Ann Dermatol.
2018 Aug;30(4):458-461. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.4.458.
Intradermal Injection of Botulinum Toxin: A Safer Treatment Modality for Forehead Wrinkles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bell711@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Medical Device Management & Research, SAIHST, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Yemiwon Dermatologic Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2457524
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.4.458
Abstract
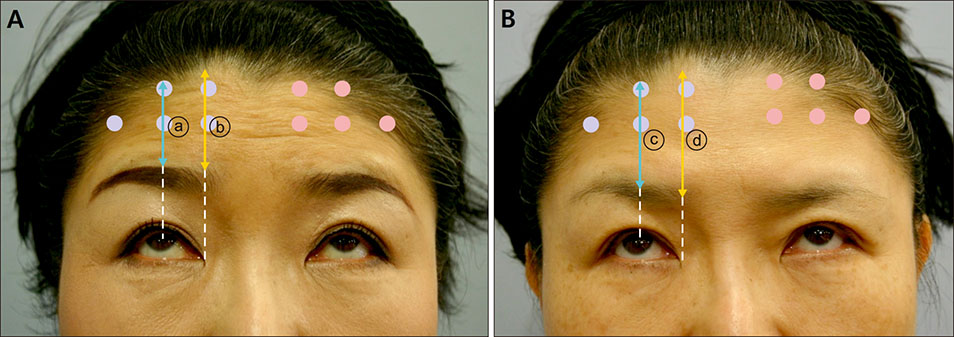
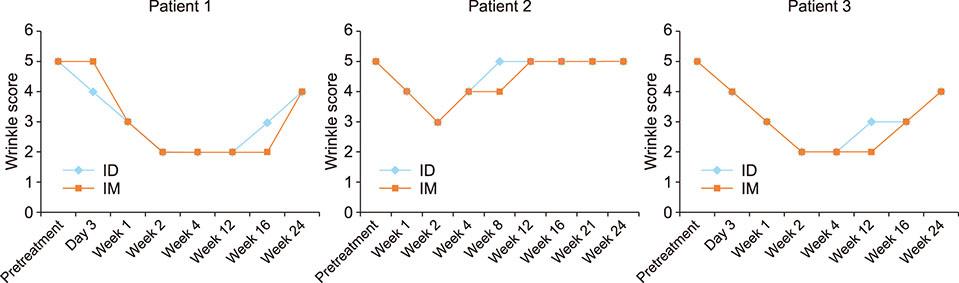
- Intramuscular injection of botulinum toxin A (BTXA) is commonly used for the treatment of forehead wrinkles. In practice, physicians often use an intradermal injection for this purpose, as they feel that there is a lower risk of adverse effects compared with intramuscular injection. However, there are no direct comparative studies between those two injection modalities. We conducted a 24-week long, double-blinded, split-face, pilot study of three participants to compare the efficacy and safety of intradermal or intramuscular injection of BTXA for the treatment of forehead wrinkles. Maximum improvement of wrinkles and the time to achieve maximum effect were similar for both methods. The brow level was lower on the intramuscular injection side throughout the follow-up period for all participants. Subjective satisfaction with wrinkles was similar on both sides, but patients felt more heaviness of the eyebrow on the intramuscular side. No serious side effects were noted. In conclusion, the anti-wrinkle effect of BTXA was not significantly different between intramuscular and intradermal injections. However, side effects such as eyebrow ptosis, and heaviness were more prominent after intramuscular injection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Carruthers A, Carruthers J. Botulinum toxin. 3rd ed. London: Saunders Elsevier;2013. p. 183.2. Kapoor R, Shome D, Jain V, Dikshit R. Facial rejuvenation after intradermal botulinum toxin: is it really the botulinum toxin or is it the pricks? Dermatol Surg. 2010; 36:Suppl 4. 2098–2105.
Article3. Chang SP, Tsai HH, Chen WY, Lee WR, Chen PL, Tsai TH. The wrinkles soothing effect on the middle and lower face by intradermal injection of botulinum toxin type A. Int J Dermatol. 2008; 47:1287–1294.
Article4. Tsukahara K, Takema Y, Kazama H, Yorimoto Y, Fujimura T, Moriwaki S, et al. A photographic scale for the assessment of human facial wrinkles. J Cosmetic Sci. 2000; 51:127–139.5. Redaelli A, Forte R. How to avoid brow ptosis after forehead treatment with botulinum toxin. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2003; 5:220–222.
Article6. Sapra P, Demay S, Sapra S, Khanna J, Mraud K, Bonadonna J. A single-blind, split-face, randomized, pilot study comparing the effects of intradermal and intramuscular injection of two commercially available botulinum toxin a formulas to reduce signs of facial aging. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017; 10:34–44.7. Lee SK. Multiple intradermal small bolus injection of botulinum toxin: the limit and the potentiality. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2012; 14:304–306.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Botulinum Toxin (BTXA(R)) Dermal Injections on Facial Wrinkle Lines
- Application of Botulinum Toxin Injection in Plastic Surgery
- Exaggeration of Wrinkles after Botulinum Toxin Injection for Forehead Horizontal Lines
- A Double-Blind, Split-Face, Randomized Study on the Effects and Safety of Intradermal Injection of Botulinum Toxin A (Incobotulinum Toxin A) in the Cheek
- A Clinical Study of Facial Wrinkles Affected by Facial Expression Muscles Treated with Botulinum Toxin(Botox(R))