Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2016 Mar;8(2):156-160. 10.4168/aair.2016.8.2.156.
Diagnostic Value of Specific IgE to Peanut and Ara h 2 in Korean Children with Peanut Allergy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Medical Research Institute of Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhlovechild@gmail.com
- 3Environmental Health Center for Atopic Diseases, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Biostatistics, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2165932
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2016.8.2.156
Abstract
- PURPOSE
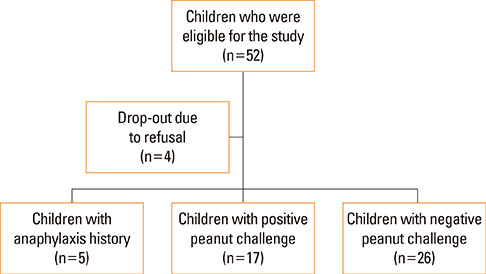
The purpose of this study was to establish the diagnostic decision point (DDP) of peanut specific IgE (sIgE) for predicting the outcome of oral food challenge (OFC). We also evaluated the usefulness of sIgE to peanut components (Ara h 1, 2, 3, 8, and 9) in diagnosing peanut allergy.
METHODS
Korean children aged over 12 months with a suspected peanut allergy were enrolled. Diagnosis of peanut allergy was confirmed by an open OFC or through the convincing history of anaphylaxis. Cutoff levels of sIgE to peanut and peanut components were determined by analyzing receiver operating characteristic curves.
RESULTS
Forty-eight children (22 boys and 26 girls) with a suspected peanut allergy were enrolled. The previously established DDP for peanut-sIgE antibodies (14 kU/L) showed a sensitivity of 22.7%, specificity of 100%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 100%, and negative predictive value of 60.4% in our study population. The median levels of peanut-sIgE (5.4 kU/L vs 1.1 kU/L, P<0.001) and Ara h 2-sIgE (0.8 kU/L vs 0 kU/L, P<0.001) were significantly higher in the peanut allergy group than in the peanut tolerance group. The peanut-sIgE concentration indicating a PPV of 100% was 10.3 kU/L. The Ara h 2-sIgE level of 4.0 kU/L had a PPV of 100%.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results showed that the cutoff levels for peanut (10.3 kU/L) and Ara h 2 (4.0 kU/L) established in this study is useful for the diagnosis of peanut allergy in Korean children.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Update on Early Nutrition and Food Allergy in Children
Sun Eun Lee, Hyeyoung Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(3):542-548. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.3.542.The past, present, and future of the research on food allergy in Korean children
Kangmo Ahn
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(Suppl 1):S44-S51. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.S1.S44.
Reference
-
1. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Peanut allergy: emerging concepts and approaches for an apparent epidemic. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:491–503.2. Le TM, Lindner TM, Pasmans SG, Guikers CL, van Hoffen E, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, et al. Reported food allergy to peanut, tree nuts and fruit: comparison of clinical manifestations, prescription of medication and impact on daily life. Allergy. 2008; 63:910–916.3. Shek LP, Cabrera-Morales EA, Soh SE, Gerez I, Ng PZ, Yi FC, et al. A population-based questionnaire survey on the prevalence of peanut, tree nut, and shellfish allergy in 2 Asian populations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:324–331. 331.e1–331.e7.4. Lao-araya M, Trakultivakorn M. Prevalence of food allergy among preschool children in northern Thailand. Pediatr Int. 2012; 54:238–243.5. Sicherer SH. Epidemiology of food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:594–602.6. Sicherer SH, Muñoz-Furlong A, Godbold JH, Sampson HA. US prevalence of self-reported peanut, tree nut, and sesame allergy: 11-year follow-up. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:1322–1326.7. Sicherer SH, Wood RA. Advances in diagnosing peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2013; 1:1–13.8. Kim J, Chang E, Han Y, Ahn K, Lee SI. The incidence and risk factors of immediate type food allergy during the first year of life in Korean infants: a birth cohort study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011; 22:715–719.9. Park M, Kim D, Ahn K, Kim J, Han Y. Prevalence of immediate-type food allergy in early childhood in seoul. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:131–136.10. Fleischer DM. The natural history of peanut and tree nut allergy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2007; 7:175–181.11. Sampson HA. Update on food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:805–819.12. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:S116–S125.13. Kim J, Kim HY, Park MR, Choi J, Shim JY, Kim MJ, et al. Diagnostic decision points of specific IgE concentrations in Korean children with egg and cow's milk allergies. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:332–338.14. Sampson HA. Utility of food-specific IgE concentrations in predicting symptomatic food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:891–896.15. Klemans RJ, Otte D, Knol M, Knol EF, Meijer Y, Gmelig-Meyling FH, et al. The diagnostic value of specific IgE to Ara h 2 to predict peanut allergy in children is comparable to a validated and updated diagnostic prediction model. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:157–163.16. Codreanu F, Collignon O, Roitel O, Thouvenot B, Sauvage C, Vilain AC, et al. A novel immunoassay using recombinant allergens simplifies peanut allergy diagnosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 154:216–226.17. Nicolaou N, Murray C, Belgrave D, Poorafshar M, Simpson A, Custovic A. Quantification of specific IgE to whole peanut extract and peanut components in prediction of peanut allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:684–685.18. Kim J, Lee JY, Han Y, Ahn K. Significance of Ara h 2 in clinical reactivity and effect of cooking methods on allergenicity. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013; 110:34–38.19. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Dimov V, Ebisawa M, El-Gamal YM, Lockey RF, et al. World Allergy Organization Anaphylaxis Guidelines: 2013 update of the evidence base. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013; 162:193–204.20. Song TW, Kim KW, Kim WK, Kim JH, Kim HH, Park YM, et al. Guidelines for the oral food challenges in children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012; 22:4–20.21. Bindslev-Jensen C, Ballmer-Weber BK, Bengtsson U, Blanco C, Ebner C, Hourihane J, et al. Standardization of food challenges in patients with immediate reactions to foods--position paper from the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology. Allergy. 2004; 59:690–697.22. Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Assa'ad AH, Bahna SL, Bock SA, Sicherer SH, Teuber SS. Work Group report: oral food challenge testing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:S365–S383.23. Wainstein BK, Yee A, Jelley D, Ziegler M, Ziegler JB. Combining skin prick, immediate skin application and specific-IgE testing in the diagnosis of peanut allergy in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007; 18:231–239.24. Roehr CC, Edenharter G, Reimann S, Ehlers I, Worm M, Zuberbier T, et al. Food allergy and non-allergic food hypersensitivity in children and adolescents. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:1534–1541.25. Vereda A, van Hage M, Ahlstedt S, Ibañez MD, Cuesta-Herranz J, van Odijk J, et al. Peanut allergy: clinical and immunologic differences among patients from 3 different geographic regions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:603–607.26. Flinterman AE, van Hoffen E, den Hartog Jager CF, Koppelman S, Pasmans SG, Hoekstra MO, et al. Children with peanut allergy recognize predominantly Ara h2 and Ara h6, which remains stable over time. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:1221–1228.27. Chiang WC, Pons L, Kidon MI, Liew WK, Goh A, Wesley Burks A. Serological and clinical characteristics of children with peanut sensitization in an Asian community. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21:e429–e438.28. Nicolaou N, Poorafshar M, Murray C, Simpson A, Winell H, Kerry G, et al. Allergy or tolerance in children sensitized to peanut: prevalence and differentiation using component-resolved diagnostics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:191–197. e1–e13.29. Dang TD, Tang M, Choo S, Licciardi PV, Koplin JJ, Martin PE, et al. Increasing the accuracy of peanut allergy diagnosis by using Ara h 2. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:1056–1063.30. Keet CA, Johnson K, Savage JH, Hamilton RG, Wood RA. Evaluation of Ara h2 IgE thresholds in the diagnosis of peanut allergy in a clinical population. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2013; 1:101–103.31. Dyer AA, Rivkina V, Perumal D, Smeltzer BM, Smith BM, Gupta RS. Epidemiology of childhood peanut allergy. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2015; 36:58–64.32. Ho MH, Lee SL, Wong WH, Ip P, Lau YL. Prevalence of self-reported food allergy in Hong Kong children and teens--a population survey. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2012; 30:275–284.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Cooking Methods on Peanut Allergenicity
- Clinical Significance of Component Allergens in Fagales Pollen-Sensitized Peanut Allergy in Korea
- Changes in Major Peanut Allergens Under Different pH Conditions
- Development and Expression of Recombinant Ara h 1 Fragment Proteins
- A Case of Anaphylaxis Induced by Peanut