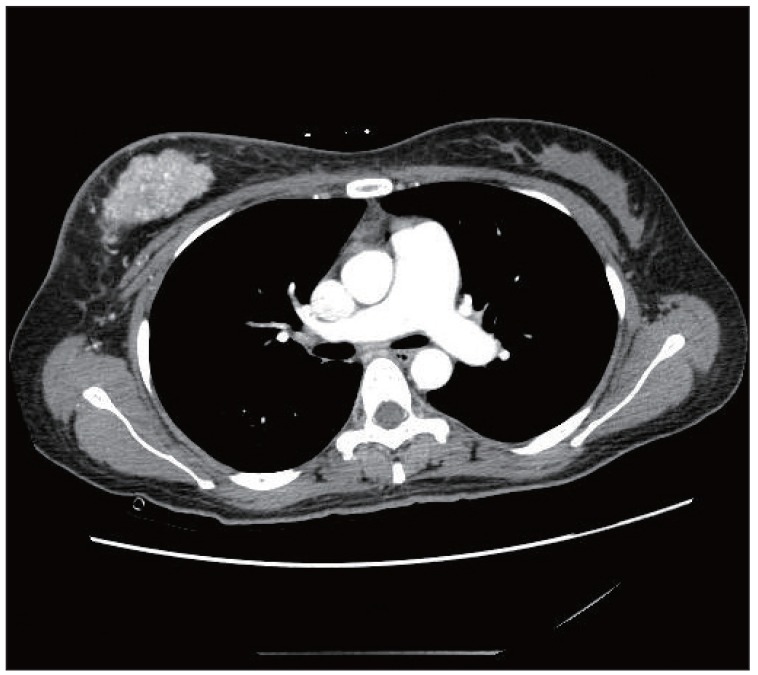
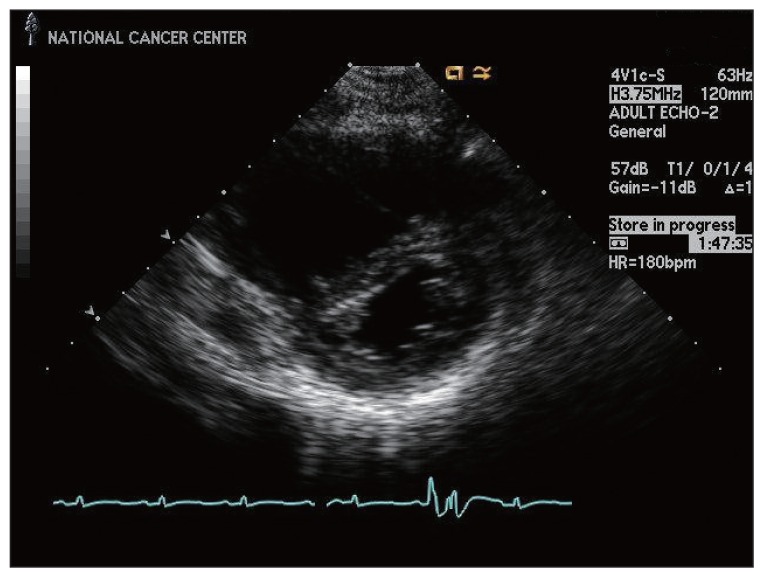
Cancer Res Treat.
2012 Dec;44(4):267-270.
A Case of Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Complicated by Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Center for Breast Cancer, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. jungsro@ncc.re.kr
Abstract
- Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy (PTTM) is a rare, malignancy-related complication that causes marked pulmonary hypertension, right heart failure, and death. We report on a patient with locally advanced breast cancer whose course was complicated by fatal PTTM based on clinical and laboratory findings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. von Herbay A, Illes A, Waldherr R, Otto HF. Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy with pulmonary hypertension. Cancer. 1990; 66:587–592. PMID: 2163747.
Article2. Pinckard JK, Wick MR. Tumor-related thrombotic pulmonary microangiopathy: review of pathologic findings and pathophysiologic mechanisms. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2000; 4:154–157. PMID: 10919385.
Article3. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 19-1995. A 55 year-old woman with acute respiratory failure and radiographically clear lungs. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332:1700–1707. PMID: 7760872.4. Chinen K, Fujino T, Horita A, Sakamoto A, Fujioka Y. Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy caused by an ovarian cancer expressing tissue factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. Pathol Res Pract. 2009; 205:63–68. PMID: 18835104.
Article5. Chinen K, Kazumoto T, Ohkura Y, Matsubara O, Tsuchiya E. Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy caused by a gastric carcinoma expressing vascular endothelial growth factor and tissue factor. Pathol Int. 2005; 55:27–31. PMID: 15660700.
Article6. Takahashi F, Kumasaka T, Nagaoka T, Wakiya M, Fujii H, Shimizu K, et al. Osteopontin expression in pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy caused by gastric carcinoma. Pathol Int. 2009; 59:752–756. PMID: 19788622.
Article7. Babar SI, Sobonya RE, Snyder LS. Pulmonary microvascular cytology for the diagnosis of pulmonary tumor embolism. West J Med. 1998; 168:47–50. PMID: 9448497.8. Miyano S, Izumi S, Takeda Y, Tokuhara M, Mochizuki M, Matsubara O, et al. Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:597–599. PMID: 17290069.
Article9. Bachelot T, Ray-Coquard I, Menetrier-Caux C, Rastkha M, Duc A, Blay JY. Prognostic value of serum levels of interleukin 6 and of serum and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in hormone-refractory metastatic breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2003; 88:1721–1726. PMID: 12771987.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in a patient with breast cancer
- Fatal progressive right heart failure in a pancreatic cancer patient
- Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy Associated with Advanced Gastric Cancer Successfully Treated with Chemotherapy
- Acute cor pulmonale due to pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy in two patients with breast cancer
- A Case Report: Cavitary Infarction Caused by Pulmonary Tumor Thrombotic Microangiopathy in a Patient with Pancreatic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm