Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2019 Sep;24(3):143-148. 10.6065/apem.2019.24.3.143.
Genetic aspects of type 1 diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University Hospital, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. seaon98@naver.com
- KMID: 2460760
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2019.24.3.143
Abstract
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is characterized by autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta-cells in genetically predisposed individuals, eventually resulting in severe insulin deficiency. It is the most common form of diabetes in children and adolescents. Genetic susceptibility plays a crucial role in development of T1DM. The human leukocyte antigen complex plays a key role in the pathogenesis of T1DM. Furthermore, genome-wide association studies and linkage analysis have recently made a significant contribution to current knowledge relative to the impact of genetics on T1DM development and progression. This review focuses on current knowledge of genetics as a pathogenesis for T1DM. It also discusses mechanisms by which genes influence the risk of developing T1DM as well as the clinical and research applications of genetic risk scores in T1DM.
MeSH Terms
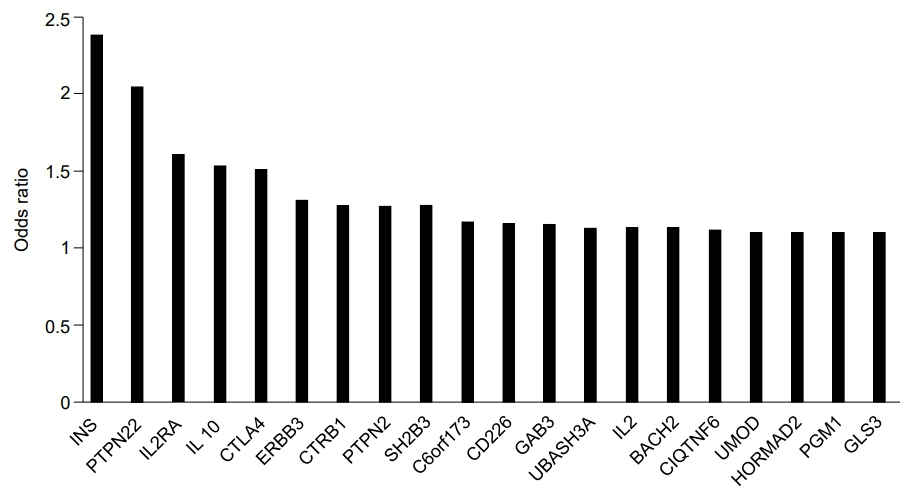
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Utilities of Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Pumps in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
Ewha Med J. 2021;44(3):55-62. doi: 10.12771/emj.2021.44.3.55.
Reference
-
References
1. Achenbach P, Bonifacio E, Koczwara K, Ziegler AG. Natural history of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2005; 54 Suppl 2:S25–31.2. DIAMOND Project Group. Incidence and trends of childhood type 1 diabetes worldwide 1990-1999. Diabet Med. 2006; 23:857–66.3. Kim JH, Lee CG, Lee YA, Yang SW, Shin CH. Increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes among Korean children and adolescents: analysis of data from a nationwide registry in Korea. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016; 17:519–24.4. Gianani R, Eisenbarth GS. The stages of type 1A diabetes: 2005. Immunol Rev. 2005; 204:232–49.5. Eisenbarth GS. Type I diabetes mellitus. A chronic autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1986; 314:1360–8.6. Wang J, Miao D, Babu S, Yu J, Barker J, Klingensmith G, et al. Prevalence of autoantibody-negative diabetes is not rare at all ages and increases with older age and obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:88–92.7. Rich SS, Akolkar B, Concannon P, Erlich H, Hilner JE, Julier C, et al. Overview of the type I diabetes genetics consortium. Genes Immun. 2009; 10 Suppl 1:S1–4.8. Frederiksen B, Liu E, Romanos J, Steck AK, Yin X, Kroehl M, et al. Investigation of the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) and its interaction with protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 2 gene (PTPN2) on risk of islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes: the Diabetes Autoimmunity Study in the Young (DAISY). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013; 133:51–7.9. Redondo MJ, Geyer S, Steck AK, Sharp S, Wentworth JM, Weedon MN, et al. A type 1 diabetes genetic risk score predicts progression of islet autoimmunity and development of type 1 diabetes in individuals at risk. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:1887–94.10. Winkler C, Krumsiek J, Lempainen J, Achenbach P, Grallert H, Giannopoulou E, et al. A strategy for combining minor genetic susceptibility genes to improve prediction of disease in type 1 diabetes. Genes Immun. 2012; 13:549–55.11. Törn C, Hadley D, Lee HS, Hagopian W, Lernmark Å, Simell O, et al. Role of type 1 diabetes-associated snps on risk of autoantibody positivity in the TEDDY study. Diabetes. 2015; 64:1818–29.12. Oram RA, Patel K, Hill A, Shields B, McDonald TJ, Jones A, et al. A type 1 diabetes genetic risk score can aid discrimination between type 1 and type 2 diabetes in young adults. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:337–44.13. Cerolsaletti K, Hao W, Greenbaum CJ. Genetics coming of age in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42:189–91.14. Jahromi MM, Eisenbarth GS. Genetic determinants of type 1 diabetes across populations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006; 1079:289–99.15. Dorman JS, Steenkiste AR, O'Leary LA, McCarthy BJ, Lorenzen T, Foley TP. Type 1 diabetes in offspring of parents with type 1 diabetes: the tip of an autoimmune iceberg? Pediatr Diabetes. 2000; 1:17–22.16. Triolo TM, Fouts A, Pyle L, Yu L, Gottlieb PA, Steck AK, et al. Identical and nonidentical twins: risk and factors involved in development of islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2019; 42:192–9.17. Michels A, Zhang L, Khadra A, Kushner JA, Redondo MJ, Pietropaolo M. Prediction and prevention of type 1 diabetes: update on success of prediction and struggles at prevention. Pediatr Diabetes. 2015; 16:465–84.18. Metcalfe KA, Hitman GA, Rowe RE, Hawa M, Huang X, Stewart T, et al. Concordance for type 1 diabetes in identical twins is affected by insulin genotype. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24:838–42.19. Singal DP, Blajchman MA. Histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens, lymphocytotoxic antibodies and tissue antibodies in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1973; 22:429–32.20. Trowsdale J, Knight JC. Major histocompatibility complex genomics and human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2013; 14:301–23.21. Nyaga DM, Vickers MH, Jefferies C, Perry JK, O'Sullivan JM. The genetic architecture of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018; 477:70–80.22. Stankov K, Benc D, Draskovic D. Genetic and epigenetic factors in etiology of diabetes mellitus type 1. Pediatrics. 2013; 132:1112–22.23. Tisch R, McDevitt H. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Cell. 1996; 85:291–7.24. Aly TA, Ide A, Jahromi MM, Barker JM, Fernando MS, Babu SR, et al. Extreme genetic risk for type 1A diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:14074–9.25. Erlich H, Valdes AM, Noble J, Carlson JA, Varney M, Concannon P, et al. HLA DR-DQ haplotypes and genotypes and type 1 diabetes risk: analysis of the type 1 diabetes genetics consortium families. Diabetes. 2008; 57:1084–92.26. Zhao LP, Alshiekh S, Zhao M, Carlsson A, Larsson HE, Forsander G, et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals that HLA-DRB3, -DRB4, and -DRB5 may be associated with islet autoantibodies and risk for childhood type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2016; 65:710–8.27. Noble JA, Valdes AM, Cook M, Klitz W, Thomson G, Erlich HA. The role of HLA class II genes in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: molecular analysis of 180 Caucasian, multiplex families. Am J Hum Genet. 1996; 59:1134–48.28. Valdes AM, Thomson G, Erlich HA, Noble JA. Association between type 1 diabetes age of onset and HLA among sibling pairs. Diabetes. 1999; 48:1658–61.29. Noble JA, Valdes AM, Varney MD, Carlson JA, Moonsamy P, Fear AL, et al. HLA class I and genetic susceptibility to type 1 diabetes: results from the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Diabetes. 2010; 59:2972–9.30. Noble JA, Martin A, Valdes AM, Lane JA, Galgani A, Petrone A, et al. Type 1 diabetes risk for human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR3 haplotypes depends on genotypic context: association of DPB1 and HLA class I loci among DR3- and DR4-matched Italian patients and controls. Hum Immunol. 