. Therapeutic role of rtms on recovery of dysphagia in patients with lateral medullary syndrome and brainstem infarction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010; 81:495–499. PMID: 19828479.
Article25. Hamdy S, Aziz Q, Thompson DG, Rothwell JC. Physiology and pathophysiology of the swallowing area of human motor cortex. Neural Plast. 2001; 8:91–97. PMID: 11530891.
Article26. Kim BR, Kim DY, Chun MH, Yi JH, Kwon JS. Effet of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on cognition and mood in stroke patients: a double-blind, sham-controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 89:362–368. PMID: 20407301.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Application of Non-invasive Brain Stimulation on Dysphagia after Stroke
- Diagnosis With Manometry and Treatment With Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Dysphagia
- Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation According to the Stimulation Site in Stroke Patients With Dysphagia
- Safety Review for Clinical Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
- Noninvasive brain stimulation: repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation