J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Dec;56(6):488-491. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.6.488.
Cortical Neuronal Loss after Chronic Prenatal Hypoxia: A Comparative Laboratory Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. chosunns@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2191139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.6.488
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the prenatal hypoxic effect on the fetal brain development.
METHODS
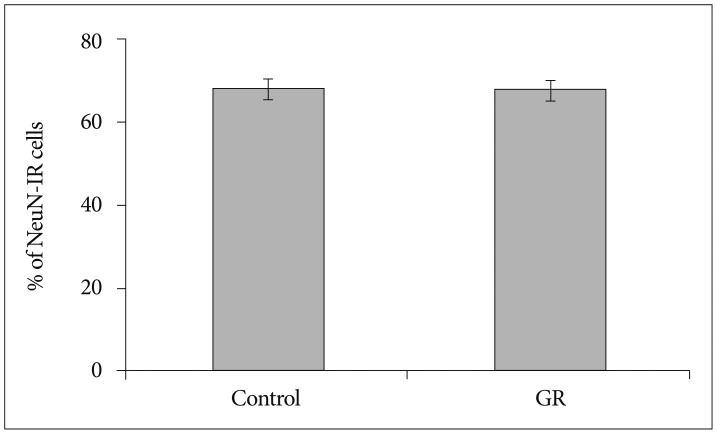
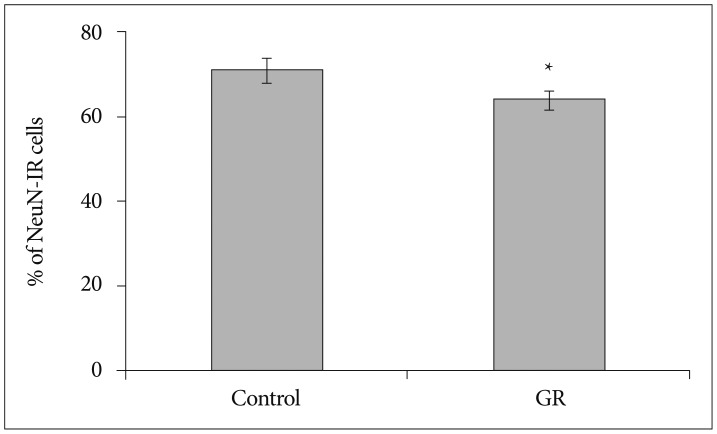
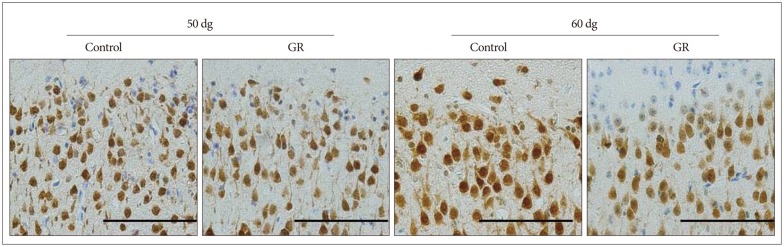
We used the guinea pig chronic placental insufficiency model to investigate the effect of hypoxia on fetal brain development. We ligated unilateral uterine artery at 30-32 days of gestation (dg : with term defined as -67 dg). At 50 dg, 60 dg, fetuses were sacrificed and assigned to either the growth-restricted (GR) or control (no ligation) group. After fixation, dissection, and sectioning of cerebral tissue from these animals, immunohistochemistry was performed with NeuN antibody, which is a mature neuronal marker in the cerebral cortex.
RESULTS
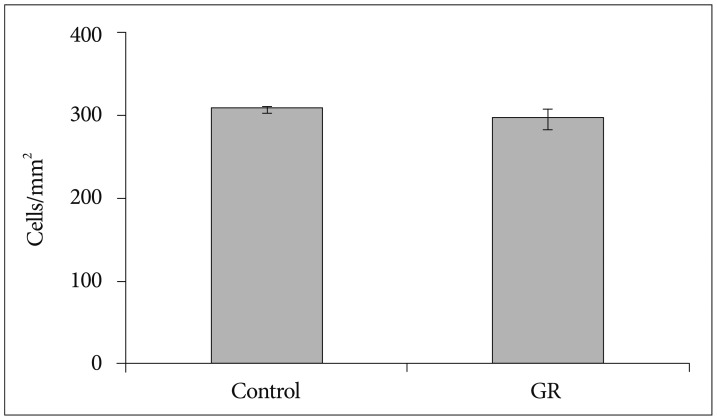
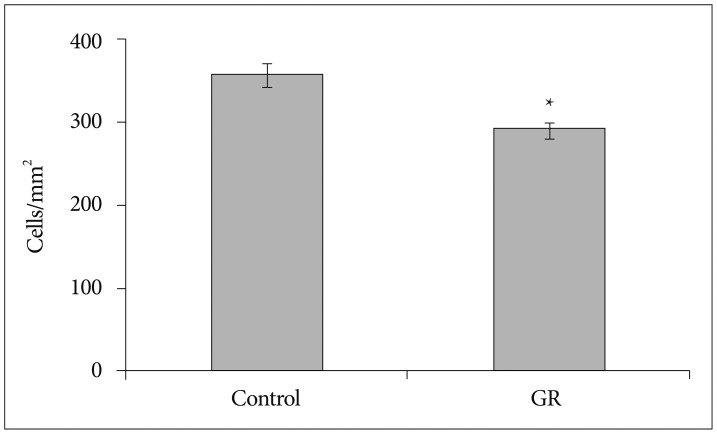
The number of NeuN-immunoreactive (IR) cells in the cerebral cortex did not differ between the GR and control groups at 50 dg. However, the number of NeuN-IR cells was lesser in GR fetuses than in controls at 60 dg (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
These findings show that chronic prenatal hypoxia affect the number of neuron in the cerebral cortex of guinea pig fetus at 60 dg. The approach used in this study is helpful for extending our understanding of neurogenesis in the cerebral cortex, and the findings may be useful for elucidating the brain injury caused by prenatal hypoxia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cho CM, Ha SU, Bae HR, Huh JT. Endothelial cell products as a key player in hypoxia-induced nerve cell injury after stroke. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2006; 40:103–109.2. Daval JL, Vert P. Apoptosis and neurogenesis after transient hypoxia in the developing rat brain. Semin Perinatol. 2004; 28:257–263. PMID: 15565785.
