Blood Res.
2023 Dec;58(4):194-200. 10.5045/br.2023.2023206.
A multi-center and non-interventional registry of brentuximab vedotin in patients with relapsed or refractory CD30-positive lymphoma: the CISL1803/BRAVO study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 5Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- 6Center of Evidence Based Medicine, Institute of Convergence Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea
- 8Hematology-Oncology Clinic, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 11Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Ulsan, Korea
- 12Department of Hematology and Oncology, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
- 13Department of Hematology and Oncology, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea
- KMID: 2550197
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2023.2023206
Abstract
- Background
Brentuximab vedotin (BV), a potent antibody-drug conjugate, targets the CD30 antigen. In Korea, BV has been approved for the treatment of relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), and cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, including mycosis fungoides (MF). However, there are limited data reflecting real-world experiences with BV treatment for HL, ALCL, and MF.
Methods
This was a multicenter, non-interventional registry study of the efficacy and safety of BV in patients with relapsed or refractory CD30-positive lymphoma (CISL1803/BRAVO). Outcomes were determined based on the occurrence of relapse or progression and overall survival after BV treatment.
Results
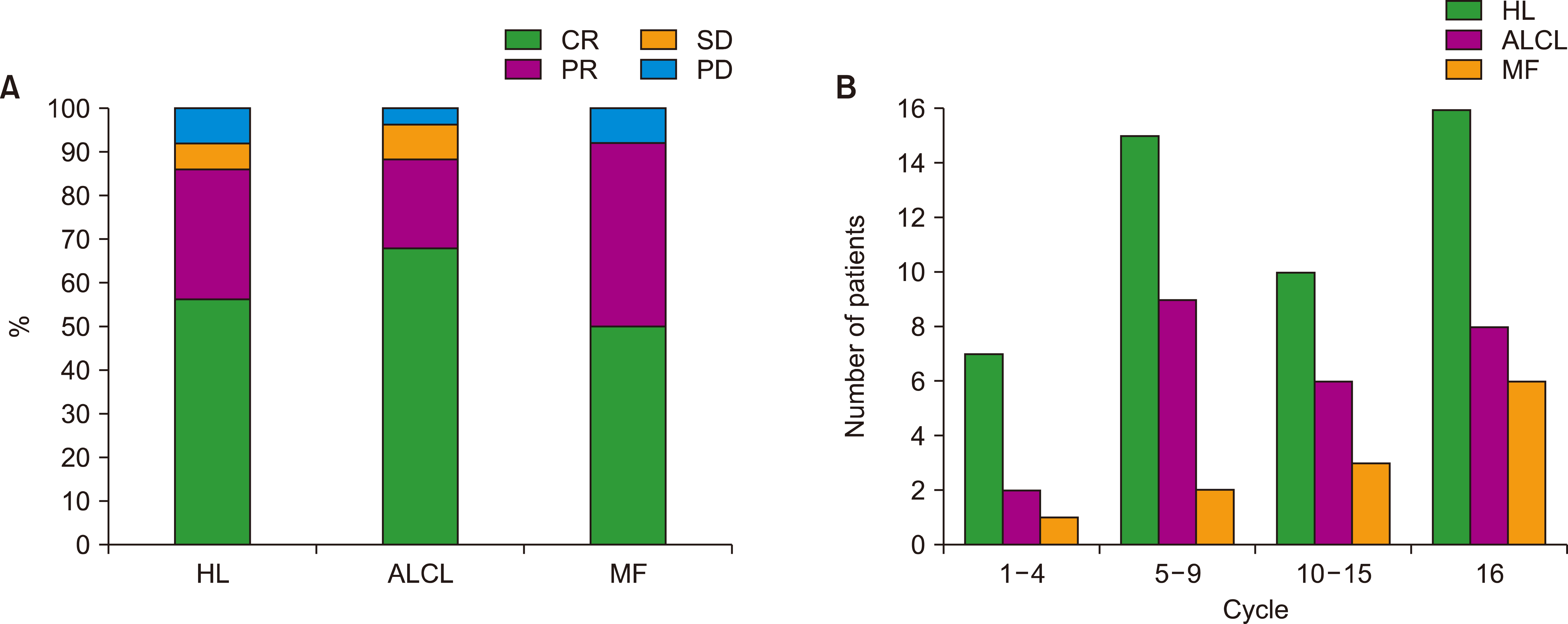
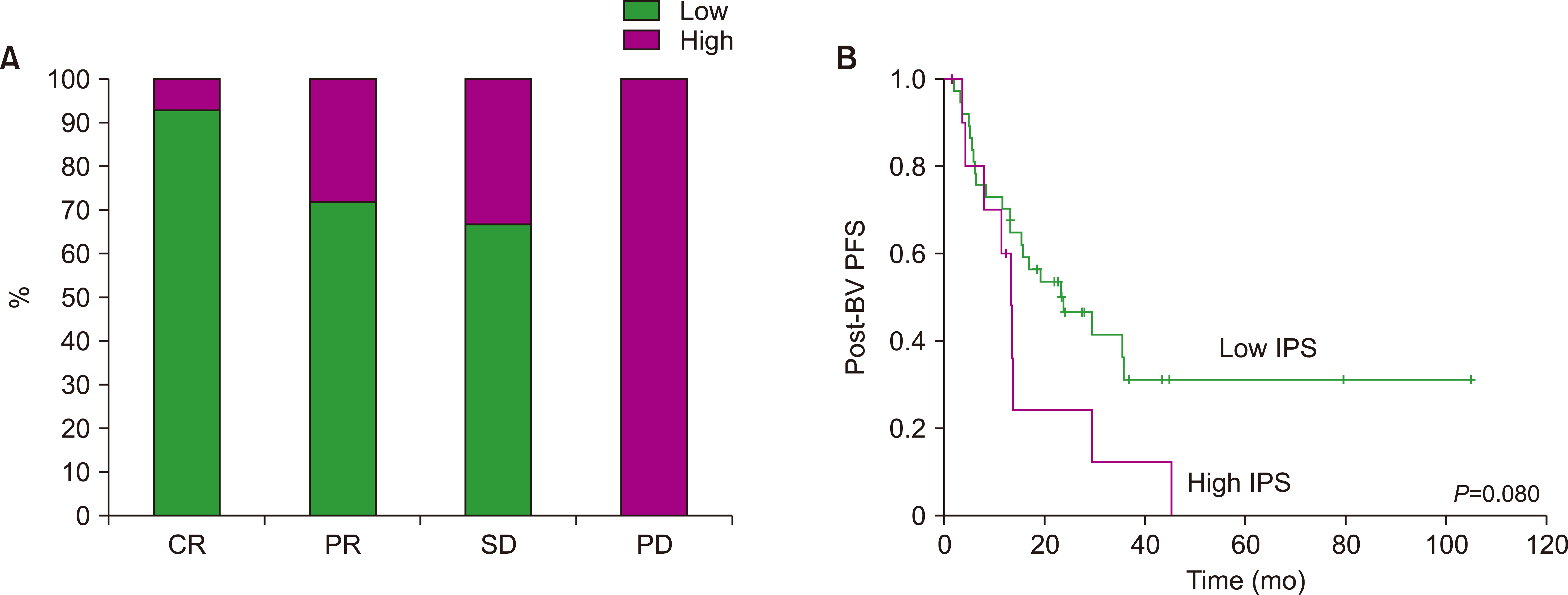
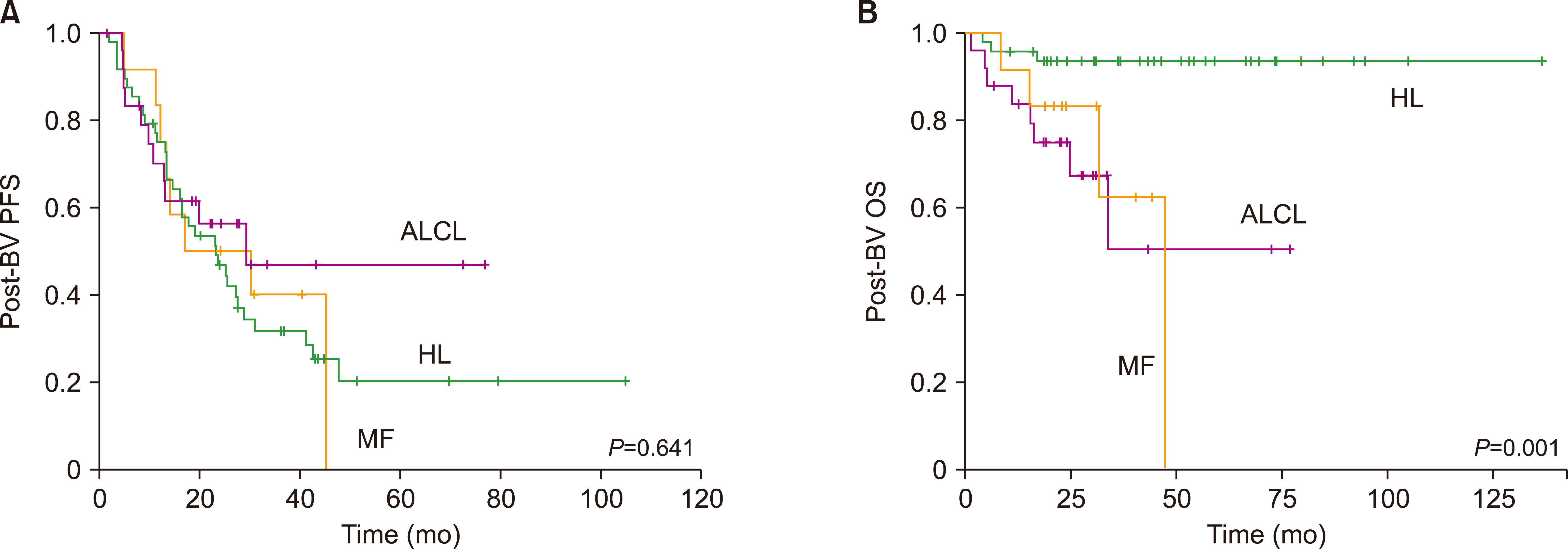
A total of 85 patients were enrolled in this study. The median number of BV cycles was 10 (range, 2‒16) in the patients with HL. The objective response rate (ORR) of patients with HL to BV was 85.4% (41/48), comprising 27 complete responses (CRs) and 14 partial responses (PRs). The ORR of ALCL was 88% (22/25), consisting of 17 CRs and five PRs, whereas the ORR of MF was 92% (11/12). At the median follow-up of 44.6 months after BV treatment, the median post-BV progression-free survival of HL, ALCL, and MF patients was 23.6 months, 29.0 months, and 16.7 months, respectively (P =0.641). The most common side effect of BV was peripheral neuropathy; 22 patients (25.9%, 22/85) experienced peripheral neuropathy (all grades).
Conclusion
The treatment outcomes of patients with relapsed or refractory CD30-positive lymphoma improved with BV treatment, and the safety profile was manageable.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Strategies for integrating ChatGPT and generative AI into clinical studies
Jeong‑Moo Lee
Blood Res. 2024;59:45. doi: 10.1007/s44313-024-00045-3.
