J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Aug;28(8):1139-1144. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1139.
The Effects of Antihypertensive Drugs on Bone Mineral Density in Ovariectomized Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. rhcow1@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Convergent Research Consortium for Immunologic Disease, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1793017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1139
Abstract
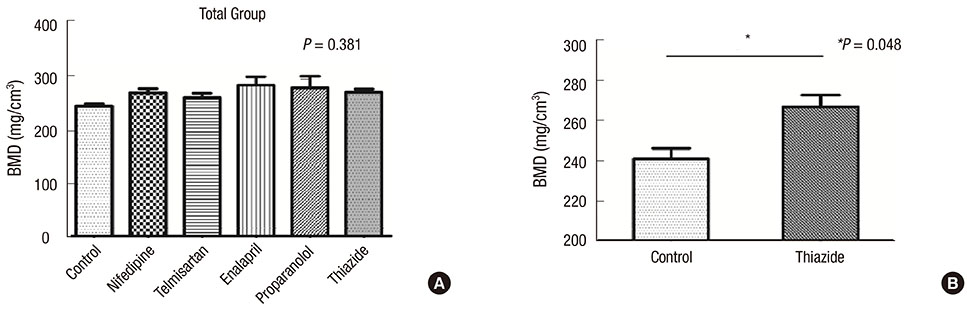
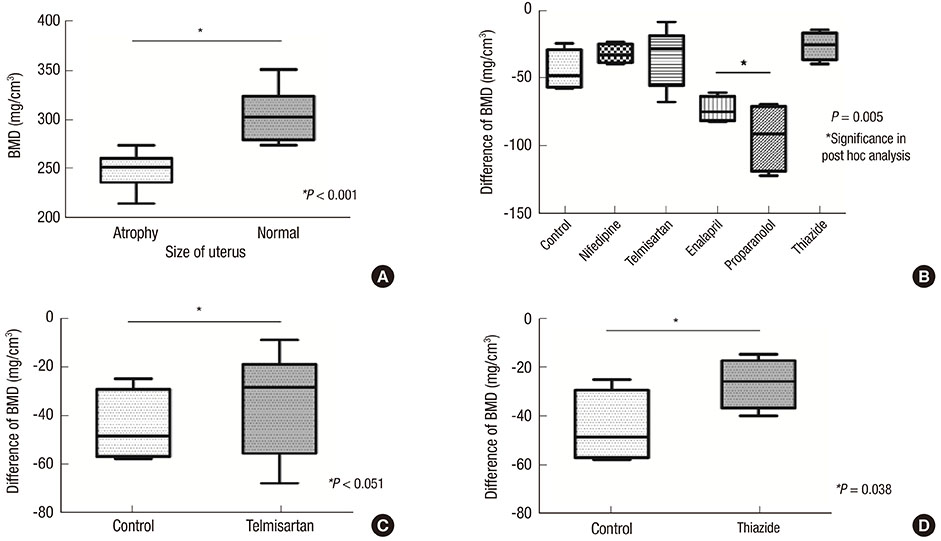
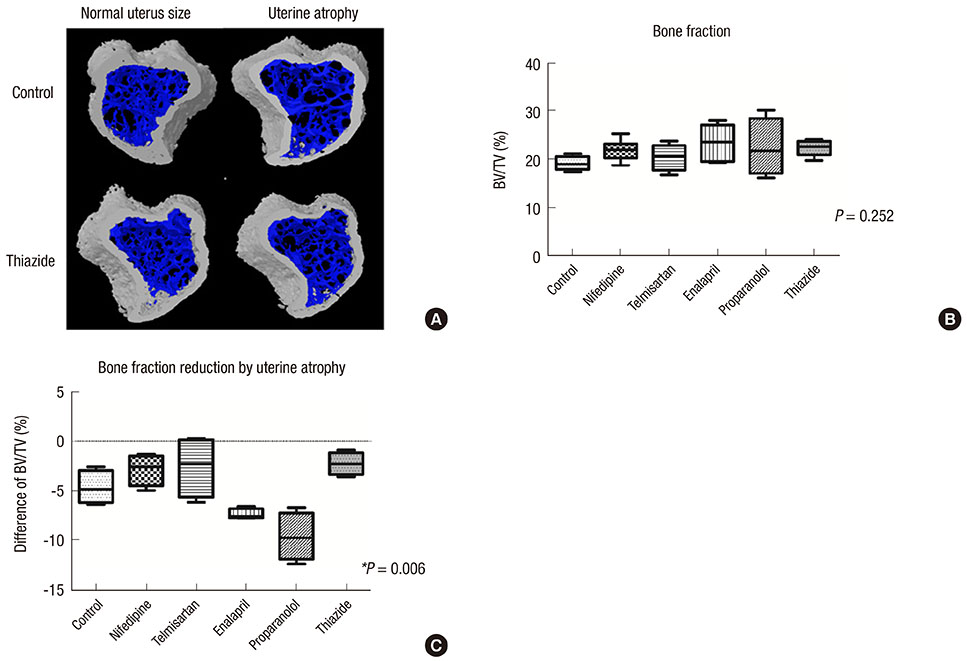
- The effects of several antihypertensive drugs on bone mineral density (BMD) and micro-architectural changes in ovariectomized (OVX) mice were investigated. Eight-week-old female C57/BL6 mice were used for this study. Three days after ovariectomy, mice were treated intraperitoneally with nifedipine (15 mg/kg), telmisartan (5 mg/kg), enalapril (20 mg/kg), propranolol (1 mg/kg) or hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg/kg) for 35 consecutive days. Uterine atrophy of all mice was confirmed to evaluate estrogen deficiency state. BMD and micro-architectural analyses were performed on tibial proximal ends by micro-computed tomography (micro-CT). When OVX mice with uterine atrophy were compared with mice without atrophy, BMD decreased (P < 0.001). There were significant differences in BMD loss between different antihypertensive drugs (P = 0.005). Enalapril and propranolol increased BMD loss in mice with atrophied uteri compared with control mice. By contrast, thiazide increased BMD in mice with uterine atrophy compared with vehicle-treated mice (P = 0.048). Thiazide (P = 0.032) and telmisartan (P = 0.051) reduced bone loss and bone fraction in mice with uterine atrophy compared with the control. Thiazide affects BMD in OVX mice positively. The reduction in bone loss by thiazide and telmisartan suggest that these drugs may benefit menopausal women with hypertension and osteoporosis.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antihypertensive Agents/*pharmacology
Atrophy
Benzimidazoles/pharmacology
Benzoates/pharmacology
Bone Density/*drug effects
Enalapril/pharmacology
Female
Mice
Mice, Inbred C57BL
Ovariectomy
Propranolol/pharmacology
Thiazides/pharmacology
Tibia/radiography
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Uterus/anatomy & histology/pathology
Antihypertensive Agents
Benzimidazoles
Benzoates
Thiazides
Enalapril
Propranolol
Figure
Reference
-
