J Bacteriol Virol.
2012 Dec;42(4):321-329. 10.4167/jbv.2012.42.4.321.
Isolation and Cloning of an ABC Transporter-Like Gene of Haemophilus parasuis and Its Use in a New Diagnostic PCR
- Affiliations
-
- 1Optipharm, 63 Osongsaengmyoung 6-ro, Osong-eup, Cheongwon-gun, Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea.
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine and Institute of Veterinary Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea. twhahn@kangwon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2168667
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2012.42.4.321
Abstract
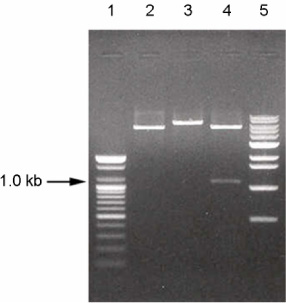
- The aim of this study was to identify a new gene of Haemophilus parasuis that could be used to develop a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for this porcine pathogen. H. parasuis genomic DNA was cloned into a set of expression vectors, and transformants expressing His-tagged polypeptides were identified by colony blotting. An ABC transporter-like gene was isolated. The cloned DNA fragment is 1,105 base pair and shows 78% similarity at the nucleotide level with an ABC transporter gene of H. ducreyi. Based on this sequence, two PCR primers were designed to amplify the entire 1,105-bp fragment in the proposed diagnostic PCR test. PCR amplification was able to detect a minimum of 1 x 10(4) CFU/ml of H. parasuis organisms. Fifteen different H. parasuis serovars were positive using the PCR test. No amplification was observed when the test was done using DNA from 16 other bacterial species commonly isolated from swine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Biberstein EL, White DC. A proposal for the establishment of two new Haemophilus species. J Med Microbiol. 1969. 2:75–78.2. Rapp-Gabrielson VJ. Straw BE, D'Allaire S, Mengeling WL, Taylor DJ, editors. Haemophilus parasuis. Diseases of swine. 1999. 8th ed. Ames: Iowa State University Press;475–481.3. Smart NL, Miniats OP, MacInnes JI. Analysis of Haemophilus parasuis isolates from southern Ontario swine by restriction endonuclease fingerprinting. Can J Vet Res. 1988. 52:319–324.4. Cai X, Chen H, Blackall PJ, Yin Z, Wang L, Liu Z, et al. Serological characterization of Haemophilus parasuis isolates from China. Vet Microbiol. 2005. 111:231–236.5. Rapp-Gabrielson VJ, Gabrielson DA. Prevalence of Haemophilus parasuis serovars among isolates from swine. Am J Vet Res. 1992. 53:659–664.6. Rapp VJ, Ross RF, Young TF. Characterization of Haemophilus spp. isolated from healthy swine and evaluation of cross-reactivity of complement-fixing antibodies to Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae and Haemophilus taxon "minor group". J Clin Microbiol. 1985. 22:945–950.
Article7. Olvera A, Cerdà-Cuéllar M, Nofrarías M, Revilla E, Segalés J, Aragon V. Dynamics of Haemophilus parasuis genotypes in a farm recovered from an outbreak of Glässer's Disease. Vet Microbiol. 2007. 123:230–237.
Article8. Oliveira S, Galina L, Pijoan C. Development of a PCR test to diagnose Haemophilus parasuis infections. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2001. 13:495–501.
Article9. Angen O, Oliveira S, Ahrens P, Svensmark B, Leser TD. Development of an improved species specific PCR test for detection of Haemophilus parasuis. Vet Microbiol. 2007. 119:266–276.
Article10. Sambrook J, Russel DW. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2001. 3rd ed. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.11. Rafiee M, Bara M, Stephens CP, Blackall PJ. Application of ERIC-PCR for the comparison of isolates of Haemophilus parasuis. Aust Vet J. 2000. 78:846–849.
Article12. Ruiz A, Oliveira S, Torremorell M, Pijoan C. Outer membrane proteins and DNA profiles in strains of Haemophilus parasuis recovered from systemic and respiratory sites. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. 39:1757–1762.
Article13. Olvera A, Segalés J, Aragón V. Update on the diagnosis of Haemophilus parasuis infection in pigs and novel genotyping methods. Vet J. 2007. 174:522–529.
Article14. Oliveira S. Haemophilus parasuis diagnostics. J Swine Health Prod. 2007. 15:99–103.15. Blackall PJ, Trott DJ, Rapp-Gabrielson V, Hampson DJ. Analysis of Haemophilus parasuis by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Vet Microbiol. 1997. 56:125–134.16. Dubosson CR, Conzelmann C, Miserez R, Boerlin P, Frey J, Zimmermann W, et al. Development of two real-time PCR assays for the detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in clinical samples. Vet Microbiol. 2004. 102:55–65.
Article17. Higgins CF. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992. 8:67–113.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of a universal plate-agglutination test for detecting Haemophilus parasuis
- Pharmacokinetics of tilmicosin in healthy pigs and in pigs experimentally infected with Haemophilus parasuis
- Cloning of ABO PCR Products Including Exon 2 to Exon 7 Using Seamless Cloning Technique
- Investigation of morphological changes of HPS membrane caused by cecropin B through scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy
- Transcriptome profiling identifies immune response genes against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and Haemophilus parasuis co-infection in the lungs of piglets