Ann Lab Med.
2012 Sep;32(5):362-365. 10.3343/alm.2012.32.5.362.
Detection of RUNX1-MECOM Fusion Gene and t(3;21) in a Very Elderly Patient Having Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Myelodysplasia-Related Changes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. 153jesus@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Hematology-Oncology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1387352
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2012.32.5.362
Abstract
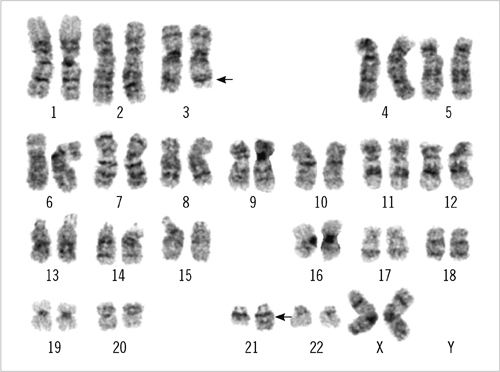
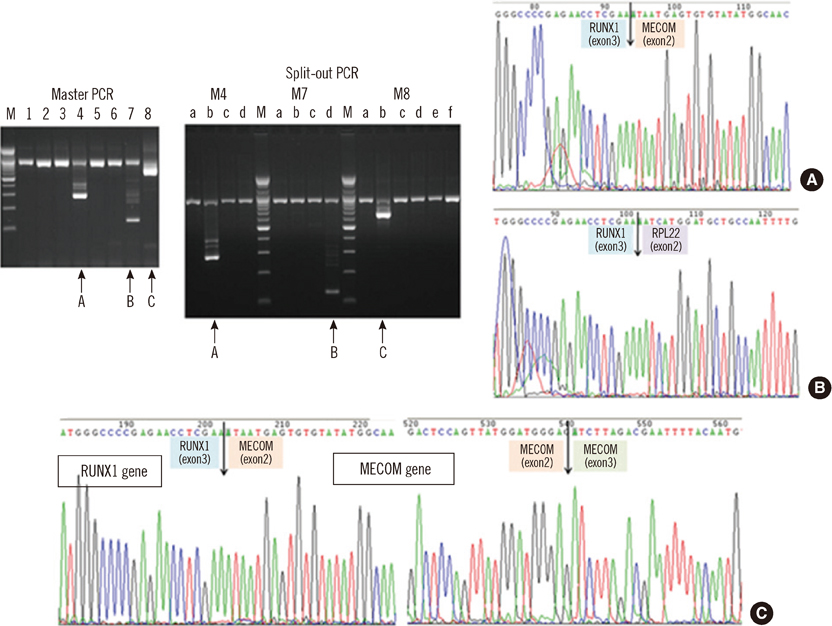
- An 87-yr-old woman was diagnosed with AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC). The initial complete blood count showed Hb level of 5.9 g/dL, platelet counts of 27x10(9)/L, and white blood cell counts of 85.33x10(9)/L with 55% blasts. Peripheral blood samples were used in all the tests, as bone marrow examination could not be performed because of the patient's extremely advanced age and poor general health condition. Flow cytometric analysis, chromosome analysis, FISH, and reverse transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR) results indicated AML-MRC resulting from t(3;21) with the RUNX1-MECOM fusion gene. To our knowledge, this is the second most elderly de novo AML patient associated with t(3;21) to be reported.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged, 80 and over
Blood Cells/pathology
Chromosomes, Human, Pair 21
Chromosomes, Human, Pair 3
Female
Humans
Karyotyping
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute/complications/*diagnosis/genetics
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
Myelodysplastic Syndromes/complications/*diagnosis/genetics
Oncogene Proteins, Fusion/*genetics
Sequence Analysis, DNA
*Translocation, Genetic
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jaffe ES, Harris NL, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics: Tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 2008. Lyon, France: IARC Press.2. Miyazaki Y, Kuriyama K, Miyawaki S, Ohtake S, Sakamaki H, Matsuo T, et al. Cytogenetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) with trilineage dysplasia: Japan Adult Leukaemia Study Group-AML 92 study. Br J Haematol. 2003. 120:56–62.
Article3. Yanada M, Suzuki M, Kawashima K, Kiyoi H, Kinoshita T, Emi N, et al. Long-term outcomes for unselected patients with acute myeloid leukemia categorized according to the World Health Organization classification: a single-center experience. Eur J Haematol. 2005. 74:418–423.
Article4. Lim G, Choi JR, Kim MJ, Kim SY, Lee HJ, Suh JT, et al. Detection of t(3;5) and NPM1/MLF1 rearrangement in an elderly patient with acute myeloid leukemia: clinical and laboratory study with review of the literature. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2010. 199:101–109.
Article5. Lim G, Kim MJ, Oh SH, Cho SY, Lee HJ, Suh JT, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia associated with t(1;3)(p36;q21) and extreme thrombocytosis: a clinical study with literature review. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2010. 203:187–192.
Article6. Park TS, Choi JR, Yoon SH, Song J, Kim J, Kim SJ, et al. Acute promyelocytic leukemia relapsing as secondary acute myelogenous leukemia with translocation t(3;21)(q26;q22) and RUNX1-MDS1-EVI1 fusion transcript. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2008. 187:61–73.
Article7. Bobadilla D, Enriguez EL, Alvarez G, Gaytan P, Smith D, Slovak ML. An interphase fluorescence in situ hybridisation assay for the detection of 3q26.2/EV1 rearrangements in myeloid malignancies. Br J Haematol. 2007. 136:806–813.8. Yin CC, Cortes J, Barkoh B, Hayes K, Kantarjian H, Jones D. t(3;21) (q26;q22) in myeloid leukemia: an aggressive syndrome of blast transformation associated with hydroxyurea or antimetabolite therapy. Cancer. 2006. 106:1730–1738.9. Jeandidier E, Dastugue N, Mugneret F, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Mozziconacci MJ, Herens C, et al. Abnormalities of the long arm of chromosome 21 in 107 patients with hematopoietic disorders: a collaborative retrospective study of the Groupe Français de Cytogénétique Hématologique. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006. 166:1–11.
Article10. Poppe B, Dastugue N, Vandesompele J, Cauwelier B, De Smet B, Yigit N, et al. EVI1 is consistently expressed as principal transcript in common and rare recurrent 3q26 rearrangements. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2006. 45:349–356.11. Fears S, Mathieu C, Zeleznik-Le N, Huang S, Rowley JD, Nucifora G. Intergenic splicing of MDS1 and EVI1 occurs in normal tissues as well as in myeloid leukemia and produces a new member of the PR domain family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. 93:1642–1647.
Article12. Sood R, Talwar-Trikha A, Chakrabarti SR, Nucifora G. MDS1/EVI1 enhances TGF-beta1 signaling and strengthens its growth-inhibitory effect but the leukemia-associated fusion protein AML1/MDS1/EVI1, product of the t(3;21), abrogates growth-inhibition in response to TGF-beta1. Leukemia. 1999. 13:348–357.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Concurrent Chromosomal Aberrations Involving Three-way t(3;21;8)(p21;q22;q22) and Two-way t(2;11)(q31;p15) Translocations in a Case of de novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Myeloid Sarcoma in Patients with RUNX1/RUNX1T1 Positive AML and a c-kit Mutation
- A Novel Translocation Involving RUNX1 and HOXA Gene Clusters in a Case of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(7;21)(p15;q22)
- A Pediatric Case of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(3;5)(q25;q34)
- Near-tetraploidy Acute Myeloid Leukemia with RUNX1-RUNX1T1 Rearrangement Due to Cryptic t(8;21)