Reference
-
1. Francisco JA, Cerveny CG, Meyer DL, et al. 2003; cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood. 102:1458–65. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2003-01-0039. PMID: 12714494.2. Chiarle R, Podda A, Prolla G, Gong J, Thorbecke GJ, Inghirami G. 1999; CD30 in normal and neoplastic cells. Clin Immunol. 90:157–64. DOI: 10.1006/clim.1998.4636. PMID: 10080826.3. Younes A, Gopal AK, Smith SE, et al. 2012; Results of a pivotal phase II study of brentuximab vedotin for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 30:2183–9. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0410. PMID: 22454421. PMCID: PMC3646316.4. Pro B, Advani R, Brice P, et al. 2012; Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35) in patients with relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: results of a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 30:2190–6. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0402. PMID: 22614995.5. Duvic M, Tetzlaff MT, Gangar P, Clos AL, Sui D, Talpur R. 2015; Results of a phase II trial of brentuximab vedotin for CD30+ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and lymphomatoid papulosis. J Clin Oncol. 33:3759–65. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.3787. PMID: 26261247. PMCID: PMC4737859.6. Kim YH, Tavallaee M, Sundram U, et al. 2015; Phase II investigator- initiated study of brentuximab vedotin in mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome with variable CD30 expression level: a multi- institution collaborative project. J Clin Oncol. 33:3750–8. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.3969. PMID: 26195720. PMCID: PMC5089160.7. Prince HM, Kim YH, Horwitz SM, et al. 2017; Brentuximab vedotin or physician's choice in CD30-positive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (ALCANZA): an international, open-label, randomised, phase 3, multicentre trial. Lancet. 390:555–66. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31266-7. PMID: 28600132.8. Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, et al. 2007; Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 25:579–86. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2403. PMID: 17242396.9. Schemper M, Smith TL. 1996; A note on quantifying follow-up in studies of failure time. Control Clin Trials. 17:343–6. DOI: 10.1016/0197-2456(96)00075-X. PMID: 8889347.10. Schwab U, Stein H, Gerdes J, et al. 1982; Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin's disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature. 299:65–7. DOI: 10.1038/299065a0. PMID: 7110326.11. Chen R, Gopal AK, Smith SE, et al. 2016; Five-year survival and durability results of brentuximab vedotin in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 128:1562–6. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-02-699850. PMID: 27432875. PMCID: PMC5034737.12. Moskowitz CH, Nademanee A, Masszi T, et al. 2015; Brentuximab vedotin as consolidation therapy after autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma at risk of relapse or progression (AETHERA): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 385:1853–62. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60165-9. PMID: 25796459.13. Ansell SM, Radford J, Connors JM, et al. 2022; Overall survival with brentuximab vedotin in stage III or IV Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 387:310–20. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206125. PMID: 35830649.14. Horwitz S, O'Connor OA, Pro B, et al. 2022; The ECHELON-2 trial: 5-year results of a randomized, phase III study of brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 33:288–98. DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.12.002. PMID: 34921960. PMCID: PMC9447792.15. Jacobsen ED, Sharman JP, Oki Y, et al. 2015; Brentuximab vedotin demonstrates objective responses in a phase 2 study of relapsed/refractory DLBCL with variable CD30 expression. Blood. 125:1394–402. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-09-598763. PMID: 25573987.16. Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Kim JS, et al. 2020; Efficacy of brentuximab vedotin in relapsed or refractory high-CD30-expressing non-Hodgkin lymphomas: results of a multicenter, open-labeled phase II trial. Cancer Res Treat. 52:374–87. DOI: 10.4143/crt.2019.198. PMID: 31476851. PMCID: PMC7176958.17. Zhao B, Chen R, O'Connor OA, et al. 2016; Brentuximab vedotin, an antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with CD30-positive haematologic malignancies and hepatic or renal impairment. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 82:696–705. DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12988. PMID: 27115790. PMCID: PMC5089583.18. Chen R, Hou J, Newman E, et al. 2015; CD30 downregulation, MMAE resistance, and MDR1 upregulation are all associated with resistance to brentuximab vedotin. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1376–84. DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0036. PMID: 25840583. PMCID: PMC4458438.19. Yi JH, Kim SJ, Kim WS. 2017; Brentuximab vedotin: clinical updates and practical guidance. Blood Res. 52:243–53. DOI: 10.5045/br.2017.52.4.243. PMID: 29333400. PMCID: PMC5762734.20. Oak E, Bartlett NL. 2016; A safety evaluation of brentuximab vedotin for the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 15:875–82. DOI: 10.1080/14740338.2016.1179277. PMID: 27139729.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Brentuximab vedotin: clinical updates and practical guidance
- Complete remission in CD30-positive refractory extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma with brentuximab vedotin
- CD30+ Large-Cell Transformation of Mycosis Fungoides Treated with Brentuximab Vedotin
- Efficacy of Brentuximab Vedotin in Relapsed or RefractoryHigh-CD30–Expressing Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas:Results of a Multicenter, Open-Labeled Phase II Trial
- Two Cases of Relapsed Primary Cutaneous CD30 Positive Large Cell Lymphoma