Efficacy and Safety of Afatinib for EGFR-mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, Compared with Gefitinib or Erlotinib
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jongmu.sun@skku.edu
- KMID: 2464397
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.117
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We tried to evaluate whether there are any specific features in treatment outcomes of firstline afatinib in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), compared with gefitinib or erlotinib.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed patients treated with first-line afatinib, gefitinib, or erlotinib for advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC at Samsung Medical Center between 2014 and 2016.
RESULTS
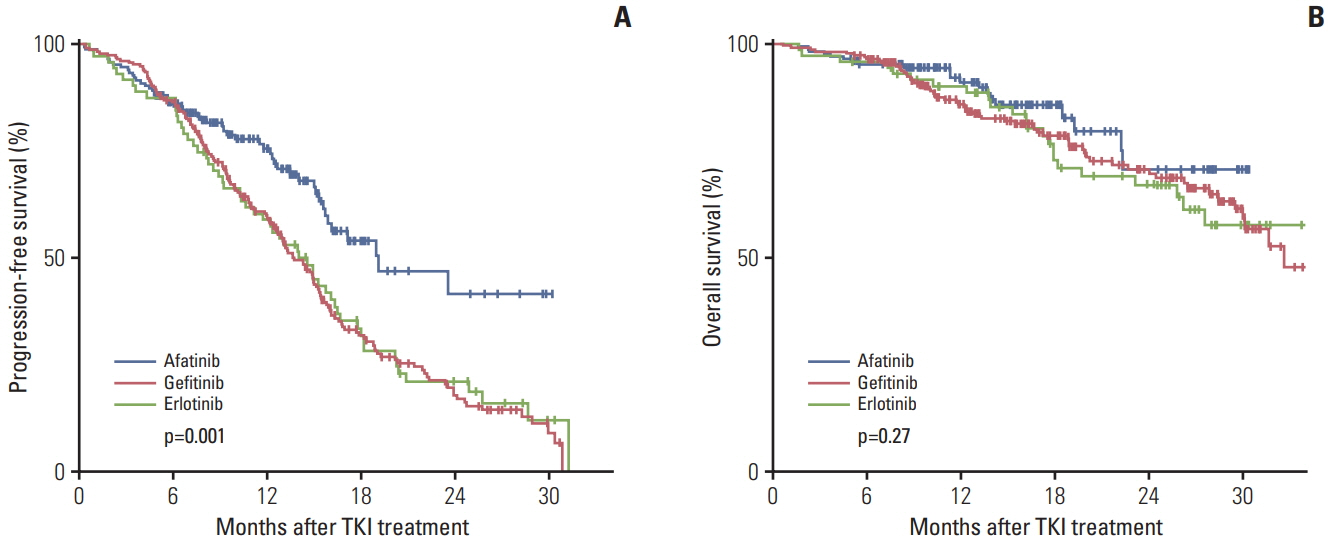
In total, 467 patients received first-line afatinib (n=165), gefitinib (n=230), or erlotinib (n=72). Afatinib was used more often in patients with tumors harboring deletion in exon 19 (Del19), whereas the gefitinib group had more elderly, females, and never smokers. The median progression-free survival (PFS) time for afatinib, gefitinib, and erlotinib was 19.1 months, 13.7 months, and 14.0 months, respectively (p=0.001). The superior PFS of afatinib was more remarkable in subgroups of Del19 or uncommon EGFR mutations. Overall toxicity profiles of the three drugs were comparable, though more grade 3 or 4 toxicities were detected in afatinib (7.3%) compared with gefitinib (2.6%) or erlotinib (1.8%). The common grade 3 or 4 toxicities of afatinib included diarrhea (3.0%), paronychia (2.4%), and skin rash (1.8%). Dose modification was more frequently required in patients treated with afatinib (112/165, 68%), compared with gefitinib (5/230, 2%) and erlotinib (4/72, 6%). Interestingly, however, dose reduction in the afatinib group did not impair its efficacy in terms of PFS (dose reduction vs. no reduction group, 23.5 months vs. 12.4 months).
