Korean J Orthod.
2014 Sep;44(5):254-262. 10.4041/kjod.2014.44.5.254.
The relation between idiopathic scoliosis and the frontal and lateral facial form
- Affiliations
-
- 1Korea University Graduate School, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Private Practice, Ansan, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthodontics, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthodontics, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. dong09@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1726419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2014.44.5.254
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relation between idiopathic scoliosis and facial deformity in the horizontal, vertical, and anteroposterior planes.
METHODS
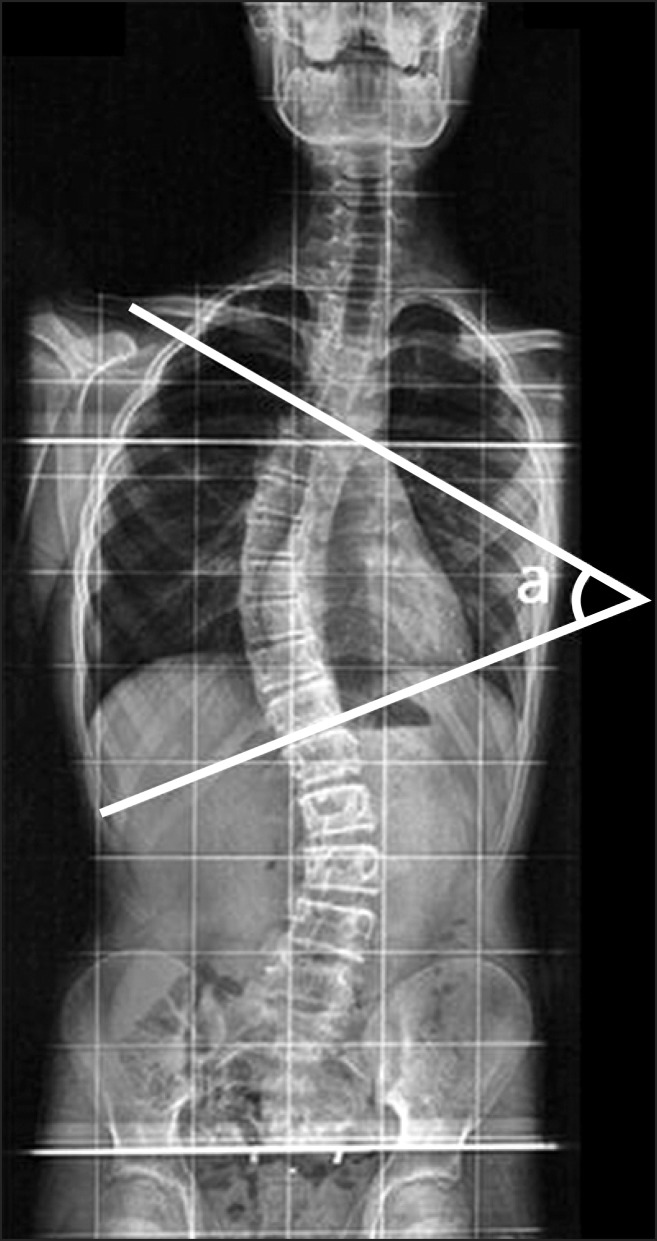
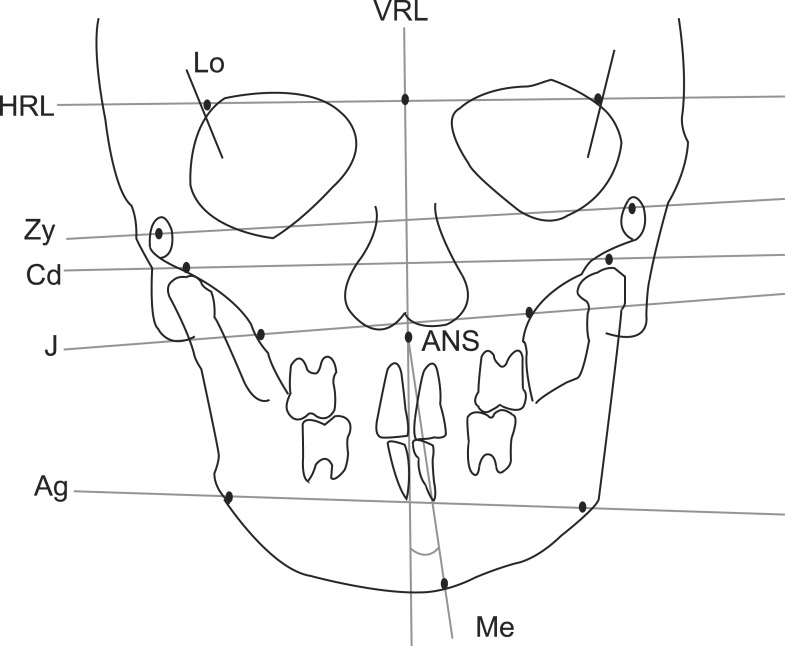
A total of 123 female patients aged 14 years or older, who visited the Spine Clinic at the Department of Orthopedics, Korea University Guro Hospital for treatment of idiopathic scoliosis, were enrolled. Whole-spine anteroposterior and lateral radiographs were taken with the patient in a naturally erect position, and frontal and lateral cephalograms were taken in an erect position with the Frankfort horizontal line parallel to the floor. Scoliosis was classified according to the Cobb angle and Lenke classification of six curve types. Cephalometric tracing in all cases was carried out with V-Ceph 5.5 by the same orthodontist. The Kruskal-Wallis test was performed to determine whether any relation existed between each group of the idiopathic scoliosis classification and the cephalometric measurements of frontal and lateral cephalograms.
RESULTS
The measurements did not reveal any significant association between the Cobb angle and cephalometric measurements and between the curve type based on the Lenke classification and cephalometric measurements.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of this study, no apparent relation was observed between the severity of scoliosis and facial form variations in idiopathic scoliosis patients.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Occlusal deviations in adolescents with idiopathic and congenital scoliosis