2008; 69:291–300.31. Kawabata Y, Ikegami H, Kawaguchi Y, Fujisawa T, Hotta M, Ueda H, et al. Age-related association of MHC class I chainrelated gene A (MICA) with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Hum Immunol. 2000; 61:624–9.32. Redondo MJ, Steck AK, Pugliese A. Genetics of type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2018; 19:346–53.33. Redondo MJ, Oram RA, Steck AK. Genetic risk scores for type 1 diabetes prediction and diagnosis. Curr Diab Rep. 2017; 17:129.34. Polychronakos C, Li Q. Understanding type 1 diabetes through genetics: advances and prospects. Nat Rev Genet. 2011; 12:781–92.35. Kennedy GC, German MS, Rutter WJ. The minisatellite in the diabetes susceptibility locus IDDM2 regulates insulin transcription. Nat Genet. 1995; 9:293–8.36. Durinovic-Belló I, Wu RP, Gersuk VH, Sanda S, Shilling HG, Nepom GT. Insulin gene VNTR genotype associates with frequency and phenotype of the autoimmune response to proinsulin. Genes Immun. 2010; 11:188–93.37. Barratt BJ, Payne F, Lowe CE, Hermann R, Healy BC, Harold D, et al. Remapping the insulin gene/IDDM2 locus in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004; 53:1884–9.38. Bottini N, Musumeci L, Alonso A, Rahmouni S, Nika K, Rostamkhani M, et al. A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat Genet. 2004; 36:337–8.39. Rawlings DJ, Dai X, Buckner JH. The role of PTPN22 risk variant in the development of autoimmunity: finding common ground between mouse and human. J Immunol. 2015; 194:2977–84.40. Bottini N, Vang T, Cucca F, Mustelin T. Role of PTPN22 in type 1 diabetes and other autoimmune diseases. Semin Immunol. 2006; 18:207–13.41. Kim MS, Polychronakos C. Immunogenetics of type 1 diabetes. Horm Res. 2005; 64:180–8.42. Nisticò L, Buzzetti R, Pritchard LE, Van der Auwera B, Giovannini C, Bosi E, et al. The CTLA-4 gene region of chromosome 2q33 is linked to, and associated with, type 1 diabetes. Belgian Diabetes Registry. Hum Mol Genet. 1996; 5:1075–80.43. Tang ST, Tang HQ, Zhang Q, Wang CJ, Wang YM, Peng WJ. Association of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen 4 gene polymorphism with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a metaanalysis. Gene. 2012; 508:165–87.44. de Jong VM, Zaldumbide A, van der Slik AR, Laban S, Koeleman BP, Roep BO. Variation in the CTLA4 3'UTR has phenotypic consequences for autoreactive T cells and associates with genetic risk for type 1 diabetes. Genes Immun. 2016; 17:75–8.45. Yang JH, Cutler AJ, Ferreira RC, Reading JL, Cooper NJ, Wallace C, et al. Natural variation in interleukin-2 sensitivity influences regulatory T-cell frequency and function in individuals with long-standing type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2015; 64:3891–902.46. Ukah TK, Cattin-Roy AN, Chen W, Miller MM, Barik S, Zaghouani H. On the role IL-4/IL-13 heteroreceptor plays in regulation of type 1 diabetes. J Immunol. 2017; 199:894–902.47. Santin I, Moore F, Colli ML, Gurzov EN, Marselli L, Marchetti P, et al. PTPN2, a candidate gene for type 1 diabetes, modulates pancreatic β-cell apoptosis via regulation of the BH3-only protein Bim. Diabetes. 2011; 60:3279–88.48. Liu S, Wang H, Jin Y, Podolsky R, Reddy MV, Pedersen J, et al. IFIH1 polymorphisms are significantly associated with type 1 diabetes and IFIH1 gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2009; 18:358–65.49. Marroquí L, Santin I, Dos Santos RS, Marselli L, Marchetti P, Eizirik DL. BACH2, a candidate risk gene for type 1 diabetes, regulates apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells via JNK1 modulation and crosstalk with the candidate gene PTPN2. Diabetes. 