Cancer Res Treat.
2010 Jun;42(2):118-120.
A Case of 5-Fluorouracil Induced Encephalopathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kimhj@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
Abstract
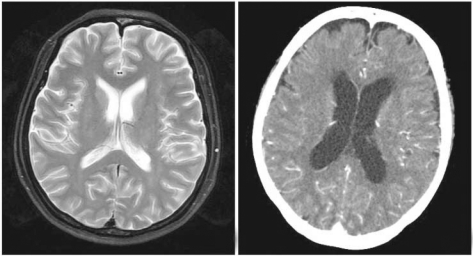
- Patients with reduced dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) activity are at risk for experiencing serious adverse effects following 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) based chemotherapy. Neurotoxicity is considered an extremely rare side effect of 5-FU. We report here on an unusual case of 5-FU induced encephalopathy. A 38-year-old woman with advanced gastric carcinoma was treated with adjuvant chemotherapy that consisted of infused 5-FU (1,000 mg/m2) for 5 days and cisplatin (60 mg/m2) on day 1 following total gastrectomy. Nineteen days after starting chemotherapy, the patient displayed a sudden onset of slurred speech, confusion, cognitive disturbances and paranoia. A magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the brain showed no structural abnormalities, and the other laboratory tests provided no explanations for her symptoms, other than a slightly elevated ammonia level. The patient was treated with a lactulose retention enema and thiamine infusion, the 5-FU was halted and her symptoms then recovered after 7 days.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Grem JL. 5-Fluorouracil: forty-plus and still ticking. A review of its preclinical and clinical development. Invest New Drugs. 2000; 18:299–313. PMID: 11081567.2. Pirzada NA, Ali II, Dafer RM. Fluorouracil-induced neurotoxicity. Ann Pharmacother. 2000; 34:35–38. PMID: 10669184.
Article3. Koenig H, Patel A. Biochemical basis for fluorouracil neurotoxicity. The role of Krebs cycle inhibition by fluoroacetate. Arch Neurol. 1970; 23:155–160. PMID: 5430334.4. Kim YA, Chung HC, Choi HJ, Rha SY, Seong JS, Jeung HC. Intermediate dose 5-fluorouracil-induced encephalopathy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2006; 36:55–59. PMID: 16436463.
Article5. Heier MS, Dornish JM. Effect of the fluoropyrimidines 5-fluorouracil and doxifluridine on cellular uptake of thiamin. Anticancer Res. 1989; 9:1073–1077. PMID: 2530931.6. Heggie GD, Sommadossi JP, Cross DS, Huster WJ, Diasio RB. Clinical pharmacokinetics of 5-fluorouracil and its metabolites in plasma, urine, and bile. Cancer Res. 1987; 47:2203–2206. PMID: 3829006.7. Etienne MC, Lagrange JL, Dassonville O, Fleming R, Thyss A, Renee N, et al. Population study of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12:2248–2253. PMID: 7964939.
Article8. Yeh KH, Cheng AL. High-dose 5-fluorouracil infusional therapy is associated with hyperammonaemia, lactic acidosis and encephalopathy. Br J Cancer. 1997; 75:464–465. PMID: 9020500.
Article9. Cho IJ, Chang HJ, Lee KE, Won HS, Choi MY, Nam EM, et al. A case of Wernicke's encephalopathy following fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:747–750. PMID: 19654964.
Article10. Cheung WY, Fralick RA, Cheng S. The confused cancer patient: a case of 5-fluorouracil-induced encephalopathy. Curr Oncol. 2008; 15:234–236. PMID: 19008998.
Article11. Takimoto CH, Lu ZH, Zhang R, Liang MD, Larson LV, Cantilena LR Jr, et al. Severe neurotoxicity following 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in a patient with dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency. Clin Cancer Res. 1996; 2:477–481. PMID: 9816193.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy after 5-fluorouracil based chemotherapy
- A Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy Following Fluorouracil-based Chemotherapy
- Four cases of transient hyperammonemic encephalopathy following continuous infusion of 5-fluorouracil
- A Case of 5-fluorouracil-induced Phototoxicity
- A Case of Baclofen-induced Encephalopathy