CONCLUSION
First-line afatinib showed satisfactory efficacy data and manageable toxicity profiles.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Effect of Combining EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Cytotoxic Agents on Cholangiocarcinoma Cells
Boonyakorn Boonsri, Kiren Yacqub-Usman, Pakpoom Thintharua, Kyaw Zwar Myint, Thannicha Sae-Lao, Pam Collier, Chinnawut Suriyonplengsaeng, Noppadol Larbcharoensub, Brinda Balasubramanian, Simran Venkatraman, Isioma U. Egbuniwe, Dhanwant Gomez, Abhik Mukherjee, Supeecha Kumkate, Tavan Janvilisri, Abed M Zaitoun, Thiti Kuakpaetoon, Rutaiwan Tohtong, Anna M Grabowska, David O. Bates, Kanokpan Wongprasert
Cancer Res Treat. 2021;53(2):457-470. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.585.The Clinical Outcomes of Different First-Line EGFR
- TKIs Plus Bevacizumab in AdvancedEGFR -Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma
Yen-Hsiang Huang, Kuo-Hsuan Hsu, Chun-Shih Chin, Jeng-Sen Tseng, Tsung-Ying Yang, Kun-Chieh Chen, Kang-Yi Su, Sung-Liang Yu, Jeremy J.W. Chen, Gee-Chen Chang
Cancer Res Treat. 2022;54(2):434-444. doi: 10.4143/crt.2021.671.
Reference
-
References
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108.
Article2. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:947–57.
Article3. Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:735–42.
Article4. Li D, Ambrogio L, Shimamura T, Kubo S, Takahashi M, Chirieac LR, et al. BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene. 2008; 27:4702–11.
Article5. Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, O'Byrne K, Hirsh V, Mok T, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:3327–34.
Article6. Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:213–22.
Article7. Urata Y, Katakami N, Morita S, Kaji R, Yoshioka H, Seto T, et al. Randomized phase III study comparing gefitinib with erlotinib in patients with previously treated advanced lung adenocarcinoma: WJOG 5108L. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:3248–57.
Article8. Park K, Tan EH, O'Byrne K, Zhang L, Boyer M, Mok T, et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): a phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016; 17:577–89.
Article9. Chen KL, Lin CC, Cho YT, Yang CW, Sheen YS, Tsai HE, et al. Comparison of skin toxic effects associated with gefitinib, erlotinib, or afatinib treatment for non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Dermatol. 2016; 152:340–2.
Article10. Yang JC, Wu YL, Schuler M, Sebastian M, Popat S, Yamamoto N, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:141–51.
Article11. Mok T, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Lee KH, Nakagawa K, Niho S, et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib for the first-line treatment of advanced EGFR mutation positive non-small cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): a randomized, open-label phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35(Suppl):LBA9007.
Article12. Jackman DM, Yeap BY, Sequist LV, Lindeman N, Holmes AJ, Joshi VA, et al. Exon 19 deletion mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor are associated with prolonged survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:3908–14.
Article13. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2129–39.
Article14. Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004; 304:1497–500.15. Wu JY, Shih JY. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on uncommon E709X epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2016; 9:6137–45.
Article16. Baek JH, Sun JM, Min YJ, Cho EK, Cho BC, Kim JH, et al. Efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer except both exon 19 deletion and exon 21 L858R: a retrospective analysis in Korea. Lung Cancer. 2015; 87:148–54.
Article17. Shen YC, Tseng GC, Tu CY, Chen WC, Liao WC, Chen WC, et al. Comparing the effects of afatinib with gefitinib or Erlotinib in patients with advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma harboring non-classical epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Lung Cancer. 2017; 110:56–62.
Article18. Yang JC, Sequist LV, Geater SL, Tsai CM, Mok T, Schuler MH, et al. Activity of afatinib in uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations: findings from three trials of afatinib in Egfr mutation-positive lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8(Suppl 2):S141.19. Liu CY, Wang CL, Li SH, Hsu PC, Chen CH, Lin TY, et al. The efficacy of 40 mg versus dose de-escalation to less than 40 mg of afatinib (Giotrif) as the first-line therapy for patients with primary lung adenocarcinoma harboring favorable epidermal growth factor mutations. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:97602–12.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Brain Radiotherapy before First-Line Afatinib Therapy, Compared to Gefitinib or Erlotinib, in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- The Clinical Outcomes of Different First-Line EGFR-TKIs Plus Bevacizumab in Advanced EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Successful Rechallenge with Gefitinib for an Initial Erlotinib-Responder with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors for patient with leptomeningeal metastasis of epidermal growth factor receptor mutant non-small cell lung cancer
- Comparison of the therapeutic outcome between gefitinib and erlotinib in female patients with non-small-cell lung cancer