1. Riggs BL, Khosla S, Melton LJ 3rd. Sex steroids and the construction and conservation of the adult skeleton. Endocr Rev. 2002; 23:279–302.2. Melton LJ 3rd, Chrischilles EA, Cooper C, Lane AW, Riggs BL. How many women have osteoporosis? JBMR Anniversary Classic: JBMR, volume 7, number 9, 1992. J Bone Miner Res. 2005; 20:886–892.3. Ott SM, LaCroix AZ, Scholes D, Ichikawa LE, Wu K. Effects of three years of low-dose thiazides on mineral metabolism in healthy elderly persons. Osteoporos Int. 2008; 19:1315–1322.4. Rejnmark L, Vestergaard P, Mosekilde L. Treatment with beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium-channel blockers is associated with a reduced fracture risk: a nationwide case-control study. J Hypertens. 2006; 24:581–589.5. Wiens M, Etminan M, Gill SS, Takkouche B. Effects of antihypertensive drug treatments on fracture outcomes: a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Intern Med. 2006; 260:350–362.6. Solomon DH, Mogun H, Garneau K, Fischer MA. Risk of fractures in older adults using antihypertensive medications. J Bone Miner Res. 2011; 26:1561–1567.7. Yang S, Nguyen ND, Center JR, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV. Association between beta-blocker use and fracture risk: the Dubbo Osteoporosis Epidemiology Study. Bone. 2011; 48:451–455.8. Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ, Müller R. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res. 2010; 25:1468–1486.9. Otto C, Kantner I, Nubbemeyer R, Schkoldow J, Fuchs I, Krahl E, Vonk R, Schüler C, Fritzemeier KH, Erben RG. Estradiol release kinetics determine tissue response in ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology. 2012; 153:1725–1733.10. Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, et al. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003; 289:2560–2572.11. Ilić K, Obradović N, Vujasinović-Stupar N. The relationship among hypertension, antihypertensive medications, and osteoporosis: a narrative review. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013; 92:217–227.12. Cauley JA, Cummings SR, Seeley DG, Black D, Browner W, Kuller LH, Nevitt MC. Effects of thiazide diuretic therapy on bone mass, fractures, and falls: the Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Ann Intern Med. 1993; 118:666–673.13. Lynn H, Kwok T, Wong SY, Woo J, Leung PC. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor use is associated with higher bone mineral density in elderly Chinese. Bone. 2006; 38:584–588.14. Bolland MJ, Ames RW, Horne AM, Orr-Walker BJ, Gamble GD, Reid IR. The effect of treatment with a thiazide diuretic for 4 years on bone density in normal postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2007; 18:479–486.15. LaCroix AZ, Ott SM, Ichikawa L, Scholes D, Barlow WE. Low-dose hydrochlorothiazide and preservation of bone mineral density in older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2000; 133:516–526.16. Reid IR, Ames RW, Orr-Walker BJ, Clearwater JM, Horne AM, Evans MC, Murray MA, McNeil AR, Gamble GD. Hydrochlorothiazide reduces loss of cortical bone in normal postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Med. 2000; 109:362–370.17. Walsh JS, Newman C, Eastell R. Heart drugs that affect bone. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 23:163–168.18. Lalande A, Roux S, Denne MA, Stanley ER, Schiavi P, Guez D, De Vernejoul MC. Indapamide, a thiazide-like diuretic, decreases bone resorption in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2001; 16:361–370.19. Pasco JA, Henry MJ, Sanders KM, Kotowicz MA, Seeman E, Nicholson GC. Geelong Osteoporosis Study. Beta-adrenergic blockers reduce the risk of fracture partly by increasing bone mineral density: geelong osteoporosis Study. J Bone Miner Res. 2004; 19:19–24.20. Rejnmark L, Vestergaard P, Kassem M, Christoffersen BR, Kolthoff N, Brixen K, Mosekilde L. Fracture risk in perimenopausal women treated with beta-blockers. Calcif Tissue Int. 2004; 75:365–372.21. Reid IR, Gamble GD, Grey AB, Black DM, Ensrud KE, Browner WS, Bauer DC. Beta-Blocker use, BMD, and fractures in the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2005; 20:613–618.22. Pierroz DD, Bouxsein ML, Rizzoli R, Ferrari SL. Combined treatment with a beta-blocker and intermittent PTH improves bone mass and microarchitecture in ovariectomized mice. Bone. 2006; 39:260–267.23. Shimizu H, Nakagami H, Osako MK, Hanayama R, Kunugiza Y, Kizawa T, Tomita T, Yoshikawa H, Ogihara T, Morishita R. Angiotensin II accelerates osteoporosis by activating osteoclasts. FASEB J. 2008; 22:2465–2475.24. Liu YY, Yao WM, Wu T, Xu BL, Chen F, Cui L. Captopril improves osteopenia in ovariectomized rats and promotes bone formation in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Metab. 2011; 29:149–158.25. Broulík PD, Tesar V, Zima T, Jirsa M. Impact of antihypertensive therapy on the skeleton: effects of enalapril and AT1 receptor antagonist losartan in female rats. Physiol Res. 2001; 50:353–358.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Nutrient Intake, Bone Mineral Density and Bone Mineral Content in Ovariectomized Women
- Erratum: Title Correction. The Role of The Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Bone Mineral Density and Bone Mineral Content in Ovariectomized Rats Compensation in Rats
- Effects of Caffeine on Bone Mineral Density and Bone Mineral Content in Ovariectomized Rats
- Differential Skeletal Response to Ovariectomy in Young and Old Rats
- Effects of taurine supplementation on bone mineral density in ovariectomized rats fed calcium deficient diet