Hao Zhang, Jingbo Ma, Zhicheng Zhang, Yafei Feng, Chuan Cai, Chao Wang
Korean J Orthod. 2022;52(3):165-171. doi: 10.4041/kjod21.259.
Reference
-
1. Severt TR, Proffit WR. The prevalence of facial asymmetry in the dentofacial deformities population at the University of North Carolina. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1997; 12:171–176. PMID: 9511487.2. Samman N, Tong AC, Cheung DL, Tideman H. Analysis of 300 dentofacial deformities in Hong Kong. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1992; 7:181–185. PMID: 1291612.3. Harila V, Valkama M, Sato K, Tolleson S, Hanis S, Kau CH, et al. Occlusal asymmetries in children with congenital hip dislocation. Eur J Orthod. 2012; 34:307–311. PMID: 21303807.
Article4. Morel-Verdebout C, Botteron S, Kiliaridis S. Dentofacial characteristics of growing patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a morphological study. Eur J Orthod. 2007; 29:500–507. PMID: 17974540.
Article5. Lee CK, Koo KH, An JH. The classification of idiopathic scoliosis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2007; 14:57–66.
Article6. Lippold C, Danesh G, Hoppe G, Drerup B, Hackenberg L. Trunk inclination, pelvic tilt and pelvic rotation in relation to the craniofacial morphology in adults. Angle Orthod. 2007; 77:29–35. PMID: 17029550.
Article7. Pedrotti L, Mora R, Bertani B, Tuvo G, Crivellari I. Association among postural and skull-cervicomandibular disorders in childhood and adolescence. Analysis of 428 subjects. Pediatr Med Chir. 2007; 29:94–98. PMID: 17461096.8. Lenke LG, Betz RR, Harms J, Bridwell KH, Clements DH, Lowe TG, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83-A:1169–1181. PMID: 11507125.9. Letzer GM, Kronman JH. A posteroanterior cephalometric evaluation of craniofacial asymmetry. Angle Orthod. 1967; 37:205–211. PMID: 19919216.10. Major PW, Johnson DE, Hesse KL, Glover KE. Landmark identification error in posterior anterior cephalometrics. Angle Orthod. 1994; 64:447–454. PMID: 7864466.11. Cho JH, Moon JY. Comparison of midsagittal reference plane in PA cephalogram and 3D CT. Korean J Orthod. 2010; 40:6–15.