2014; 63:2516–27.50. Nogueira TC, Paula FM, Villate O, Colli ML, Moura RF, Cunha DA, et al. GLIS3, a susceptibility gene for type 1 and type 2 diabetes, modulates pancreatic beta cell apoptosis via regulation of a splice variant of the BH3-only protein Bim. PLoS Genet. 2013; 9:e1003532.51. Ge Y, Paisie TK, Newman JRB, McIntyre LM, Concannon P. UBASH3A mediates risk for type 1 diabetes through inhibition of T-cell receptor-induced NF-κB signaling. Diabetes. 2017; 66:2033–43.52. Sharp SA, Weedon MN, Hagopian WA, Oram RA. Clinical and research uses of genetic risk scores in type 1 diabetes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018; 50:96–102.53. Dudbridge F. Power and predictive accuracy of polygenic risk scores. PLoS Genet. 2013; 9:e1003348.54. Rewers M, Bugawan TL, Norris JM, Blair A, Beaty B, Hoffman M, et al. Newborn screening for HLA markers associated with IDDM: diabetes autoimmunity study in the young (DAISY). Diabetologia. 1996; 39:807–12.55. Steck AK, Dong F, Wong R, Fouts A, Liu E, Romanos J, et al. Improving prediction of type 1 diabetes by testing non-HLA genetic variants in addition to HLA markers. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014; 15:355–62.56. Winkler C, Krumsiek J, Buettner F, Angermüller C, Giannopoulou EZ, Theis FJ, et al. Feature ranking of type 1 diabetes susceptibility genes improves prediction of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2014; 57:2521–9.57. Patel KA, Oram RA, Flanagan SE, De Franco E, Colclough K, Shepherd M, et al. Type 1 diabetes genetic risk score: a novel tool to discriminate monogenic and type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2016; 65:2094–9.58. Ikegami H, Noso S, Babaya N, Hiromine Y, Kawabata Y. Genetic basis of type 1 diabetes: similarities and differences between East and West. Rev Diabet Stud. 2008; 5:64–72.59. Jung MH, Suh BK, Kim TG, Shin CH, Lee BC. Association of HLA class II and non-HLA gene polymorphisms with disease susceptibility in Korean children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol. 2004; 9:136–44.60. Park Y, She JX, Wang CY, Lee H, Babu S, Erlich HA, et al. Common susceptibility and transmission pattern of human leukocyte antigen DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes to Korean and Caucasian patients with type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000; 85:4538–42.61. Jung MH, Yu J, Shin CH, Suh BK, Yang SW, Lee BC. Association of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 gene polymorphisms and HLA class II alleles with the development of type 1 diabetes in Korean children and adolescents. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:1004–9.62. Park Y, Lee H, Sanjeevi CB, Eisenbarth GS. MICA polymorphism is associated with type 1 diabetes in the Korean population. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24:33–8.63. Chung HR, Yang SW, Shin CH, Park KS, Lee YA, Kim JH, et al. The association of variable number of tandem repeats of the insulin gene with susceptibility to type 1 diabetes among Korean subjects. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010; 26:474–80.64. Stead JD, Jeffreys AJ. Structural analysis of insulin minisatellite alleles reveals unusually large differences in diversity between Africans and non-Africans. Am J Hum Genet. 2002; 71:1273–84.65. Pociot F, Akolkar B, Concannon P, Erlich HA, Julier C, Morahan G, et al. Genetics of type 1 diabetes: what's next? Diabetes. 2010; 59:1561–71.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Genetic Diseases Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
- Genetic Markers for IDDM
- Study of Genetic Imprinting on 3 Cases of Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Developed in Early Infantile Period
- Genetics in Diabetes Mellitus - Contribution to the Classification and Management
- Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young: What Do Clinicians Need to Know?