Article3. Derrick M, He J, Brady E, Tan S. The in vitro fate of rabbit fetal brain cells after acute in vivo hypoxia. J Neurosci. 2001; 21:RC138. PMID: 11264330.4. Fagel DM, Ganat Y, Silbereis J, Ebbitt T, Stewart W, Zhang H, et al. Cortical neurogenesis enhanced by chronic perinatal hypoxia. Exp Neurol. 2006; 199:77–91. PMID: 15916762.
Article5. Gross SJ, Kosmetatos N, Grimes CT, Williams ML. Newborn head size and neurological status. Predictors of growth and development of low birth weight infants. Am J Dis Child. 1978; 132:753–756. PMID: 567424.6. Herculano-Houzel S, Lent R. Isotropic fractionator: a simple, rapid method for the quantification of total cell and neuron numbers in the brain. J Neurosci. 2005; 25:2518–2521. PMID: 15758160.
Article7. Jansson T, Thordstein M, Kjellmer I. Placental blood flow and fetal weight following uterine artery ligation. Temporal aspects of intrauterine growth retardation in the guinea pig. Biol Neonate. 1986; 49:172–180. PMID: 3955109.
Article8. Kee NJ, Preston E, Wojtowicz JM. Enhanced neurogenesis after transient global ischemia in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Exp Brain Res. 2001; 136:313–320. PMID: 11243473.
Article9. Kernie SG, Parent JM. Forebrain neurogenesis after focal Ischemic and traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2010; 37:267–274. PMID: 19909815.
Article10. Lefebvre F, Bard H, Veilleux A, Martel C. Outcome at school age of children with birthweights of 1000 grams or less. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1988; 30:170–180. PMID: 2454860.
Article11. Levison SW, Rothstein RP, Romanko MJ, Snyder MJ, Meyers RL, Vannucci SJ. Hypoxia/ischemia depletes the rat perinatal subventricular zone of oligodendrocyte progenitors and neural stem cells. Dev Neurosci. 2001; 23:234–247. PMID: 11598326.
Article12. Liu J, Solway K, Messing RO, Sharp FR. Increased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia in gerbils. J Neurosci. 1998; 18:7768–7778. PMID: 9742147.
Article13. Mallard C, Loeliger M, Copolov D, Rees S. Reduced number of neurons in the hippocampus and the cerebellum in the postnatal guinea-pig following intrauterine growth-restriction. Neuroscience. 2000; 100:327–333. PMID: 11008170.
Article14. Mullen RJ, Buck CR, Smith AM. NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development. 1992; 116:201–211. PMID: 1483388.
Article15. Neerhof MG, Thaete LG. The fetal response to chronic placental insufficiency. Semin Perinatol. 2008; 32:201–205. PMID: 18482622.
Article16. Rees S, Breen S, Loeliger M, McCrabb G, Harding R. Hypoxemia near mid-gestation has long-term effects on fetal brain development. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1999; 58:932–945. PMID: 10499436.
Article17. Rees S, Stringer M, Just Y, Hooper SB, Harding R. The vulnerability of the fetal sheep brain to hypoxemia at mid-gestation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997; 103:103–118.
Article18. Rodricks CL, Gibbs ME, Castillo-Melendez M, Miller SL. The effect of hypoxia on the functional and structural development of the chick brain. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2010; 28:343–350. PMID: 20171268.
Article19. Skranes J, Vangberg TR, Kulseng S, Indredavik MS, Evensen KA, Martinussen M, et al. Clinical findings and white matter abnormalities seen on diffusion tensor imaging in adolescents with very low birth weight. Brain. 2007; 130(Pt 3):654–666. PMID: 17347255.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Recombinant EPO on Death of Cortical Neuron in Chronic Hypoxia
- A Case of Transient Cortical Blindness after Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
- Hypoxia-A Possibility in Fibromyalgia Syndrome Pathogenesis
- Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Exerts a Protective Effect via an Anti-Apoptotic Mechanism on Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury in the Rat Brain
- Effects of Hypoxia on the Ubiquitin-proteasome System in Primary Cortical Neuronal Cell Cultures