Article12. Huggare J. Association between morphology of the first cervical vertebra, head posture, and craniofacial structures. Eur J Orthod. 1991; 13:435–440. PMID: 1817068.
Article13. Solow B, Sonnesen L. Head posture and malocclusions. Eur J Orthod. 1998; 20:685–693. PMID: 9926635.
Article14. Ozbek MM, Köklü A. Natural cervical inclination and craniofacial structure. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993; 104:584–591. PMID: 8249934.15. Houston WJ. Mandibular growth rotations--their mechanisms and importance. Eur J Orthod. 1988; 10:369–373. PMID: 3061834.
Article16. Solow B, Sandham A. Cranio-cervical posture: a factor in the development and function of the dentofacial structures. Eur J Orthod. 2002; 24:447–456. PMID: 12407940.
Article17. Motoyoshi M, Shimazaki T, Sugai T, Namura S. Biomechanical influences of head posture on occlusion: an experimental study using finite element analysis. Eur J Orthod. 2002; 24:319–326. PMID: 12198861.
Article18. Ben-Bassat Y, Yitschaky M, Kaplan L, Brin I. Occlusal patterns in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006; 130:629–633. PMID: 17110260.
Article19. Hong JY, Suh SW, Modi HN, Yang JH, Hwang YC, Lee DY, et al. Correlation between facial asymmetry, shoulder imbalance, and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Orthopedics. 2011; 34:187. PMID: 21667906.
Article20. Saccucci M, Tettamanti L, Mummolo S, Polimeni A, Festa F, Tecco S. Scoliosis and dental occlusion: a review of the literature. Scoliosis. 2011; 6:15. PMID: 21801357.
Article21. Segatto E, Lippold C, Végh A. Craniofacial features of children with spinal deformities. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008; 9:169. PMID: 19102760.
Article22. Korbmacher H, Koch L, Eggers-Stroeder G, Kahl-Nieke B. Associations between orthopaedic disturbances and unilateral crossbite in children with asymmetry of the upper cervical spine. Eur J Orthod. 2007; 29:100–104. PMID: 17290022.
Article23. King HA, Moe JH, Bradford DS, Winter RB. The selection of fusion levels in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983; 65:1302–1313. PMID: 6654943.
Article24. Cummings RJ, Loveless EA, Campbell J, Samelson S, Mazur JM. Interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility of the system of King et al. for the classification of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80:1107–1111. PMID: 9730119.
Article25. Lenke LG, Betz RR, Bridwell KH, Clements DH, Harms J, Lowe TG, et al. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability of the classification of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80:1097–1106. PMID: 9730118.
Article26. Lenke LG, Betz RR, Haher TR, Lapp MA, Merola AA, Harms J, et al. Multisurgeon assessment of surgical decision-making in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: curve classification, operative approach, and fusion levels. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:2347–2353. PMID: 11679820.27. Puno RM, An KC, Puno RL, Jacob A, Chung SS. Treatment recommendations for idiopathic scoliosis: an assessment of the Lenke classification. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:2102–2114. discussion 2114-5. PMID: 14501921.28. Suk SI. Introduction of spinal deformity and idiopathic scoliosis. Spinal surgery. 2nd ed. Seoul: Newest Medical Publishing;2004. p. 311–361.29. Huggare J, Pirttiniemi P, Serlo W. Head posture and dentofacial morphology in subjects treated for scoliosis. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1991; 87:151–158. PMID: 2057482.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Classification of Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Relation of Radiographic Parameters and Psychosocial Condition in Idiopathic Adolescent Scoliosis
- The association between idiopathic scoliosis and growth hormone treatment in short children
- Correction in Rotational Deformity with Thoracolumbosacral Orthosis in Idiopathic Scoliosis
- A Clinical Study of Scoliosis